|
|
 |
|
Cyclopoida ( Order ) |
|
|
|
Corycaeidae ( Family ) |
|
|
|
Farranula ( Genus ) |
|
|
| |
Farranula concinna (Dana, 1849) (F,M) | |
| | | | | | | Syn.: | Corycńus concinnus : Giesbrecht, 1892 (p.661, 675, figs.F);
Corycaeus cobcinnus : Carl, 1907 (p.18);
Corycella concinna : Farran, 1911 a (p.286, Rem.); Farran, 1936 a (p.139); Dakin & Colefax, 1940 (p.110, figs.F); Moore, 1949 (p.64); De Decker, 1964 (p.15, 21, 30, 31, 32); De Decker & Mombeck, 1964 (p.12); KÔ & Hwang, 2011 (p.155, Table 3: occurrence %, as Cor. concinnuns);
Corycaeus concinnus : F. Dahl, 1894 (p.69); A. Scott, 1902 (p.421); Thompson & Scott, 1903 (p.240, 286); Carl, 1907 (p.18); A. Scott, 1909 (p.246, Rem.); Mori, 1937 (1964) (p.138, figs.F,M); Chiba & al., 1957 (p.312); 1957 a (p.12); Yamazi, 1958 (p.155, Rem.); Furuhashi, 1961 a (p.110); Tanaka, 1964 (p.17); Sen˘ & al., 1966 (p.5); Furuhashi, 1966 a (p.295, vertical distribution in Kuroshio region, Table 9); Suvapepun & Suwanrumpha, 1970 (p.5); Hirakawa & al., 1990 (tab.3); Go & al., 1997 (tab.1); Noda & al., 1998 (p.55, Table 3, occurrence); Tseng & al., 2009 (p.327, fig.5, feeding); Maiphae & Sa-ardrit, 2011 (p.641, Table 2, 3, Rem.); Hwang & al., 2014 (p.43, Appendix A: seasonal abundance, as concinna);
Corycaeus (Corycella) concinnus : M. Dahl, 1912 (p.121, figs.F,M); FrŘchtl, 1923 (p.450); 1924 b (p.94); Dakin & Colefax, 1933 (p.209); Sewell, 1948 (p.393, 398); Tanaka, 1957 (p.96, figs.F,M, Rem); 1960 (p.88, figs.F,M, Rem.); Chen & al., 1974 (p.66, figs.F,M); Frontier, 1977 a (p.18); Zheng & al., 1982 (p.150, figs.F); Zheng Zhong & al., 1984 (1989) (p.268, Rem.); Guangshan & Honglin, 1984 (p.118, tab.); Shih & Young, 1995 (p.76);
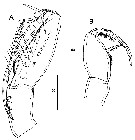
Corycaeus (Farranula) concinna : Hwang & al., 2006 (p.943, tabl. I); Hwang & al., 2007 (p.25); Tseng & al., 2013 (p.507, seasonal abundance); Tseng & al., 2013 a (p.1, Table 3, 5, abundance) | | | | Ref.: | | | Wilson, 1942 a (p.186, fig.F); 1950 (p.228); Fagetti, 1962 (p.49); Motoda, 1963 (p.257, figs.F); Marques, 1976 (p.1002); 1982 (p.777); Yoo, 1991 (tab.1); Chihara & Murano, 1997 (p.967, Pl.219: F,M); Bradford-Grieve & al., 1999 (p.888, 975, figs.F,M); Ueda & al., 2000 (tab.1); Conway & al., 2003 (p.259, figs.F,M, Rem.); Boxshall & Halsey, 2004 (p.493); Wi & Soh, 2013 (p.5, Redescr.F,M, figs.F,M, Rem.); Soh & al., 2013 (p.142, figs.F,M) | 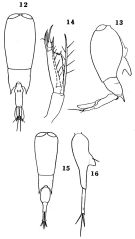 issued from : O. Tanaka in J. Fac. Agricult. Kyushu Univ., 1957, 11 (1). [Pl.10, Figs.12-16]. As Corycaeus (Corycella) concinnus. Female (from Japanese waters): 12, habitus (dorsal); 13, idem (lateral right side); 14, A2. Male: 15, habitus (dorsal); 16, urosome (lateral right side).
