|
|
 |
|
Cyclopoida ( Order ) |
|
|
|
Oncaeidae ( Family ) |
|
|
|
Triconia ( Genus ) |
|
|
| |
Triconia hawii (Böttger-Schnack & Boxshall, 1990) (F,M) | |
| | | | | | | Syn.: | Oncaea sp. Böttger-Schnack, 1988; 1990;
Oncaea hawii Böttger-Schnack & Boxshall, 1990 (p.865, Descr.F, figs.F, tab.III); 1992 (p.304); 1994 (p.277); 1996 (p.1086); Ohtsuka & al., 1996 a (p.91) | | | | Ref.: | | | Böttger-Schnack, 1999 (p.43, 85, Redescr.F, Descr.M, figs.F,M); Böttger-Schnack & al., 2001 (p.1029, tab.1, 2); Böttger-Schnack & al., 2004 (p.1130, tab.1, Rem). Böttger-Schnack, 2004 (p.220: tab.2, Rem.); Di Capua & Boxshall, 2008 (p.1410, figs.F, table 1, 2); Vives & Shmeleva, 2010 (p.344, figs.F,M, Rem.) | 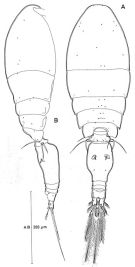 issued from : R. Böttger-Schnack in Mitt. hamb. zool. Mus. Inst., 1999, 96 [p.87, Fig.21]. Female (from Red Sea): A, habitus (dorsal); B, idem (lateral right side). Nota: Proportional lengths (%) of urosomites and caudal rami 9.2:54.3:6.2:6.2:13.6:10.5. Relative lengths (%) of segments of A1 measured along posterior non-setigerous margin 7:22:44:11:4:11.
|
 issued from : R. Böttger-Schnack in Mitt. hamb. zool. Mus. Inst., 1999, 96 [p.89, Fig.22]. Female: A, A2 (anterior); B, labrum (anterior); C, idem (posterior); D, Md (showing individual elements); E, Mx1; F, Mx2; G, P5 (dorsal); H, caudal ramus (dorsal, terminal setae omitted); I, P6; J, egg-sac.
|
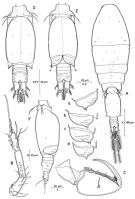 issued from : R. Böttger-Schnack in Mitt. hamb. zool. Mus. Inst., 1999, 96 [p.90, Fig.23]. Male (from Red Sea): A, habitus (dorsal); B, A1; C, Mxp (anterior); D, urosome (dorsal, spermatophores fully developed); E, idem (ventra)) [a, b, right and left genital aperture, showing bifid tips of posterolateral corners; c, d, variation in posterolateral corners of genital apertures]; F, idem (lateral left side). Nota: Proportional lengths (%) of urosomites and caudal rami 10.2:54.4:4.8:4.1:4.1:12.2:10.2. Relative lengths (%) of segments of A1 measured along posterior non-setigerous margin 7.6:21.8:40.6:30.0.
The males were identified on the length of the terminal accessory seta on the caudal ramus, which is about equal in length to the dorsal seta; males of T. rufa also share this character, but they can br distinguished by the length ratios of spines on P4 endop-3, by the sexual dimorphism in the lateral armature of A2 (which is not found in T. hawii), by the pore pattern on the dorsal surface of the genital double-somite and by their larger size (see Table 3). The conspicuous bifid posterolateral corners on the genital flaps appear to be rather variable, and consequently cannot be used to separate the males from those of the closely related T. rufa.
|
 issued from : R. Böttger-Schnack in Mitt. hamb. zool. Mus. Inst., 1999, 96 [p.77, Table 3]. Morphological characters separating males of Triconia minuta, T. umerus, T.rufa and T. hawii. ODS = outer distal spine; OSDS = outer subdistal spine; endp-3 = 3th endopod segment; l = length; sex dimorph. = sexually dimorphic; GS = genital somite; P4, P5 = thoracopods 4, 5; A2 = antenna; CR = caudal rami; lat. arm = lateral armature.
| | | | | Compl. Ref.: | | | Nishibe & al., 2009 (p.491, Table 1: seasonal abundance); Zenetos & al., 2010 (p.397) | | | | NZ: | 4 | | |
|
Distribution map of Triconia hawii by geographical zones
|
| | | | | | | | | | Loc: | | | Medit. (G. of Napoli), G. of Aqaba, Red Sea (N-S), Arabian Sea, Japan (Tosa Bay) | | | | N: | 6 | | | | Lg.: | | | (688) F: 0,56-0,49; (810) M: 0,49-0,48; (1014) F: 0,497; {F: 0,49-0,56; M: 0,48-0,49} | | | | Rem.: | mesopelagic. Epipelagic in the Gulf of Naples.
According to Di Capua & Boxshall (2008, p.1411, this species is unusual in exibiting variation in the position of the gonopores on the genital double-somite: with Böttger-Schnack (1999) showing gonopores located between 33 % and 50 % of the distance along the double-somite; the authors connsider this degree of variability to indicate a possible taxonomic problem; also in this species, the dorsal integumental pore is located at about 71 % of distance along double-somite from anterior margin in Red Sea compared with only 56 % in Gulf of Napoli. In addition, the Gulf of Napoli material has spinular ornamentation, not reported by Böttger-Schnack (1999). These results cause some uncertainty over the identity of the specimen from the Gulf of Napoli.
According to Mazzocchi & Di Capua (2010, p.429) the occurrence of this form would be an alien-species. | | | Last update : 02/02/2015 | |
|
|
 Any use of this site for a publication will be mentioned with the following reference : Any use of this site for a publication will be mentioned with the following reference :
Razouls C., Desreumaux N., Kouwenberg J. and de Bovée F., 2005-2025. - Biodiversity of Marine Planktonic Copepods (morphology, geographical distribution and biological data). Sorbonne University, CNRS. Available at http://copepodes.obs-banyuls.fr/en [Accessed January 05, 2026] © copyright 2005-2025 Sorbonne University, CNRS
|
|
 |
 |