|
|
 |
|
Calanoida ( Order ) |
|
|
|
Diaptomoidea ( Superfamily ) |
|
|
|
Centropagidae ( Family ) |
|
|
|
Centropages ( Genus ) |
|
|
| |
Centropages ponticus Karavaev, 1894 (F,M) | |
| | | | | | | Syn.: | Centropages kroyeri pontica Karavaev, 1894 (p.24, figs.F,M); Delalo, 1966 (1968) (p.138)
Centropages kröyeri : Porumb, 1968 a (p.509) | | | | Ref.: | | | Gurney, 1927 (p.150, figs.M, Rem.M); Kovalev, 1967 a (p.94, figs.F,M); Sazhina & Kovalev, 1971 (p.1099, figs.F,M); Garcia-Rodriguez, 1985 b (p.47, figs.F,M, Rem.); Sazhina, 1985 (p.62, figs.N); Soler & al.,1988 (p.129, Descr.F,M, figs.F,M, Rem.); Avancini & al., 2006 (p.95, Pl. 64, figs.F,M, Rem.); Vives & Shmeleva, 2007 (p.474, figs.F,M, Rem.); Gubanova & al., 2013 (in press, Rem: p.2, Table 1, 2, 4, fig.2); Prusova & al., 2019 (p.516, Redescr. F, M, figs.F, M, Table 3: Key F, M for the hamaus Group; Table 4: differences between the Mediterranean and Black Sea) |  issued from : Gurney R. in Trans. zool. Soc. Lond., 1927, 22. [Fig.19, p.151]. Male (from Le Cap, Suez Canal): A, habitus (dorsal view); B, part of right A1; C, side view of head; D, side view of last thoracic somite; E, P5 (anterior view). Nota: - Body slender, the greatest width about the middle of cephalothorax. - Ventral margin of head not protuberant. - Rostral filaments long and slender. - Last somite with posterior angles rounded, bearing a small spine on either side. - Proportion prosome to urosome (included furca) 65 : 33; furca 11. - Abdomen and furca symmetrical - A1 reaching to end of furca, very slender, segments 13-18 being but little broadened; a small spine on segments 15 and 16. Relative lengths of segments 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19-20 as 25 : 23 : 27 : 36 : 32 : 39 : 65, respectively. - P5 almost exactly as in C. hamatus, but endopod of left leg with a peculiar rounded prominence at outer distal angle; basal process of 2nd exopodal segment of right leg shorter than terminal spine. - Exopodal segment 2 of right P4 with a very long outer curved spine, but in the left leg the spine is scarcely longer than those of exopodal segments 1 and 3. - In P2 and P3 the outer spine of exopodal segment 2 is but little longer than that of exopodal segments 1 and 3.
|
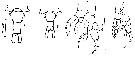 issued from : A.V. Kovalev in Akad. Nauk SSSR, Okeanogr. Komm., 1967. [p.97, Fig.3]. Comparison between urosome female and male P5 from Centropages kröyeri (1) and Centropages ponticus (2).
|
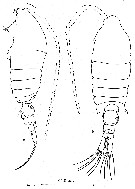 issued from : E. Soler, J.G. Del Rio & F. Vives in Crustaceana, 1988, 55 (2). [p.132, Figs. 1]. Female (from 39°8'-39°12'N, 0°13'-0°15'E): 1 a-b, habitus (lateral and dorsal, respectively). Nota: Measurements for N = 33 adult females ( unit = mm). Total length: Range = 0.772-0.973; Mean = 0.845; S.D. = 0.038. Cephalothorax length: Range = 0.522-0.587; Mean = 0.587; S.D. = 0.034. Abdomen length : Range = 0.222-0.293; Mean = 0.259; S.D. = 0.019. Ratio Cephalothorax/ abdomen: Range = 2.00-3.12; Mean = 2.27; S.D. = 0.24. In the samples from Thau lagoon (northern Gulf of Lion), measurements for 24 females (init in mm) are: Toatal length: Range = 0.704-1.040; Mean = 0.819; Ecart -type = 0.082. Cephalothorax length: Range = 0.464-0.720; Mean = 0.569; Ecart-type = 0.064. Abdomen length: Range = 0.224-0.288; Mean = 0.251; Ecart-type = 0.025. Ratio cephalothorax/abdomen = 2.27.
|
 issued from : E. Soler, J.G. Del Rio & F. Vives in Crustaceana, 1988, 55 (2). [p.133, Figs. 2]. Female: a, forehead (lateral); b, rostrum (ventral); c, 5th thoracic degment 'dorsal); d-e, urosome (dorsal and lateral, respectively). Nota: Proportional lengths of urosomal segments: 33: 20: 20: 27 = 100.
