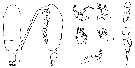|
|
 |
|
Calanoida ( Order ) |
|
|
|
Clausocalanoidea ( Superfamily ) |
|
|
|
Aetideidae ( Family ) |
|
|
|
Chiridius ( Genus ) |
|
|
| |
Chiridius gracilis Farran, 1908 (F,M) | |
| | | | | | | Syn.: | Chiridius poppei : Farran, 1905 (p.35);
no C. gracilis : Farran, 1929 (p.229, fig.F, Rem.); Bradford, 1970 a (p.353, figs.M)
? Chiridius gracilis : Tanaka, 1937 (p.255, fig.F, Rem.) | | | | Ref.: | | | Farran, 1908 b (p.30, Descr.F, figs.F); A. Scott, 1909 (p.42, figs.F, Rem.); With, 1915 (p.85, figs.F); ? Farran, 1926 (p.248: juv.); Sewell, 1929 (p.100); Farran, 1936 a (p.87); Vervoort, 1952 c (n°44, p.3, figs.F); 1957 (p.6, 55, Rem.); Tanaka, 1957 a (p.48, figs.M, Rem.F); Grice, 1963 a (p.495); Bradford, 1969 a (p.97); Tanaka & Omori, 1970 (p.117); Bradford, 1972 (p.38, figs.F, Rem.); Shih & al., 1971 (p.143); Maclellan & Shih, 1974 (p.1337, figs. juv., F,M); Park, 1975 b (p.283, figs.F,M); 1978 (p.122, figs.F); Björnberg & al., 1981 (p.604, 632, fig.F); Gardner & Szabo, 1982 (p.212, figs.F,M); Mazzocchi & al., 1995 (p.138, figs.F,M, Rem.); Markhaseva, 1996 (p.111, figs.F,M); Chihara & Murano, 1997 (p.683, Pl.34: F,M); Bradford-Grieve & al., 1999 (p.879, 920, figs.F,M); G. Harding, 2004 (p.54, figs.F); Mulyadi, 2004 (p.56, figs.M, Rem.); Yamaguchi & al., 2005 (p.835, Tabl. VIII); Vives & Shmeleva, 2007 (p.553, figs.F,M, Rem.)
|  issued from : T. Park in Antarctic Res. Ser. Washington, 1978, 27. [p.123, Fig.13]. Female: A, habitus (dorsal view); B, idem (lateral view); C, urosome (dorsal view); D, idem (left lateral view); E, Mx1; F, P1; G, P2; H, P3. Legs 1-3: anterior view.
|
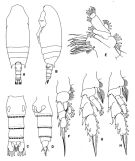
 issued from : E.L. Markhaseva in Trudy Zool. Inst. RAN, St. Petersburg, 1996, 268. [p.112, Fig.83]. Female. figures from specimens from different stations. Gn: genital field (ventral); Gntb Md: gnathobase of Md (partial).
|
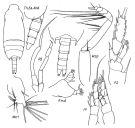 issued from : E.L. Markhaseva in Trudy Zool. Inst. RAN, St. Petersburg, 1996, 268. [p.113, Fig.84]. Male (from different specimens, SE Pacif.). P.md: mandibular palp..
|
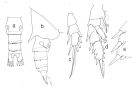 issued from : T. Park in Bull. Mar. Sci., 1975, 25 (2). [p.283, Fig.7] Female (from Gulf of Mexico): a, urosome (dorsal); b, posterior part of metasome and urosome (right side, lateral); c, exopod of P1 (anterior); d, P2 (anterior); e, lateral portion of third exopodal segment of P2 (anterior). P1-2: legs.
|
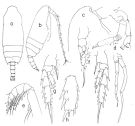 issued from : T. Park in Bull. Mar. Sci., 1975, 25 (2). [p.284, Fig.8]. Male (from Gulf of Mexico): a, b, habitus (dorsal, lateral, respectively); c, forehead (lateral); d, A2; e, distal part of Mxp; f, P1 (anterior); g, P2 (anterior); h, third exopodal segment of P2 (anterior); i, P3 (anterior); j, fifth pair of legs (posterior). P1-3: legs.