|
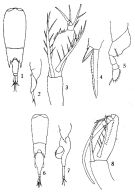 issued from : Q.-c Chen & S.-z. Zhang & C.-s. Zhu in Studia Marina Sinica, 1974, 9. [Pl.23, Figs.1-8]. As Corycaeus (Corycella) concinnus. Female (from China Seas): 1, habitus (dorsal); 2, last portion of thorax and urosome (lateral left side); 3, A2; 4, distal part of exopodite segment 3 of P2; 5, P4. Male: 6, habitus (dorsal); 7, last portion of thorax and urosome (lateral left side); 8, A2.
|
 issued from : Z. Zheng, S. Li, S.J. Li & B. Chen inMarine planktonic copepods in Chinese waters. Shanghai Sc. Techn. Press, 1982 [p.151, Fig.96]. Female: a-b, habitus (dorsal and lateral, respectively); c, urosome (lateral, right side); d, A2; e, P4.
|
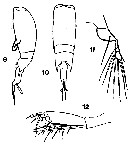 issued from : T. Mori in The Pelagic copepoda from the neighbouring waters of Japan, 1937 (1964). [Pl.77, Figs.9-12]. As Corycaeus concinnus. Female : 9, habitus (lateral); 10, idem (dorsal); 11, P4; 12, A2.
|
 issued from : T. Mori in The Pelagic copepoda from the neighbouring waters of Japan, 1937 (1964). [Pl.77, Figs.5-8]. As Corycaeus concinnus. Male: 5, A2; 6, P4; 7, habitus (lateral); 8, idem (dorsal).
|
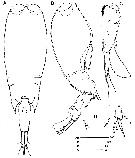 Issued from : J.H. Wi & H.Y. Soh in J. Nat. Hist., 2013. [p.6, Fig.2]. Female (from 32░00'N, 126░5'E): A-B, habitus (dorsal and lateral, respectively); C, urosome (lateral); D, P5; R, caudal setae left. Scale bars in Ám.
|
 Issued from : J.H. Wi & H.Y. Soh in J. Nat. Hist., 2013. [p.8, Fig.3]. Female: A, A1; B, A2 (posterior); C, distal margin of A2 (anterior), arrow indicating naked seta on distal outer margin; D, Md, left side; E, Md, right side; F, Mx1, indivudual elements designated using capital letters; G, Mx2; H, Mxp. Scale bars in Ám. Nota: Md with 2 elements on gnathobase: 1 spine and 1 blade. Spine broad and robust, with 2 naked slender setae on medial area and 2 basal setae. Blade forming spinuos processes, surronded by patch of spinules aroud base. Mx1 reduced, bearing 4 articulated spinous elements: innermost (A) at some distance from other elements and distal margin serrated, element (B) longest and stout, and distal margin with spinous process, element (C) short and serrated, and element (D) short and naked. Mx2: 2-segmented, allobasis shorter than syncoxa: syncoxa unarmed; allobasis produced distally into strong spine, carrying 2 naked setae proximally, inner margin bearing 3 spines of different lengths: 2 naked spines and longest, unipinnate innermost spine with slender naked seta at base of spine. Mxp: 3-segmented: syncoxa unarmed; basis robust and expanded, with 2 elements along margin: 1 proximal short, located at base of distal one, 1 distal element with 2 to 4 spinules along inner margin, located at two-thirds distance of inner margin , 3 times shorter than basis; endopodal segment drawn out into long curved claw, unornamented and slightly shorter than basis, accessory armature consisting of slender long, unipinnate seta on inner proximal margin, and short unipectinate spine laterally on outer proximal margin of claw.
|
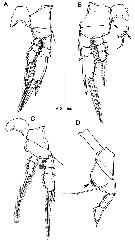 Issued from : J.H. Wi & H.Y. Soh in J. Nat. Hist., 2013. [p.9, Fig.4]. Female: A, P1; B, P2; C, P3; D, P4. Arrows indicate row of spinules along inner margin of basis. Scale bar in Ám.