|
 issued from : E. Soler, J.G. Del Rio & F. Vives in Crustaceana, 1988, 55 (2). [p.134, Figs. 3]. Female: a, A1; b, A2; c, Md; d, Md (cutting edge of gnathobase); e, Mx1; f, Mx2; g, Mxp. Nota: Cutting edge od Md with 8 sharp teeth and a basal seta. 1st and 2nd teeth bigger and hooked, and the 3rd to 8th forked.. Basis with 3 long abd 2 short internal setae.
|
 issued from : E. Soler, J.G. Del Rio & F. Vives in Crustaceana, 1988, 55 (2). [p.132]. Female: Proportional lengths of segments A1.
|
 issued from : E. Soler, J.G. Del Rio & F. Vives in Crustaceana, 1988, 55 (2). [p.136, Figs. 4]. Female: a-e, P1 to P5.
|
 issued from : E. Soler, J.G. Del Rio & F. Vives in Crustaceana, 1988, 55 (2). [p.135, Table 2]. Female: Setal formula of swimming legs P1 to P5. C = coxa, B = basis.
|
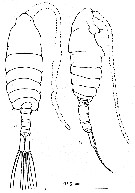 issued from : E. Soler, J.G. Del Rio & F. Vives in Crustaceana, 1988, 55 (2). [p.137, Figs. 5]. Male: a-b, habitus (dorsal and lateral, respectively). Nota: Measurements for N = 30 adult males; unit = mm. Total length: Range = 0.657-0.843; Mean = 0.759; S.D. = 0.053. Cephalothorax length: Range = 0.431-0.578; Mean = 0.513; S.D. = 0.039. Abdomen length : Range =0.196-0.284; Mean = 0.246; S.D. = 0.019. Ratio Cephalothorax/ abdomen: Range = 1.69-2.40; Mean = 2.09; S.D. = 0.15. In the samples from Thau lagoon (northern Gulf of Lion), measurements for 47 males (init in mm) are: Toatal length: Range = 0.912-0.544; Mean = 0.0.753; Ecart -type = 0.067. Cephalothorax length: Range =0.368-0.608; Mean = 0.522; Ecart-type = 0.049. Abdomen length: Range = 0.176-0.304; Mean = 0.235; Ecart-type = 0.027. Ratio cephalothorax/abdomen = 2.22.
|
 issued from : E. Soler, J.G. Del Rio & F. Vives in Crustaceana, 1988, 55 (2). [p.138, Figs. 6]. Male: a, forehead (lateral); b, rostrum (ventral); c, 5th thoracic segment and 1st urosomal segment; d, 5th thoracic segment and urosome (dorsal). Nota: Caudal rami ratio length/width : 2.69-4.40 (n = 30 individuals).
|
 issued from : E. Soler, J.G. Del Rio & F. Vives in Crustaceana, 1988, 55 (2). [p.139, Figs. 7]. Male: a, left A1; b, right A1; c, A2; d, Md; e, Md (cutting edge of gnathobase); f, Mx1; g, Mx2; h, Mxp.
|
 issued from : E. Soler, J.G. Del Rio & F. Vives in Crustaceana, 1988, 55 (2). [p.140, Figs. 8]. Male: a, right A1 (segments 10 to 16); b, same (segments 16 to 24-25). Nota: The right A1 from Cullera Bay has a tooth on the segments 10, 11 and 12, while Gracia-Rodriguez (1985 b) only found teeth on segments 10 and 11.
|
 issued from : E. Soler, J.G. Del Rio & F. Vives in Crustaceana, 1988, 55 (2). [p.139]. Male: Proportional lengths of segments right A1. Clasping joint between segments 18 and 19-21.
|
 issued from : E. Soler, J.G. Del Rio & F. Vives in Crustaceana, 1988, 55 (2). [p.140]. Male: Proportional lengths of segments left A1.
|
 issued from : E. Soler, J.G. Del Rio & F. Vives in Crustaceana, 1988, 55 (2). [p.141, Fig.9, a-d]. Male: a-d, P1 to P4.
|
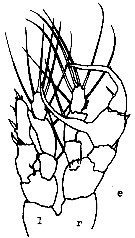 issued from : E. Soler, J.G. Del Rio & F. Vives in Crustaceana, 1988, 55 (2). [p.141, Fig. 9, e]. Male (Cullera Bay): e, P5. l = left leg; r = right leg.
|
 issued from : E. Soler, J.G. Del Rio & F. Vives in Crustaceana, 1988, 55 (2). [p.141, Table IV]. Male: Setal formula of swimming legs (elements computed from outer margins to inner margins). C = coxa; B = basis; P5 (l) = left P5; P5 (r) = right P5; Arabic numerals = setae; Roman numerals = spines.
|
 issued from : E. Soler, J.G. Del Rio & F. Vives in Crustaceana, 1988, 55 (2). [p.143, Table V]. Main morphological differences between females C. ponticus Karavaev, C. hamatus Lilljeborg and C. kroeyeri Giesbrecht. T5 = 5th thoracic segment; -- = no distinct differences with C. ponticus; St = terminal seta; Ri = endopodite; Re = exopodite.
