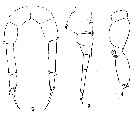|
|
 |
|
Calanoida ( Order ) |
|
|
|
Diaptomoidea ( Superfamily ) |
|
|
|
Pseudodiaptomidae ( Family ) |
|
|
|
Pseudodiaptomus ( Genus ) |
|
|
| |
Pseudodiaptomus pelagicus Herrick, 1884 (F,M) | |
| | | | | | | Syn.: | Pseudodiaptomus coronatus Williams,1906; Wilson, 1932 a (p.101); Marsh, 1933 (p.32, figs.F,M); Wright, 1936 (p.18-19: Rem., fig.M), Rem.; 1937 a (p.159, Pl.1, fig.3: M); Davis, 1948 (p.82, fig.M); Deevey, 1956 (tab.IV); Grice, 1956 (p.64); Deevey, 1960 (p.5, Table II, fig.7, 11, 14: annual abundance, Rem.: p.28, fig.18, 19) ; Martin, 1965 (p.188); Faber, 1966 (p.191, 198, figs.N); 1966 a (p.418, 419); Shih & al., 1971 (p.46); Katona, 1973 (p.574, Table 1, 2, sex pheromones); Knatz, 1978 (p.68, Table 1, abundance, %); Paffenhöfer & Knowles, 1978 (p.574, feeding); Paffenhöfer & Knowles, 1980 (p.355, feeding); Citarella, 1982 (p.791, 798: listing, frequency, Tableau II, V); Jacoby & Youngbluth, 1983 (p.77, Table 2, 3, Rem: mating behavior); Tremblay & Anderson, 1984 (p.6); Citarella, 1989 (p.123, abundance); Mauchline, 1998 (tab.46, 47, 56, 64); G. Harding, 2004 (p.37, figs.F,M); Ferrari & Dahms, 2007 (p.22, Rem. N);
? P. americanus Wright, 1937 (p.157, Pl.1, fig.2) | | | | Ref.: | | | Marsh, 1933 (p.38, figs.F,M); Dussart & Defaye, 1983 (p.29); Walter, 1986 (p.131, 162); 1986 a (p.503, fig.1); 1987 (p.366); 1989 (p.591, Redescr.F, M, figs.F,M, zoogeogr.) | 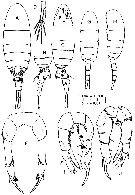 issued from : T.C. Walter in Bull. Mar. Sc., 1989, 45 (3). [p.594, Fig.2]. Female: A, habitus (dorsal); B, last thoracic segments and urosome (lateral right side); C, idem (lateral left side); D, caudal rami; E, head (ventral view); F, P5 (anterior view). Male: G, habitus (dorsal); H, idem (lateral left side); I, P5 (posterior view); J, idem (anterior view).
|
 issued from : T.C. Walter in Bull. Mar. Sc., 1989, 45 (3). [p.595, Fig.3]. Intersex variation. Female: A, habitus (lateral left side); B, idem (dorsal); C, last thoracic segments and urosome (lateral right side); D, P5 (anterior view). Male: E, habitus (dorsal); F, thoacic segments and urosome (lateral left side); G, P5 (posterior view); H, idem (anterior view); I-J, variations noted in posterior of basipod 1; K, P5 (anterior view; from additional male variant).
|
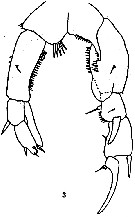 issued from : S. Wright in Ann. Acad. Brasileira Sci., 1937, 9 (2). [Pl.1, Fig.3]. As Pseudodiaptomus coronatus. Male: 3, P5.
|
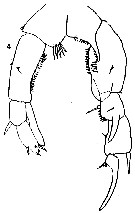 issued from : S. Wright in Ann. Acad. Brasileira Sci., 1936, VIII (1). [Pl.II, Fig.4]. As Pseudodiaptomus coronatus. Male (from Mississippi River): 4, P5.
|
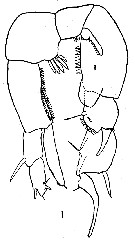 issued from : C.C. Davis in Q. Jl. Fla Acad. Sci., 1948, 10 (2-3). [Pl. I, Fig.1]. Male (from Long Lake, Florida): 1, P5.