|
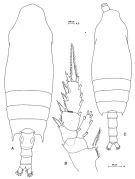 Issued from: M.G. Mazzocchi, G. Zagami, A. Ianora, L. Guglielmo & J. Hure in Atlas of Marine Zooplankton Straits of Magellan. Copepods. L. Guglielmo & A. Ianora (Eds.), 1995. [p.139, Fig.3.23.1]. Female: A, habitus (dorsal); B, P2. Nota: Proportional lengths of urosomites and furca 37:22:19:8:14 = 100. Exopod 3 of P2 with outer margins between spines, moderately bulged in the middle (as compared to C. molestus). Male: C, habitus (dorsal). Nota: Proportional lengths of urosomites and furca 17:27:22:19:2:13 = 100. Mxp with last endopod segment bearing strong seta ornated with two rows of small teeth.
|
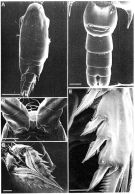 Issued from: M.G. Mazzocchi, G. Zagami, A. Ianora, L. Guglielmo & J. Hure in Atlas of Marine Zooplankton Straits of Magellan. Copepods. L. Guglielmo & A. Ianora (Eds.), 1995. [p.140, Fig.3.23.2]. Female (SEM preparation): A, habitus (dorsal); B, forehead (ventral); C, urosome (ventral); D, P2; E, last exopod segment of P2. Bars: A 0.500 mm; B-D 0.100 mm; E 0.050 mm.
|
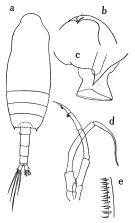 issued from : O. Tanaka in Publ. Seto Mar. Biol. Lab., 1957, VI (1). [p.49, Fig.30]. Male: a, habitus (dorsal); b, forehead (anterior view); c, last thoracic segment (lateral); d, P5; e, detail of the characteristic setae of 5th segment of endopod of Mxp. Nota: Head and 1st thoracic segment fused, 4th and 5th fused. Rostrum represented by a thin triangular plate. Proportional lengths of urosomites and furca 18:26:25:17:2:12 = 100. 2nd to 4th urosomal segments are fringed with fine teeth on the distal margin. A1 (23-segmented) extends to distal margin of last thoracic segment. mx1: 5 setae on outer lobe, 9 setae on exopod, 9 setae on endopod, 1st inner lobe with aesthetask-like filaments.
|
 issued from : A. Scott in Siboga-Expedition, 1909, XIX a. [Plate XI, Figs.1-9]. With doubt. Female (from Indonesia-Malaysia): 1, habitus (dorsal); 2, forehead (lateral); 3, last thoracic and genital segments (left side); 4, A1; 5, Md; 6, Mxp; 7, P1; 8, P2; 9, P4. Nota: The spines of the last thoracic segment are produced distinctly beyond the middle of the genital segment. Terminal spine of the seopodite of P4 with 22 teeth.
|
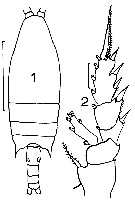 issued from : J.M. Bradford in Mem. N. Z. Oceonogr. Inst., 1972, 54. [p.39, Fig.7, (1-2)]. Female (from Kaikoura, New Zealand): 1, habitus (dorsal); 2, P2. Scale bars: 1 mm (1): 0.1 mm (2).
|
 issued from : G.P. Farran in Fish. Ire. Sci. Invest., 1906, II [1908]. [Pl. II, Figs.1-3]. Female (from 52°6N, 12°0'W): 1-2, habitus (dorsal and lateral, respectively); 3, P2.
|
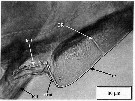 issued from : A.G. Lewis, S. Allen & G. Martens in Crustaceana, 2006, 79 (4). [p.505, Fig.3]; Male (from off British Columbia coast): lateral view of the median intersomitic ridge (MIR) with right 1st pereiopod (P-1) removed. P-1 = left 1st periopod; rc= ridge crest; TR = transverse ridge.; IcS = intercoxal sclerite.
|
 issued from : Mulyadi in Published by Res. Center Biol., Indonesia Inst. Sci. Bogor, 2004. [p.57, Fig.31]. Male (from Flores Sea): a, habitus (dorsal); b, forehead (lateral); c, posterior end of last thoracic segment and genital somite; d, P1; e, P2; f, P3 (exopodite segments 2 and 3 missing); g, P5.
|
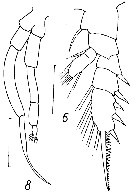 issued from : D.F. Arcos in Rev. Com. Perm. Pacifico Sur, 1976, 5. [Figs. 6, 8]. Male (from Magallanes region): 6, P2; 8, P5. Scale bars: 200 µ.
