|
|
 |
|
Calanoida ( Order ) |
|
|
|
Diaptomoidea ( Superfamily ) |
|
|
|
Pseudodiaptomidae ( Family ) |
|
|
|
Pseudodiaptomus ( Genus ) |
|
|
| |
Pseudodiaptomus nansei Sakaguchi & Ueda, 2010 (F, M) | |
| | | | | | | Syn.: | Pseudodiaptomus inopinus : Oka & al., 1991 (p 85, fig.3).
Pseudodiaptomus inopinus : Oka & Saisho, 1994 (p.51). | | | | Ref.: | | | Sakaguchi & Ueda, 2010 (p.53, Descr.F,M; figs.F,M,. molecular biology; map of the Nansei Islands and Kyushu Island, S Japan); Sakaguchi & Ueda, 2018 Rem.: (p.178) |  issued from : S.O. Sakaguchi & H. Ueda in Zootaxa, 2010, 2623. [p.56, Fig.2]. Female (from Nansei Islands): A-B, habitus (dorsal and lateral, respectively); C-D, genital double-somite (ventral and right lateral, respectively); Ecaudal rami (dorsal); F, A1; G, seta on 20th segment of A1; H, caudal rami with slightly thickened setae (dorsal). A-G: holotype; H, specimen from Yakugachi-gawa River, Amami-ohsima Island. Nota: head and 1st pedider segment fused, 4th and 5th fused. 3-4 spinules on each posterolateral rounded corner of 5th pediger. Genital operculum with broad hyaline frill laterally and rounded posterior process (indicated by arrowhead in fig C). Caudal rami symmetrical, 3.3 times longer than wide. A1 22-segmented with incomplete suture between 6th to 7th segments.
|
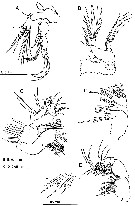 issued from : S.O. Sakaguchi & H. Ueda in Zootaxa, 2010, 2623. [p.58, Fig.4]. Female: A, A2; B, Md; C, Mx1; D, Mx2; E, Mxp; F, setae on 3rd endopodal segment of Mxp. Nota: A2: Coxa and basis and 1st endopodal segment completely fused (coxa with 1 seta, basis with 2 setae, 1st endopodal segment with 2 setae); 2nd endopodal segment with 9 subterminal and 7 terminal setae. Exopod 5-segmented (setal formula: 1, 5, 1, 2, 3). Md: Basis with 4 setae; exopod 5-segmented, with seta on each 1st to 4th segments and 2 setae o 5th segment; endopod 2-segmented, with 4 setae on 1st segment and 9 setae. Mx1: praecoxal arthrite (inner lobe 1) with 9 spines and 6 setae; coxal endite with 4 setae; epipodite (outer lobe 1) with 9 setae; basal endites with 3 and 5 setae; exite (outer lobe 2) with 1 seta; exopod with 9 setae; endopod 3-segmented (setal formula 4, 4, 7). Mx2: praecoxal with 4 setae on 1st endite and 3 setae on 2nd endite; coxal endites with 3 and 3 setae; basal endite with 4 setae; endopod 4-segmented (setal formula 2, 3, 2, 2). Mxp: coxa with 2, 3, 4 setae on 1st to 3rd endites; basis with 3 setae; endopod 6-segmented (setal formula 2, 3, 2, 3, 3, 4), 2 setae on 2nd segment and 1 seta on 3rd segment modified (as shown in fig F) and 1 seta on 4th segmnt short and beering teeth-like spinules.
|
 issued from : S.O. Sakaguchi & H. Ueda in Zootaxa, 2010, 2623. [p.59, Fig.5]. Female: A-D, P1 to P4 respectively (poserior view); E, P5 (posterior view); F, base of 3rd exopodal segment of P5 (posterior view); G, base of 3rd exopodal segment of P5 (anterior view). A-F: holotype; G: paratype.
|
 issued from : S.O. Sakaguchi & H. Ueda in Zootaxa, 2010, 2623. [p.57, Fig.3]. Female (from Hirakubo-gawa River) : SEM photograph of genital flaps (ventral view).
|
 issued from : S.O. Sakaguchi & H. Ueda in Zootaxa, 2010, 2623. [p.60, Fig.6]. Male: A-B, habitus (dorsal and lateral, respectively); C, 2nd urosomite (ventral); D, right A1; E, P5 (posterior); F, P5 (anterior); G, moderately paddle-shaped 2nd exopodal segment of left P5. A-F: allotype; G: specimen from Ura-gawa River. Nota: Right A1 20-segmented with 6th to 7th segments incompletely fused. Genital segment with small posterolateral process on each side. Except P5, other appendages as in female.
| | | | | Compl. Ref.: | | | Ohtsuka & Nishida, 2017 (p.565, 578, Rem., Table 22.1) | | | | NZ: | 2 | | |
|
Distribution map of Pseudodiaptomus nansei by geographical zones
|
| | | | | | | Loc: | | | S Japan (Nansei Islands, Kyushu: Amamioshima Island: Sumiyo Bay) | | | | N: | 1 | | | | Lg.: | | | (1099) F: 1,10-1,13; M: 0,86-0,91; {F: 1,10-1,13; M: 0,86-0,91} | | | | Rem.: | brackish waters (salinity 0.3 - 28.5).
Closely related Pseudodiaptomus inopinus Burckhardt, 1913.
Sakaguchi & Ueda (2018, p.178) indicated in 2010, morphological and genetic differences between P. nansei and the cryptic species P. inopinus and P. japonicus (as P. inopinus from the Tsuri-kawa River (33°50'53''N, 130°30'10''E), in this form, shorter posterior processses of the female genital operculum than those in P. japonicus Kikuchi, 1928, and a pointed distomedial process of the first exopodal segment of the female P5. The morphological differences are evident between P. nansei, japonicus and P inopinus (LP-form). The COI sequences of P. nansei (Sakaguchi & Ueda, 1010) also revealed 21% or more from P.japonicus. Therefore, the two species are different, although both formerly identified as the same species-P. inopinus. | | | Last update : 28/08/2019 | |
|
|
 Any use of this site for a publication will be mentioned with the following reference : Any use of this site for a publication will be mentioned with the following reference :
Razouls C., Desreumaux N., Kouwenberg J. and de Bovée F., 2005-2026. - Biodiversity of Marine Planktonic Copepods (morphology, geographical distribution and biological data). Sorbonne University, CNRS. Available at http://copepodes.obs-banyuls.fr/en [Accessed February 11, 2026] © copyright 2005-2026 Sorbonne University, CNRS
|
|
 |
 |