|
 Issued from : J.H. Wi & H.Y. Soh in J. Nat. Hist., 2013. [p.10, Table 2]. Female: Armature formula of swimming legs P1 to P4; Roman numerals indicate spines; arabic numerals indicate setae, note for each segment from outer to inner.
|
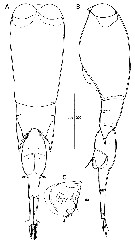 Issued from : J.H. Wi & H.Y. Soh in J. Nat. Hist., 2013. [p.11, Fig.5]. Male (from 32░00'N, 126░5'E): A-B, habitus (dorsal and lateral, respectively); C, genital flap, large denticles indicated by arrow. Scale bars in Ám.
|
 Issued from : J.H. Wi & H.Y. Soh in J. Nat. Hist., 2013. [p.13, Fig.6, A-B]. Male: A, A2; B, Mxp. Scale bars in Ám.
|
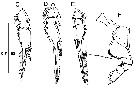 Issued from : J.H. Wi & H.Y. Soh in J. Nat. Hist., 2013. [p.3, Fig.6, C-F]. Male: C, exopod of P1; D, exopod of P2; ; E, exopod of P3; F, P4. Scale bar in Ám.
|
 Issued from : J.H. Wi & H.Y. Soh in J. Nat. Hist., 2013. [p.3, Table I]. Length and width proportions of body segments of Farranula concinna. Nota: Compare with other species of Farranula (on line: http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/00222933.2012.708454).
|
 Issued from : O. Tanaka in Spec. Publs. Seto mar. biol. Lab., 10, 1960 [Pl. XXXVIII, 4-7]. As Corycaeus (Corycella) concinnus. Female (from South China Sea and Indian Ocean): 4, abdomen (dorsal); 5, same (lateral); 6, abdomen (dorsal; other specimen measuring 0.81 mm). Nota: Cephalothorax and abdomen in the proportional lengths 68 to 32. Abdominal segment and caudal rami in the proportional lengths 70 to 30. Genital segment broadest at the anterior 1/5 of the segment, and 2.6 times as long as broad. Caudal rami about 5 times as long as broad (17 : 3.5). Caudal rami straight and set closely together. Male: 7, abdomen (lateral). Nota: Cephalothorax and abdomen in the proportional lengths 58 to 42. Abdominal segment and caudal rami in the proportional lengths 69 to 31. Genital segment in lateral view slender, 3 times as long as high.
|
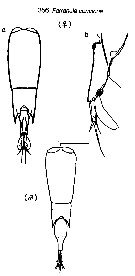 Issued from : M. Chihara & M. Murano (eds) inAn illustrated Guide to the Marine Plankton in Japan, 1997. [p.977, Pl. 219, fig.356]. Female: a, habitus (dorsal), b, urosome with spermatophore (lateral). Male (after Tanaka, 1957): habitus (dorsal).
|
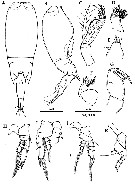 Issued from : H.Y. Soh, S.Y. Moon & J.H. Wi in Invertebrate Fauna of Korea (eds) Incheon: NIBR, 2013, 21 (28). [p.144, Fig.83]. Female (from Korean waters): A-B, habitus (dorsal and lateral, respectively); C, A2; D, Md; E, Mx1; F, Mx2; G, Mxp; H, P1; I, P2; J, P3; K, P4. Scale bars: A, B = 200 Ám; C, G, J = 100 Ám; D-F , H, I, K = 50 Ám.
|
 Issued from : H.Y. Soh, S.Y. Moon & J.H. Wi in Invertebrate Fauna of Korea (eds) Incheon: NIBR, 2013, 21 (28). [p.145, Fig.84]. Male: A, habitus (dorsal); B, A2; C, Mxp; D, exopod of P1; E, exopod of P2; F, exopod of P3; G, P4; H, P6. Scale bars: A = 200 Ám; B, C, H = 50 Ám; D-G = 100 Ám.