|
 Chiridius gracilis Chiridius gracilis Female: 1 - Exopod of Mx1 with 8 setae. Points of last thoracic segment reaching the midlength of the genital segment, usually longer. 2 - Exopodal segment 3 of P2 without bulge and excavation between 2nd and 3rd external spines. Endopodal segment 2 of Md commonly with 9 setae. 3 - Exopodal segments 1 and 2 of P1 with external spines reaching or exceeding the base of next spine. Endopod of P2 2-segmented (sometimes separation obscure), mostly not reaching the border between exopodal segments 2-3.
|
 Chiridius gracilis Chiridius gracilis male: 1 - Points of last thoracic segment not longer than genital segment. 2 - Right P5 longer than left. Exopodal segments 1 and 2 of P1 with external spines reaching the midlength of the next segment or longer. 3 - Points of last thoracic segment reaching the posterior border of genital segment. Endopodal segment 1 of Mxp with 3 medial setae. 4 - Exopodal segment 1 of P1 not reaching the base of following spine. 5 - P5 longer than than half length of P4. 6 - Distal segment of left P5 3 times longer than wide.
|
 Issued from : O. Tanaka in Japanese J. Zool., 1937, VII, 13. [p.256, Fig.6]. Female (from coast of Heda, Japan): a, habitus (dorsal); b, abdomen (dorsal); c, last thoracic segment and abdomen (lateral), right side); d, spine of last thoracic segment; e, P1; f, P2. Nota: Cephalothorax: 1.94 mm; abdomen: 0.66 mm. Lateral spines on the last thoracic segment rather convergent and project to the middle of the genital segment; the distance between spines half the greatest width of the cephalothorax. Combined length of the abdomen and caudal rami slightly longer than 1/3 of the cephalothorax. Genital segment about as long as the 2nd and 3rd segment together. 2nd abdominal segment longer than the 3rd. Anal segment equal to half the length of the 3rd segment. Caudal rami longer than the anal segment and 1 1/3 as long as wide. 20th segment of A1 more than 4-times as long as wide. Outer marginal spine of the 1st exopodal segment of P1 extends to the base of the 2nd segment. In P2: Endopodite does not extend to the base of the 3rd segment of the exopodite [doubtful in the figure]. In P3: Endopodite shorter than that of Chiridius poppei. Terminal spine on the exopodite of P2 to P4 with 24, 28 and 26 teeth respectively.
|
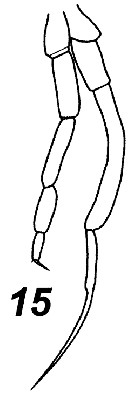 Issued from : V.N. Andronov in Russian Acad. Sci. P.P. Shirshov Inst. Oceanol. Atlantic Branch, Kaliningrad, 2014. [p.85, Fig.22: 15]. after Markhaseva, 1996. Male P5.
|
 Issued from : D.C. Maclellan & C.-T. Shih in J. Fish Res. Board Can., 1974, 31 (8). [p.1347, Figs. 91-101]. Female (from Gulf of St. Lawrence): 91-92, habitus (dorsal and lateral, respectively); 93, A1; 94, Md; 95, Mx1; 96, Mx2; 97, Mxp; 98-101, P1 to P4. Upper scale for whole specimens, middle for legs, and lower for mouthparts. Nota: A1 and A2 similar to those of male. Remaining cephalic appendages showing great sexual dimorphism.- Metasomal process directed backwards and reaching end of genital segment. - Urosome 4-segmented. - Genital segment (= genital double-somite) symmetrical in dorsal view, with a slight swelling on each side at middle of segment, width subequal to length. - Ratio of prosome to urosome 3.53 ± 0.14. - Md: gnathobase strongky developed and nearly twice as long as 3-segmented proptipod. Cutting edge with 8 teeth; 5 anterior teeth strong and, excepting 1st, bicuspidate, following 2 weak and bifid; posterior one strong and acuminate; posterior margin of gnathobase wuth a spinulose seta near posterior tooth. Protopod B1 (= coxa) small and lacking setae or spines; B2 (= basis) with a strong arched spine near distal medial margin and 1 small seta at middle of medial margin; endopod 2-segmented, 1st segment with 2 medial setae, 2nd segment with 9 apical setae; exopod 5-segmented, about twice as long as endopod, with 1 medial seta on each of first four segments and 2 apical setae on distal segment. - Mx1: 1st outer lobe (= basal exite) with 7 long and 2 short marginal setae; no 2nd outer