|
 issued from : G. Harding in Key to the adullt pelagic calanoid copepods found over the continental shelf of the Canadian Atlantic coast. Bedford Inst. Oceanogr., Dartmouth, Nova Scotia, 2004. [p.37]. As Pseudodiaptomus coronatus. Female & Male. Nota: Female: metasome symmetrical. P5 tipped with curved serrate spine and toothed lamella. Male: right P5 (R) tipped with curved claw and stout plumose setae. Left P5 (L) biramous with elongated endoodite.
|
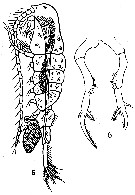 Issued from : C.D. Marsh in Proc. U.S. natn. Mus., 1933, 82 (18) (2959). [Pl. 19, figs.5-6]. After Herrick, 1887. Female (from Mississipi Sound): 5, habitus (lateral) with egg sac; 6, P5.
|
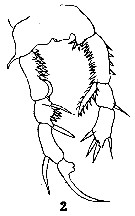 Issued from : C.D. Marsh in Proc. U.S. natn. Mus., 1933, 82 (18) (2959). [Pl. 20, fig.2]. After Herrick, 1887. Male: P5.
|
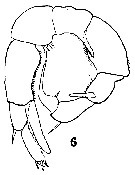 Issued from : C.D. Marsh in Proc. U.S. natn. Mus., 1933, 82 (18) (2959). [Pl. 16, fig.6]. As Pseudodiaptomus coronatus. Male (from Narragansett Bay): 6, P5. Nota: The 1st segment of basipod of the right P5 extended on the inner distal angle into a stout spine reaching about 1/2 the length of the 2nd segment of basipod; its inner border has a short spine. 1st segment of the right exopod with a stout blunt spine projecting from its dorsal surface, this spine is 3/4 as long as the segment; the inner border of the segment has short spines like those on the 2nd segment of the basipod and near the proximal end a a flask-shaped spine (this spine seems to be constant in the species). The 2nd exopodal segment has an acute external spine at about 3/4 of its length; the terminal hook is nearly as long as the two segments of the exopod; on its inner border, near the base, is an acute spine. The 1st basipodal segment of the left P5 has 4 slender acute spines on its inner border; 2nd basipodal segment with short spines along its inner border; the 1st exopodal segment is short, with an acute spine at its outer distal border; 2nd exopodal segment about twice the length of the 1st, and is pointed at the end where there are 3 acute spines. There is an endopod on the left P5.
|
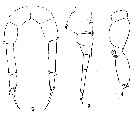 Issued from : C.D. Marsh in Proc. U.S. natn. Mus., 1933, 82 (18) (2959). [Pl. 16, figs.3-5]. As Pseudodiaptomus coronatus. Female: 3, urosome (lateral); 4, exopod of A2; 5, P5. Nota: Urosome 4-segmented, 2nd and 3rd ordinarily imperfectly separated. 1st urosomal segment with rows of small spines on the dorsal surface at about 1/2 its length and spines on the distal margin; it is enlarged in front and has a pair of linguiform flaps over the genital aperture. Length of the caudal rami about 8 times their width, ciliate on both inner and outer margins. There are 2 egg sacs, but the right is aborted, containing only 2 eggs (sometimes the right is entirely lacking). A1 22-segmented, about equal in length the cephalothorax. Exopod of A2 apparently 6-segmented. In P5, the distal margins of the 2nd basipodal segment and the 1st exopodal segment armed with small spines. There is a spine at the exterior distal angle of the 1st exopodal segment. The 2nd exopodal segment terminates in a rather long curved hook; there is a spine at the outer distal angle and, near the inner angle, a broad plumose spine. A small spine is attached to the base of the hook. The 1st exopodal segment is more than twice as long as the 2nd.
