|
|
 |
|
Calanoida ( Order ) |
|
|
|
Diaptomoidea ( Superfamily ) |
|
|
|
Centropagidae ( Family ) |
|
|
|
Sinocalanus ( Genus ) |
|
|
| |
Sinocalanus sinensis (Poppe, 1889) (F,M) | |
| | | | | | | Syn.: | Limnocalanus sinensis Poppe, in de Guerne & Richard, 1889 (p.131, figs.F,M) | 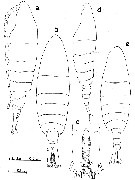 issued from : J. Hiromi & H. Ueda in Proc. jap. Soc. Syst. Zool., 1987, 35. [p.21, Fig.1]. Female (from Ushizu & Chikugo Rivers, Ariake-kai, Kyushu): a-b, habitus (lateral and dorsal, respectively); c, caudal rami (dorsal). Male: d-e, habitus (lateral and dorsal, respectively).
|
 issued from : J. Hiromi & H. Ueda in Proc. jap. Soc. Syst. Zool., 1987, 35. [p.22, Fig.2]. Female: a, P5 (posterior); b, 2nd exopodal segment of P5. Male: c, P5 (anterior); d, left P5 (anterior).
|
 issued from : J. Hiromi & H. Ueda in Proc. jap. Soc. Syst. Zool., 1987, 35. [p.20, Table 1]. Descriptive differences in S. sinensis between Ariake-kai and Chinese waters. Ansgm = anal segment; FR = caudal rami; Re1, 2 = exopodite 1, 2; St = terminal spine on distalmost exopodal segment of leg. +: yes or present; -: no or absent.
|
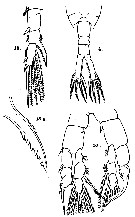 issued from : J. de Guerne & J. Richard in Mém. Soc. zool. Fr., 1889, 2. [Pl.IV, Figs.4, 15, 15a, 16]. As Limnocalanus sinensis. Female (from Sitai Lake and Whangpoo River, China): 4, last portion of prosome and urosome (dorsal); 15, P5; 15a, inner process spine-like (magnified) of P5 exopod. Male: 16, P5.
|
 issued from : W. Zhang, N. Zhao, Z. Tao & C. Zhang in An Illustrated Guide to Marine Planktonic Copepods in China Seas, Science Press, Beijing. [p.456, Fig.514]. Male: a, P5; b, right P5; c, left P5.
|
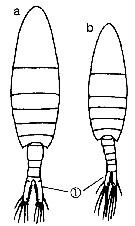 Issued from : M. Chihara & M. Murano in An Illustrated Guide to Marine Plankton in Japan, 1997. [p.774, Pl. 87, fig.120 a-b]. After Chen & Zhang, 1965. Female: a, habitus (dorsal). Male: b, habitus (dorsal). Nota: numbers show characteristics of this species to compare with S. tenellus.
|
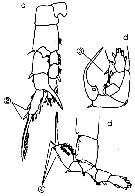 Issued from : M. Chihara & M. Murano in An Illustrated Guide to Marine Plankton in Japan, 1997. [p.774, Pl. 120, fig.8 c-d]. After Hiromi & Ueda, 1987. Female: c, P5. Male: d, P5 (right and left legs). Nota: numbers show characteristics of this species to compare with S. tenellus.
| | | | | Compl. Ref.: | | | Ohtsuka & al., 1995 (p.159); Islam & Tanaka, 2007 (p.579, Table 1, fig.4); Suzuki & al., 2008 (p.541, predation); Zhang G.-T. & al., 2010 (p.492, Table 1); Sakaguchi & al., 2011 (p.18, Table 1, 2, occurrences); Gao X. & al., 2011 (p.591, p.597: occurrence); Suzuki, K.W. & al., 2013 (p.15, Table 2, 3, 4, estuaries, annual occurrence); Ohtsuka & Nishida, 2017 (p.579, 586, Rem.) | | | | NZ: | 2 | | |
|
Distribution map of Sinocalanus sinensis by geographical zones
|
| | | | | | 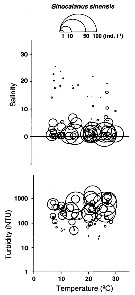 Issued from : K.W. Suzuki, K. Nakayama & M. Tanaka in J. Oceanogr., 2011, 69. [p.23, Fig.5]. Issued from : K.W. Suzuki, K. Nakayama & M. Tanaka in J. Oceanogr., 2011, 69. [p.23, Fig.5].
Bubble plots of densities of the semi-endemic calanoid Sinocalanus sinensis in relation to temperature, salinity, and turbidity observed in the Chikugo River estuary (south Japan) in 2005 and 2006. |
| | | | Loc: | | | China Seas (Bohai Sea, East China Sea, South China Sea, Changjiang River estuary, Whangpoo River, Shanghai, coats of Yellow Sea), Japan (Chikugo estuary, Ariake-kai, Kyushu, south estuaries: Chikugo, Midori & Kuma Rivers), Korea | | | | N: | 10 | | | | Lg.: | | | (1022) F: 1,47-2,05; M: 1,10-1,96; (1054) F: 1,60-1,80; M: 1,40-1,50; {F: 1,47-2,05; M: 1,10-1,96} | | | | Rem.: | brackish waters.
For Hiromi & Ueda (1987, p.23) the species, first discovered in the Whanpoo River, Shanghai, is restricted to brackish waters along the coasts of the Yello Sea and East China Sea. In Japan, there are several records, but it is not certain weither this copepod is conspecific to S. sinensis. the species seems stricktly restricted to the northernmost part of Ariake-kai. It is less likely that the species has been introduced to Japan by ocean currents and also by ships-transport, because the ports in the northern part of Ariake-kai are not so large. Considering the geological history of the Japanese Islands and the characteristics of the fauna in Ariake-kai, it is most likely that the species is a continental relict. Before the Würm glacial period, when Japan was linked to the Continent of China as a result of regression, the Chinese population could have spread out in the northeasterly direction because the East China Sea at that time was mostly covered with brackish water. Later, about 6,000-10,000 years ago, Japan began to be isolated as the sea level rose with the Jômonian transgression and an isolated population would have remained in Ariake-kai.
The Ariake-kai specimens need to be compared with the Chinese ones; a comparative study may show geographic divergences.
After Ohtsuka & Nishida (2017, p.579), the brackish species , aggregated just above the bottom in submerged channels outside the mouth during heavy flooding. Losses from the population, in particular of immature copepodids, were compebsated by reproduction after the flood. Relationships between feeding behavior of fish juveniles and the distribution of planktonic copepods have been investigated in the mouth of Chikugo River (Kyushu, Japan). Larvae and early juveniles of Japanese temperate bass Lateolabrax japonicus migrate to the turbid, low-saliniry area of the river, where the prey upon the abundant calanoid Sinocalanus sinensis (See Hibino & al., 1999; Suzuki @ al., 2008) | | | Last update : 14/05/2019 | |
|
|
 Any use of this site for a publication will be mentioned with the following reference : Any use of this site for a publication will be mentioned with the following reference :
Razouls C., Desreumaux N., Kouwenberg J. and de Bovée F., 2005-2026. - Biodiversity of Marine Planktonic Copepods (morphology, geographical distribution and biological data). Sorbonne University, CNRS. Available at http://copepodes.obs-banyuls.fr/en [Accessed February 27, 2026] © copyright 2005-2026 Sorbonne University, CNRS
|
|
 |
 |