| | | | | Compl. Ref.: | | | Zalkina, 1977 (p.339, tab.1); Star & Mullin, 1981 (p.1322, abundance); Dessier, 1983 (p.89, Tableau 1, Rem., %); Binet, 1984 (tab.3); 1985 (p.85, tab.3); Dessier, 1988 (tabl.1); Othman & al., 1990 (p.561, 564, Table 1); Hsieh & Chiu, 1998 (tab.2); Lan & al., 2004 (p.332, tab.1); Lo & al., 2004 (p.89, tab.1); McKinnon & al., 2008 (p.843: Tab.1); Tseng L.-C. & al., 2008 (p.153, Table 2, occurrence vs geographic distribution); Lan Y.-C. & al., 2008 (p.61, Table 2: indicator species); C.-Y. Lee & al., 2009 (p.151, Tab.2); Lan Y.-C. & al., 2009 (p.1, Table 2, % vs hydrogaphic conditions); Hsiao S.H. & al., 2011 (p.475, Appendix I); Johan & al., 2012 (2013) (p.1, Table 1); Zakaria & al., 2016 (p.1, Table 1, Rem.) | | | | NZ: | 11 | | |
|
Distribution map of Farranula concinna by geographical zones
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | Loc: | | | Agulhas Current, South Africa (off Cape of Good Hope, E & W), Bermuda (in Moore, 1949, p.64), E Medit. (Egyptian coast), Seychelles, Madagascar (Nosy BÚ), Rodrigues Is., Sri Lanka, Indian, G. of Thailand, Indonesia-Malaysia, Sarawak: Bintulu coast, Ambon Bay, Sulu Sea, Philippines, China Seas (Yellow Sea, East China Sea, South China Sea), Taiwan Strait, Taiwan (E, S, W, NW, N: Mienhua Canyon, NE), Okinawa, Jeju Island, Japan, Kuchinoerabu Is., Tanabe Bay, Pacif. (W equatorial), Pacif. (N Central Gyre), Australia (Great Barrier, New South Wales, North West Cape, G. of Carpentaria), New Caledonia, off Hawaii, N Pacif., off N Tuamotu Is., Pacif. (E equatorial), off Chile | | | | N: | 92 | | | | Lg.: | | | (34) F: 0,88; (46) F: 0,9-0,85; (66) F: 0,97-0,84; M: 0,84-0,82; (104) F: 0,9; (107) F: 0,9-0,84; M: 0,78-0,73; (109) F: 0,92-0,87; M: 0,87-0,82; (114) F: 0,93-0,88; (332) F: 0,9; M: 0,9-0,8; (333) F: 0,91; (666) F: 0,84; (667) F: 1,04-0,79; (786) F: 0,86; M: 0,81; (866) F: 0,84-0,90; M: 0,73-0,78; (991) F: 0,84-0,9; M: 0,73-0,78; (1023) F: 0,94; (1116)* F: 0,93; M: 0,845; {F: 0,79-1,04; M: 0,73-0,90}
*: measured in lateral view. Average: F : 0.885 (n = 4); M: 0.820 (n = 7)
| | | | Rem.: | Epipelagic.
Zakaria & al. (2016) note the occurrence of this species for the first time in the East Mediterranean Sea (West Egyptian coast).
See in DVP Conway & al., 2003 (version 1) | | | Last update : 14/05/2019 | |
|
|
 Any use of this site for a publication will be mentioned with the following reference : Any use of this site for a publication will be mentioned with the following reference :
Razouls C., Desreumaux N., Kouwenberg J. and de Bovée F., 2005-2026. - Biodiversity of Marine Planktonic Copepods (morphology, geographical distribution and biological data). Sorbonne University, CNRS. Available at http://copepodes.obs-banyuls.fr/en [Accessed March 14, 2026] © copyright 2005-2026 Sorbonne University, CNRS
|
|
 |
 |