lobe; basis with 4 setae on medial distal end; exopod short, with 8 setae; endopod 2-segmented, each segment with 5 strong and 1 feeble seta; 3 inner lobes: 1st lobe (= arthrite) with 13 spines (9 strong and setiform at or near margin, 4 small on interior surface and armed with comb-like spinules near their bases); 2nd inner lobe (= coxal endite) with 4apical setae; 3rd inner lobe (= basal endite) with 4 apical setae and a few spinules on medial distal margin. - Mx2: Each of 1st to 5th lobes with 3 setae, 1 short and slightly curved and 2 strong and straight; anterior superior surface of 1st to 4th lobes with comb-like spinules; endopod 3-segmented, with 2, 2, and 3 setae on 1st, 2nd and 3rd segments, respectively. - Mxp: protopod B1 (praecoxa + coxa) with 3 lobes, with 2, 3, 3 setae, respectively; basis with 3 setae near middle of medial margin and 2 distal setae; endopod 5-segmented,1st and 2nd segment each with 3 strong and 1 small seta, 3rd and 4th segment each with 2 strong and 1 small seta, 5th segment with 3 apical setae and 1 small lateral seta. - P5 wanting.
|
 Issued from : D.C. Maclellan & C.-T. Shih in J. Fish Res. Board Can., 1974, 31 (8). [p.1345, Figs. 77-90]. Male (from Gulf of St. Lawrence): 77-78, habitus (dorsal and lateral, respectively; 79, A2; 80, Md; 81, Mx1; 82, Mx2; 83, Mxp; 84-88P1 to P5; 89, P5 of South Pacific specimen; 90, P5 of Tasman Sea specimen. Upper scale for whole specimens, middle for legs, and lower for mouthparts. Nota: - Prosome to urosome ratio 3.41 ±0.11. - From dorsal view, cephalosome with 2 lateral body surfaces diverging greatly over antennula - Suture between cephalosome and 1st thoracic segment = (1st pedigeous somite) indistinct. - Metasomal processes slightly bent inwards and reaching posterior margin of 1st urosomal somite. - Urosome slender and straight, 5 free somites; percentages of length 16 : 32 : 26 : 20 : 6. - Ratioo of prosome to urosome 3.46. - Caudal rami about 1/3 longer than width. - Md: gnathobase degenerated to a weak and toothless remnant; protopod (coxa and basis) 2-segmented; endopod 2-segmented, 1st segment with 2 setae on medial margin, 2nd segment with 8 long and 1 short medial setae; exopod 5-segmented, slightly longer than endopod, each of first 4 segments with 1 medial seta, 5th segment with 2 apical setae. - Mx1: Degeneration obvious in size, segmentation, and armature; all inner lobes degenerated; outer lobe visible but very much reduced and with 5 setae; exopod fairly well developed, with 7 long curved setae and 2 small straight setae; endopod reduced to small bulb-like segment with 8 setae; protopod 2nd segment with 2 setae on medial margin. - Mx2: Degree of degeneration in size, segmentation, and armature exceeding that of all other cephalic appendages in adult. Entire appendages reduced to a small blade-like structure bearing several lobular processes without setae. - Mxp: Propotod B1 (praecoxa and coxa) rectangular with 2 short setae distally; basis about 1/3 longer than B1, with3 setae (1 long and 2 short) on medial margin in distal 3rd, and 2 long distal setae; setation on 5-segmented endopod 4, 4, 3, 3-1, and 3-1, respectively; 1 apical seta of distal segment with spinules. - P5 assymetrical, uniramous. Left leg straight, 5-segmented and slightly longer than first three segments of right leg combined; 1sy and 2nd segments naked, 3rd segment with short tooth-like process at lateral distal end, 4th segment with hair-like setae distally on medial margin, 5th segment with hairs on medial margin, and a distal lobular process nearly half as long as segment. Roght leg 4-segmented, 1st and 2nd segments naked, shprter than those of left leg, 3rd segment bent slightly near middle, and almost twice as long as first two segments combined, 4th segment naked, with a small expansion in the proximal third and a thin blade-like distal portion. - P5 of specimens from South Pacific off Chile and Tasman Sea differ from the above description in lacking lateral distal process in 3rd segment of left leg and in relative lengths of segments.
