|
|
 |
|
Calanoida ( Order ) |
|
|
|
Clausocalanoidea ( Superfamily ) |
|
|
|
Aetideidae ( Family ) |
|
|
|
Comantenna ( Genus ) |
|
|
| |
Comantenna crassa Bradford, 1969 (F) | |
| | | | | | | Ref.: | | | Bradford, 1969 b (p.484, Descr.F, figs.F); Bradford & Jillett, 1980 (p.29, figs.F, distribution chart); Markhaseva, 1996 (p.138, figs.F); Schulz, 2002 (p.106, Rem.); Markhaseva & al., 2017 a (p.26, Redescr.F, figs.F, Table 1, Rem.) |  issued from : J.M. Bradford in N.Z. Jl Mar. Freshw. Res., 1969, 3 (4). [p.485, Figs 70-80]. Female (from NE New Zealand: Bay of Plenty]: 70, Mxp; 71, habitus (dorsal); 72, Mx1; 73, P3; 74, habitus (lateral right side); 75, Md; 76, urosome (dorsal); 77, Mx2; 78, P1; 79, urosome (lateral right side); 80, P2 (incomplete); 81, A2. Nota: Head and 1st thoracic segment fused (but fusion line visible), 4th and 5th separate. Rostrum absent. Npta after Markhaseva (1996, p.138): Cephalothorax nearly 4 times longer than urosome. Cephalon and thoracic segment 1 fused, 4th and 5th segments separated. Gnathobase of Mx1 with 14 setae (9 terminal large, 1 small and 4 setae on the posterior surface); 2nd and 3rd internal lobes with 4 and 3 setae respectively; protopodite with 4 setae near endopod base; endopod with 12 setae; exopod with 11 setae and external lobe with 4 setae.
|
 issued from : M.P.J. Alvarez in J. Crustacean Biol., 1986, 614. [p.873, Figs.71-73]. After Bradford (1969). Female: 71, A2; 72, Mx2; 73, Mxp.
|
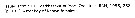 Comantenna crassa Comantenna crassa female: 1 - Endopod of P1 with external lobe strongly reduced. Bapipoite of P1 without seta near endopod base. 2 - Right posterior corner of last thoracic segment as long as left (dorsal view). Protopodite of Mxp with 3 medial setae. Endopodal segment 2 of Md with 4 setae.
|
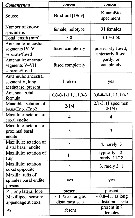 Issued from : E.L. Markhaseva, J.M. Bradford-Grieve & J. Renz in Arthropodia Selecta, 2017, 26 (1). [p.29, Table 1]. Selected characters in female.
Compare with other species in Comantenna
KuramBio (Kurile Kamchatka Biodiversity Study) expedition using an epibenthic sledge (Brenke, 2005). Samples collected in 2012 in the vicinity of the seabed at depths from 4859 to 5399 m. Individuals were present both, the supranet (sampling layer ca. 0.77)1.12 m above the bottom) and the epinet subsamples (0.25-0.60 m above the bottom).
|
 Issued from : E.L. Markhaseva, J.M. Bradford-Grieve & J. Renz in Arthropoda Selecta, 2017, 26 (1). [p.27, Fig.1]. Female (from Kuril-Kamchatka Trench): A-B, habitus (dorsal and lateral, respectively); C, D, E, F,posterior prosome and genital double-somite (lateral view); G, genital field (ventral); H, right A1 (ancestral segments I-XIX; I, same (ancestral segments XX-XXVIII). A-D, H-I: specimen from Sta 2 (46°14.77' N, 155°32.79' E; at depths 4859-4865 m); E-G, J: specimens from Sta 10-12 Scale bars: : A-B 1mm, remaining figures 0.1 mm . Nota: - Prosome 3.05-4.2 times as long as urosome. -- Cephalosome and pediger 1 partly fused (holotype) or fused, pedigers 4 & 5 separate. - Posterior corners of prosome upturned dorsally. - Genital double-somite with spermathecae directed dorsoanteriorly, bent at midlength at various obtuse angles, not visible in ventral view. - Rostrum absent. - Caudal rami with 4 terminal (III-VI), 1 ventral (VII) and 2 dorsolateral (I-II) setae. - A1 21-segme,ted, reaching to middle of pediger 2, or to posterior part of pediger 3; ancestral segments II_VII usually fused although signs of demarcation between segments IV-V, V-VI and VI-VII evident and segments X-XI, XXVII-XXVIII also fused.; aesthetasc long with an oval tip on ancestral segment V. For the authors (see remarks p.30), the specimens from the Kuril-Kamchatka have been attributed to the species C. crassa, which description was based on a moderately damaged single female holotype, further analysis reveals specimens to share the general features of C. crassa as updated from reexamination of the holotype by J. Bradford-Grieve.. The NW Pacific specimens and the holotype differ in minor details : 1- their smaller size; 2- the cephalosome and pediger 1 are fused (vs partly partly fused in the holotype); 3- the spermathecae narrow or expanded anteriotly (narrow in the holotype); 4- A1 ancestral segment XIV short terminal seta is not broad at its base (vs seta seems to be distinctively broad in holotype); 5- Mxp distal sensory appendage about 0.8-1.1 as long as the distalmost coxal seta (vs sensory appendage definitely longer in the holotype); 6- Mxp distal praecoxal endite is smooth (supplied by small denticles in the holotype). These differences are regarded as reflecting intraspecific variation as the range of this variation among NW Pacific specimens. The NW Pacific specimens show a considerable variability concerning the curvature of the spermathecae, the degree of fusion between antennal ancestral segments IV-VII (sehgments IV-V can be fused completely or incompletely; V-VI and VI-VII can be fused , incompletely fused or separate; Mxp coxal sensory appendage varies in length from 0.8 to 1.1 times as long as the distalmost coxal seta; P5 is absent or present §in 9 specimens), when present, then of various configurations (see fig. 2H-L). Yje presence or absence of P5 was not found to be associated with variability of the posterior prosomal corners, spermathecae, oral parts or legs.
