|
|
 |
|
Calanoida ( Order ) |
|
|
|
Calanoidea ( Superfamily ) |
|
|
|
Paracalanidae ( Family ) |
|
|
|
Bestiolina ( Genus ) |
|
|
| |
Bestiolina inermis (Sewell, 1912) (F,M) | |
| | | | | | | Syn.: | Acrocalanus inermis Sewell, 1912 (p.321, 334, figs. juv.F,M); Früchtl, 1924 b (p.39, figs.M, Rem.); Sewell, 1924 (p.781); 1929 (p.38, 81); 1933 (p.26); Vervoort, 1946 (p.132); Sewell, 1948 (p.324, 418, 426); Bowman, 1958 (p.121-123); Silas, 1972 (p.645, Rem.); Kimmerer, 1983 (p.1); 1984 (p.165, egg production); Huntley & Lopez, 1992 (p.201, Table 1, eggs, temperature-dependent production); Suarez-Morales & Gasca, 1998 a (p.110); Hernandez-Trujillo & Esqueda-Escargera, 2002 (in Appendix); Calbet & al., 2000 (p.75); Miller C.B., 2005 (p.147);
Acrocalanus inermis s.l. : Brinton & al., 1986 (p.228, Table 1); Jungbluth & Lenz, 2013 (p.630, Table I) ;
Bestiola inermis : Andronov, 1972 a (p.292); Madhupratap & Haridas, 1986 (p.105, tab.1) | | | | Ref.: | | | Ali, Al-Yamani & Prusova, 2007 (p.203: Tab.II, Rem.) | 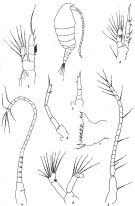 Issued from : R.B.S. Sewell in Rec. Indian Mus., 1912, 7. [Pl.XVI, figs.1-9]. As Acrocalanus inermis. Female (from Bay of Bengal): 1, habitus (lateral right side); 2, P1; 3, P2; 4, A1. Head and 1st thoracic segment separate, 4th and 5th separate. The posterior margin of the thorax is rounded and bears a row of small spines. Abdomen 4-segmented, contained 3 times in the length of the cephalothorax. Proportional lengths of urosomites and furca as 24:14:11:18:12. Caudal rami symmetrical and bear 4 terminal setae. A1 23-segmented (segments 2 fused, 8-9 partially fused) reach to the end of the caudal rami; each or the first six segments bears a transverse row of very small delicate spines. Endopodite (7-segmented) and exopodite nearly equal length. P5 practically absent, being only represented by short rounded unsegmented processes. Male: 5, A1; 6, A2; 7, Md (masticatory edge); 8, P5; 9, P5 immature. Abdomen 5-segmented. Proportional lengths of urosomites and furca as 5:8:6:6:6:5. A1 19-segmented (segments 1-6 and 7-8 fused). A2 differ from those of the female in that the last segment of the exopodite ends in a stump devoid of bristhes.. P5 only present on the left side.
|
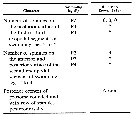 issued from : S.Y. Moon, W. Lee & H.Y. Soh in Proc. Biol. Soc. Washington, 2010, 123 (1). [p.44, Table 1]. Presence and number of spinules on the anterior surface of the exopods and endopods of swimming legs 2 - 4 from (Sewell, 1912). These characteristics were taken from Ali & al. (2007).
| | | | | NZ: | 3 + 1 doubtful | | |
|
Distribution map of Bestiolina inermis by geographical zones
|
| | | | | | | Loc: | | | Indian, Sri Lanka (Pearl Banks), Bay of Bengal, Chilka Lake, Is. Nicobar (Nankauri Harbour), Burman coast, Rangoon River mouth), Indonesia-Malaysia (Verlatan Is., Aru, Riv. Kurau), Hawaii, Kaneohe Bay, Gulf of California (in Brinton & al., 1986, p.245) | | | | N: | 8 | | | | Lg.: | | | (81) F: 1,08; M: 0,86; {F: 1,08; M: 0,86} | | | | Rem.: | estuary zones.
The form, recorded in the Gulf of California needs to be confirmed.
See remarks in Bestiolina similis.
Miller (2005) note from Kimmerer (1983) that tiny tropical copepod productivity (ratio of production to biomass) is of the order of 0.3 mgC/ mgC-1d-1. | | | Last update : 10/09/2020 | |
|
|
 Any use of this site for a publication will be mentioned with the following reference : Any use of this site for a publication will be mentioned with the following reference :
Razouls C., Desreumaux N., Kouwenberg J. and de Bovée F., 2005-2025. - Biodiversity of Marine Planktonic Copepods (morphology, geographical distribution and biological data). Sorbonne University, CNRS. Available at http://copepodes.obs-banyuls.fr/en [Accessed August 17, 2025] © copyright 2005-2025 Sorbonne University, CNRS
|
|
 |
 |