|
 Issued from : D.C. Maclellan & C.-T. Shih in J. Fish Res. Board Can., 1974, 31 (8). [p.1345]. Male: Percentages of lengths of the segments in total length of A1. Nota: A1 23-segmented with fusions of 8th-9th and 24th-25th segments and reaching to tip of metasomal process.
|
 Issued from : D.C. Maclellan & C.-T. Shih in J. Fish Res. Board Can., 1974, 31 (8). [p.1344, Figs.66-76]. Copepodite V Female (from Gulf of St. Lawrence): 66-67, habitus (dorsal and lateral, respectively); 68, A2; 69, Md; 70, Mx1; 71, Mx2; 72, Mxp; 73-76, P1 to P4. Upper scale for whole specimens, middle for legs, and lower for mouthparts. Nota: - Total length 2.21 ± 0.12 mm. - Prosome 1.67 ± 0.10 mm. - Incomplete suture between cephalosome and 1st pedigerous somite, but present. - Urosome 4-segmented. - Ratio of prosome to urosome 3.78 ± 0.15 mm. - Exopods of P1 to P4 3-segmented; endopods of P1 and P2 1-segmented; of P3 2-segmented, and P4 3-segmented. - A distal pointed process on lateral margin of endodal segment 1 of P3 and segment 2 of P4.
|
 Issued from : D.C. Maclellan & C.-T. Shih in J. Fish Res. Board Can., 1974, 31 (8). [p.1343, Figs. 54-65]. Copepodite V Male (from Gulf of St. Lawrence): 54-55, habitus (dorsal and lateral, respectively; 56, A2; 57, Md; 58, Mx1; 59, Mx2; 60, Mxp; 61-65, P1 to P5; Upper scale for whole specimens, middle for legs, and lower for mouthparts. Nota: - Total length 2.25 ± 0.21 mm. - Prosome 1.71 ± 0.10 mm. - Incomplete suture between cephalosome and 1st pedigerous somite, but present. - Urosome 4-segmented. - Ratio of prosome to urosome 3.87 ± 0.30 mm. - P1 to P4 similar yo those of female, except P3 endopod with 3 segments and with distal pointed process on lateral margin of segment 2. - P5 exopod more elongate than that of previous stage IV and provided with 5 spines (2 lateral, 2 medial, 1 distal).
|
 Issued from : D.C. Maclellan & C.-T. Shih in J. Fish Res. Board Can., 1974, 31 (8). [p.1342, Figs. 43-53]. Copepodite IV Female (from Gulf of St. Lawrence): 43-44, habitus (dorsal and lateral, respectively; 45, A2; 46, Md; 47, Mx1; 48, Mx2; 49, Mxp; 50-53, P1 to P4. Upper scale for whole specimens, middle for legs, and lower for mouthparts. Nota: - Sexe distinguable on appearance of P5 male. - Total length 1.61 ± 0.11 mm . - Prosome 1.25 ± 0.10 mm. - Metasome 3-segmented, last segment formed by the fusion of 4th and 5th pedigerous somites.. - Suture between cephalosome band 1st pedigerous somite, obscure in previous stages, now relatively distincy but incomplete. - Metasomal posterior processes charactyeristic of the species, well developed. - Ratio of prosome to urosome 4.21 ± 0.28. - A1 23-segmented, with fusions at 8th-9th and 24th-25th segments. - Endopod of Mxp 5-segmented.
|
 Issued from : D.C. Maclellan & C.-T. Shih in J. Fish Res. Board Can., 1974, 31 (8). [p.1341, Figs. 31-42]. Copepodite IV Male (from Gulf of St. Lawrence): 31-32, habitus (dorsal and lateral, respectively; 33, A2; 34, Md; 35, Mx1; 36, Mx2; 37, Mxp; 38-42, P1 to P5. Upper scale for whole specimens, middle for legs, and lower for mouthparts. Nota: - Sexe distinguable on appearance of P5 male. - Total length 1.66 ±0.11 mm. - Prosome 1.29 ± 0.08 mm. - Metasome 3-segmented, last segment formed by the fusion of 4th and 5th pedigerous somites.. - Suture between cephalosome band 1st pedigerous somite, obscure in previous stages, now relatively distincy but incomplete. - Metasomal posterior processes charactyeristic of the species, well developed. - Ratio of prosome to urosome 4.31 ± 0.27. - A1 23-segmented, with fusions at 8th-9th and 24th-25th segments. - Endopod of Mxp 5-segmented. - P5 appears only in male; uniramous, 2-segmented, and nearly symmetrical. 2nd segment of left leg slightly narrower and longer than right; each with 3 spines, 1 at middle of lateral margin and 2 at distal margin, medial distal being longest.