|
 Issued from : E.L. Markhaseva, J.M. Bradford-Grieve & J. Renz in Arthropoda Selecta, 2017, 26 (1). [p.28, Fig.2]. Female: A, caudal rami ( ventral view); B, A2 (two proximal setae marked by arrows; coxa indicated by dotted line added after another specimen) ; C, A1 (3 terminal exopod segments); D, Mxp syncoxa; E- F, Mxp coxa distal setae and sensory appendage (arrows mark proximalmost seta); G, P1; H-L, P5. A, K: specimens from Sta 10-12; B-D, G: specimens from Sta 2-10; H-I, L: specimens from Sta 9-12; F, J: specimens from Sta 8-12. Scale bars = 0.1 mm. Nota: Sta 9-12 (40°34.49' N, 150°59.87' E at depths 5399-5392 m); Sta 8-12 (42°14.38' N, 151°43.12' E at depths 5117-5124 m). Nota: - A2 with the 1st endopodal segment longer than exopod; 2nd enopodal segment with 8+7 setae; exopod indistinctly 6-segmented, setal formula 0, [0-0-1-1], 1, 1, 1, [0-3]; terminal exopodal segment nearly as long as 2 preceding segments, with 3 setae - Md: basis with 2 setae; exopod 5-segmented with 1, 1, 1, 1, 2 setae; endopoal segment 1 with 1 seta, segment 2 with 4+5 setae. - Mx1: praecoxal arthrite (inner lobe 1) with 9 terminal, 4 posterior and 1 anterior setae; coxal endite with 4 setae; proximal basal endite with 3 setae; distal basal endite with 4 (rarely 3) setae; endopod with 12 (rarely 11) setae; exopod with 11 setae; coxal epipodite with 3 (rarely4) setae. - Mx2: all endites with 3 setal elements; praecoxal to basal endites with tufts of spinules; endopod with 6 setae. - Mxp: praecoxal endites of syncoxa with 1, 2 and 3 setae §from proximal to distal); coxal endite of syncoxa with 3 setae, sensory appendage varies in length from about 0.8 to 1.1 as long as the distalmost coxal seta (proximmalmost seta 0.1 to 0.5 as long as coxal plumose middle seta); basis with 3 medial setae; endopod witth 2, 4, 4, 3, 3+1 and 4 setae.
| | | | | Compl. Ref.: | | | Markhaseva, 1998 (p.250, Fig.3, as crassus); Bradford-Grieve, 2004 (p.284) | | | | NZ: | 2 | | |
|
Distribution map of Comantenna crassa by geographical zones
|
| | | | Loc: | | | SW Pacif. (NE New Zealand), NW Pacif. (Kuril Trench).
Type locality: 37°07'S, 177°14'E. | | | | N: | 2 | | | | Lg.: | | | (230) F: 3,8; (1214) F: 3,10-3,50; {F: 3,10-3,80} | | | | Rem.: | hyperbenthic; bathypelagic (Depths: 1234-1260 m). Abyssal (2000-5000 m)
See remarks in Comantenna recurvata from Alvarez (1986, p.862).
For Markhaseva (1996, p.138) this species, not examined by her, is very similar if not identical to C. brevicornis. For Markhaseva & al. (2017 a, p.30) tis species is closely related to C. recurvata, nevertheless C. crassa may be distinguished from C. recurvata by: 1- A1 ancestral segments V-VII partly or completely fused anteriorly and completely fused posteriorly (vs segments separate in C. recurvata; 2- P1 endopod lateral lobe developed (vs lateral lobe absent in C. recurvata). Compare the selected characters of the different species in Comantenna females (Table 1, p.29). | | | Last update : 01/04/2018 | |
|
|
 Any use of this site for a publication will be mentioned with the following reference : Any use of this site for a publication will be mentioned with the following reference :
Razouls C., Desreumaux N., Kouwenberg J. and de Bovée F., 2005-2025. - Biodiversity of Marine Planktonic Copepods (morphology, geographical distribution and biological data). Sorbonne University, CNRS. Available at http://copepodes.obs-banyuls.fr/en [Accessed January 05, 2026] © copyright 2005-2025 Sorbonne University, CNRS
|
|
 |
 |