| | | | | Compl. Ref.: | | | Sewell, 1948 (p.465); Jacobs, 1961 (p.443, rearing); Suarez-Morales & Gasca, 1998 a (p.111); Alvarez-Silva & Gomez-Aguirre, 2000 (p.163: tab.2); Rhyne & al., 2009 (p.53, reproduction & survival vs temperature); Ohs & al., 2010 (p.219, salinity effects vs survival); Ohs & al. 2010 (p.225, dietary-reproduction); Gusmao & al., 2013 (p.279, Table 4, sex ratio) | | | | NZ: | 2 | | |
|
Distribution map of Pseudodiaptomus pelagicus by geographical zones
|
| | |  issued from : T.C. Walter in Bull. Mar. Sc., 1989, 45 (3). [p.625, Fig.18]. issued from : T.C. Walter in Bull. Mar. Sc., 1989, 45 (3). [p.625, Fig.18].
Map of American continents showing the zoogeography of Pseudodiaptomus species. |
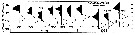 issued from : G.B. Deevey in Bull. Bingham Oceanogr. Coll., 1960 (2). [p.27, Fig.14]. issued from : G.B. Deevey in Bull. Bingham Oceanogr. Coll., 1960 (2). [p.27, Fig.14].
Variations in length (from the topof the head to the base of the caudal rami) of Pseudodiaptomus coronatus females in outside the Delaware Bay (NW Atlantic Ocean). |
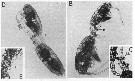 Issued from : C.A. Jacoby & M.J.Y. Youngbluth in Mar. Biol., 1983, 76. [p.79, Fig.1 B, C, D, E]. Issued from : C.A. Jacoby & M.J.Y. Youngbluth in Mar. Biol., 1983, 76. [p.79, Fig.1 B, C, D, E].
Mating sequence of Pseudodiaptomus coronatus (= P. pelagicus) pairs from the Indian River lagoon near Fort Pierce, Florida, USA . B, male (M) grasps the urosome of the female (F) with his right P5 (RL), note the darkly pigmented oocystes (O) in the female\"s metasome; C: position of male\"s right P5 (RL) just posterior to female's genital somite (GS); D,copulating male (M) and female (F) showing male's left P5 (LL); E, spermatophore (S) attached to female and male's left P5 (LL). |
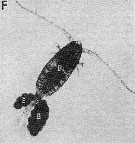 Issued from : C.A. Jacoby & M.J.Y. Youngbluth in Mar. Biol., 1983, 76. [p.79, Fig.1 F]. Issued from : C.A. Jacoby & M.J.Y. Youngbluth in Mar. Biol., 1983, 76. [p.79, Fig.1 F].
Pseudodiaptomus coronatus ( = P. pelagicus) female bearing a pair of egg sacs (E), note the lack of darkly pigmented oocytes in the female's matasome |
| | | | Loc: | | | G. of Mexico (mouth of Mississipi River), lagunas de Veracruz, Puerto Rico, Mississipi estuary, Florida, NE American coast, Georgia estuaries, Navesink River estuary, Delaware Bay (in Bay primarily), Long Island Sound, Narragansett Bay, Bay of Fundy, Bay of Shédiac, Northumberland Strait, G. of St. Lawrence) | | | | N: | 23 | | | | Lg.: | | | (177) F: 1,23-1,33; M: 0,92-0,97; (1012) F: 1,43; M: 0,98; (1148) F: 1,5; M: 1,2; {F: 1,23-1,50; M: 0,92-1,2} | | | | Rem.: | Marine & brackish form.
Incomplete data.
In Americanus species group (pelagicus subgroup) after Walter & al. 2006, p.203.
See Jacoby & Youngbluth (1983, Table 2 and 3): Life histories and characteristics of mating behavior for heterospecific and conspecific pairs in P. acutus. | | | Last update : 10/11/2018 | |
|
|
 Any use of this site for a publication will be mentioned with the following reference : Any use of this site for a publication will be mentioned with the following reference :
Razouls C., Desreumaux N., Kouwenberg J. and de Bovée F., 2005-2026. - Biodiversity of Marine Planktonic Copepods (morphology, geographical distribution and biological data). Sorbonne University, CNRS. Available at http://copepodes.obs-banyuls.fr/en [Accessed February 20, 2026] © copyright 2005-2026 Sorbonne University, CNRS
|
|
 |
 |