|
 Issued from : D.C. Maclellan & C.-T. Shih in J. Fish Res. Board Can., 1974, 31 (8). [p.1340, Figs. 20-30]. Copepodite III (from Gulf of St. Lawrence): 20-21, habitus (dorsal and lateral, respectively; 22, A2; 23, Md; 24, Mx1; 25 Mx2; 26, Mxp; 27-30, P1 to P4. Upper scale for whole specimens, and lower for appendages.
Nota:
- Total length 1.16-1.28 mm.
- Ratio of prosome to urosome 4.0-4.5.
- Metasome 3-segmented.
- A1 22-segmented
- Endopod of Mxp 4-segmented.
|
 Issued from : D.C. Maclellan & C.-T. Shih in J. Fish Res. Board Can., 1974, 31 (8). [p.1339, Figs. 10-19]. Copepodite II (from Gulf of St. Lawrence): 10-11, habitus (dorsal and lateral, respectively; 12, A2; 13, Md; 14, Mx1; 15, Mx2; 16, Mxp; 17-19, P1 to P3. Upper scale for whole specimens, and lower for appendages. Nota; - Total length 0.85-0.92 mm. - Ratio of prosome to urosome 4.0-4.5. - A1 17-segmented. - Endopod of Mxp 3-segmented.
|
 Issued from : D.C. Maclellan & C.-T. Shih in J. Fish Res. Board Can., 1974, 31 (8). [p.1339, Figs. 1-9]. Copepodite I (from Gulf of St. Lawrence): 1-2, habitus (dorsal and lateral, respectively; 3, A2; 4, Md; 5, Mx1; 6, Mx2; 7, Mxp; 8, P1; 9, P2. Upper scale for whole specimens, and lower for appendages. Nota: - Total length (excluding caudal setae): 0.56-0.60 mm. - 1st pedigerous somite fused with cephalosome. - Metasome 1-segmented, with rounded posterior margin bearing a blunt process on each posterior lateral corner. - Urosome 2-segmented. - 2nd urosomal somite twice the length of 1st. - Ratio of prosome to urosome about 4. - A1 10-segmented. - Md protopod 2-segmented, endopod 2-segmented; exopod 5-segmented; gnathobase with 7 teeth. P1 and P2 with 2-segmented protopod; exopod and endopod 1-segmented each.
| | | | | Compl. Ref.: | | | Lysholm & Nordgaard, 1921 (p.12); Sewell, 1948 (p.347); C.B. Wilson, 1950 (p.189); Mazza, 1966 (p.70); Furuhashi, 1966 a (p.295, vertical distribution in Kuroshio region, Table 10) ;Park, 1970 (p.475); Björnberg, 1973 (p.323, 389); Arcos, 1976 (p.85, Rem.: p.93, Table II); Vives, 1982 (p.291); Brenning, 1983 (p.2, Rem.); Roe, 1984 (p.356); Tremblay & Anderson, 1984 (p.3); Brenning, 1985 a (p.28, Table 2); Mackas & Anderson, 1986 (p.115, Table 2); Wiebe & al., 1988 (tab.7); Shih & Marhue, 1991 (tab.2, 3); Errhif & al., 1997 (p.422); Suarez-Morales & Gasca, 1998 a (p107); Dolganova & al., 1999 (p.13, tab.1); Razouls & al., 2000 (p.343, Appendix); Holmes, 2001 (p.47); Sameoto & al., 2002 (p.12); Bradford-Grieve, 2004 (p.284); Hsiao & al., 2004 (p.325, tab.1); Park, W & al., 2004 (p.464, tab.1); Lo & al., 2004 (p.89, tab.1); Lewis & al., 2006 (p.501, Table I, fig.3); Kosobokova & al., 2007 (p.929: Tab.7); Gaard & al., 2008 (p.59, Table 1, N Mid-Atlantic Ridge); Darnis & al., 2008 (p.994, Table 1, figs.8, 9); Pepin & al., 2008 (p.1, 44, figs. 25 cont'd, 33, interannual variations); Galbraith, 2009 (pers. comm.); Park & Ferrari, 2009 (p.143, Table 4, Appendix 1, biogeography); Lewis & al., 2010 (p.695, Table I); Hidalgo & al., 2010 (p.2089, Table 2); Teuber & al., 2013 (p.1, Table 1, abundance vs oxygen minimum zone); Bonecker & a., 2014 (p.445, Table II: frequency, horizontal & vertical distributions); Belmonte, 2018 (p.273, Table I: Italian zones) | | | | NZ: | 21 | | |
|
Distribution map of Chiridius gracilis by geographical zones
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Loc: | | | Antarct. (S Atlant., S & SE Pacif.), Magallones region, sub-Antarct. (Indian, S & SE Pacif.), South Africa, Angola, off Mauritania, Brazil, G. of Mexico, G. of St. Lawrence, off E Nova Scotia, Flemish Cape, S Iceland, off Ireland (S & W), N Scotland, Faroe Is., Norway Sea, Bay of Biscay, off W Cape Finisterre, Medit. (Tyrrhenian Sea, Lebanon), off S Laccadive Is., N Indian, S Indian (subtropical convergence), Indonesia-Malaysia, Flores Sea, Molucca Sea, Halmarea Sea, Philippines, China Seas (East China Sea, South China Sea), Taiwan (E, N: Mienhua Canyon), Japan Sea, Japan, Suruga Bay, SW Bösö, G. of Alaska (Icy Strait), NE Pacif. (Strait of Georgia, ? Reine Charlotte Is., British Columbia, Fjord system (Alice Arm & Hastings Arm), Portland Inlet, Saanich Inlet), Guaymas Basin, New Zealand (Kaikoura), Australia (Great Barrier), Chile (N-S), Straits of Magellan (Pacific and central area), Arct. (SE Beaufort Sea in Darnis & al., 2008 (p.994, Table 1)
| | | | N: | 54 | | | | Lg.: | | | (5) F: 2,4; (7) F: 2,69; (24) F: 2,8-2,4; (25) F: 2,79; (29) F: 2,2; (34) F: 2,7; (35) F: 2,4-2,3; (36) F: 2,88-2,65; M: 2,43-2,29; (37) F: 2,8-2,45; M: 2,32-1,96; (39) F: 2,55; M: 2,32; (113) F: 2,87-2,4; M: 2,25-2,03; (116) F: 2,61; 2,54; (128) F: 2,64-2,57; (227) F: 3,1-2,68; M: 2,57-2,33; (231) M: 2,03; 2; (866) F: 2,2-2,87; M: 2,03-2,32; (1089) F: 2,6-3,1; M: 2,3-2,6; (1109) F; 2,5; (1122) M: 2,32; {F: 2,20-3,10; M: 1,96-2,60} | | | | Rem.: | Mesopelagic.
Sampling depth (Antarct., sub-Antarct.) : 0-1000 m
There are some disagreements on synonymies between the authors.
Found by Markhaseva (1996, p.111) in the southernmost from the Antarctic sector of the Pacific Ocean and for the first time in the north-eastern part the Indian Ocean.
Found in the Namibia-Angola region by Teuber & al., 2013 (Table 1) for the first time (epipelagic and mesopelagic).
For Maclellan & Shih (1974, p.1348) the pattern of egg laying exibits a difference between our study and that of Matthews (1964). The latter reported that the females of the four aetideid species in his investigation shed their eggs directly into the water. In our study the ovigerous female of Chiridius gtracilis retain the eggs on the genital segment in a medially placed ovisac. | | | Last update : 05/02/2020 | |
|
|
 Any use of this site for a publication will be mentioned with the following reference : Any use of this site for a publication will be mentioned with the following reference :
Razouls C., Desreumaux N., Kouwenberg J. and de Bovée F., 2005-2026. - Biodiversity of Marine Planktonic Copepods (morphology, geographical distribution and biological data). Sorbonne University, CNRS. Available at http://copepodes.obs-banyuls.fr/en [Accessed February 04, 2026] © copyright 2005-2026 Sorbonne University, CNRS
|
|
 |
 |