|
 ssued from : E. Soler, J.G. Del Rio & F. Vives in Crustaceana, 1988, 55 (2). [p.143, Table V]. Main morphological differences between males C. ponticus Karavaev, C. hamatus Lilljeborg and C. kroeyeri Giesbrecht. T5 = 5th thoracic segment; -- = no distinct differences with C. ponticus; St = terminal seta; Ri = endopodite; Re = exopodite.
|
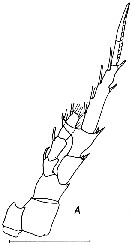 issued : C. Razouls,1987. Female (from Thau lagoon, Gulf of Lion, NW Mediterranaean Sea): A, P5. Scale bar: 0.100 mm. Nota: Separation between exopodites 2 and 3 obvious.
|
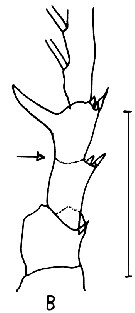 issued : C. Razouls,1987. Another Female (from Thau lagoon, Gulf of Lion, NW Mediterranaean Sea): B, P5. Scale bar: 0.100 mm. Nota: Separation between exopodites 2 and 3 barely visible (arrowed).
|
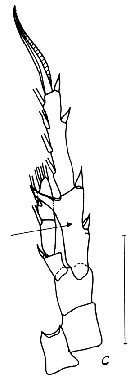 issued : C. Razouls,1987. Another Female (from Thau lagoon, Gulf of Lion, NW Mediterranaean Sea): C, P5. Scale bar: 0.100 mm. Nota: No separation between exopodite 2 and 3 (arrowed). Nota: After Soler & al. (1988, p.142) there are slight morphological differences between indivuduals from different localities. In Cullera Bay in the Mar Menor (Garcia-Rodriguez, 1985 b, that exopodite has 3 segments, though the suture is poorly visible
|
 issued : C. Razouls,1987. Male (from Thau lagoon, Gulf of Lion, NW Mediterranaean Sea): D, P5.. Scale bar: 0.100 mm. Nota: The displacement of the proximal external spine of the 3rd exopodal segment of the right P4 has been noticed in some individuals from the Thau lagoon (Razouls), this does not occur in Cullera Bay population, where the males have these spines normally inserted on the margin of that segment.
|
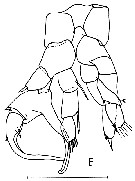 issued : C. Razouls,1987. Male (from Thau lagoon, Gulf of Lion, NW Mediterranaean Sea): E, P5.. Scale bar: 0.100 mm. Nota: Arrow point to process on distal outer margin of the left P5.
|
 Issued from : I.Yu. Prusova, Z.A. Galagovets & E.V. Popova in Arthropoda Selecta, 2019, 28 (4). [p.517, Fig.1]; Female (from Sevastopol Bay): a-b, habitus (dorsal and lateral, respectively); c, forehead (ventral view); d, A1 segments I-XIX; e, A1 segments XX-XXVIII; f, urosome (dorsal); g, same (left lateral view); h, same (right lateral view); i, genital double-somite (ventral). Nota: - Prosome about 2.5 times as long as urosome. - Cephalosome and 1st pediger, 4th and 5th pedigers separate. Last thoracic segment symmetrical with 2 conspicuous, caudally produced posterolateral projections. - Rostrum rxtends into 2 long, thin filaments directed postero-ventrally. - Urosome 3-segmenteed. - Genital double-somite the biggest, asymmetrical in dorsal view, widest at its posterior one-half, swollen more conspicuously on the right, with both left and right lateral swellings covered with small spinules, dorsal surface of the somite flat, without spinules; genital area postero-ventral, genital operculum large, located ventrolaterally on left side occupying about 1/3 of the widest width of genital double-somite, triangular in shape and with a slightly curved distal margin; left ventrolateral edge of genital double-somite with a rounded protrusion (arrowed in fig. 1g,i) better noticeable when genital operculum adjoins the somite not tightly. - Caudal rami symmetrical, slightly dilated posteriorly, approximately 3 times as long as wide, with 6 terminal setae and small setules in the inner border; ancestral seta I absent, seta VII inserted immediately anterior to seta VI; seta V longest being approximately as long as urosome including caudal rami; seta VII shortest. A1 symmetrical, 24-segmented, extending to a posterior border of caudal rami; ancestral segments II-IV completely fused with 3 setae + 1 aesthetasc; segment I with 2 setae + 1 aesthetasc; segment V with 1 seta + 1 aesthetasc; segment VII with 2 setae + 1 aesthetasc; segment VIII with 1 seta + 1 aesthetasc; segment IX with 2 setae + 1 aesthetasc; segment X with 2 setae + 1 aesthetasc (distalmost seta modified- short and curved); segments XI to XXI each with 2 setae + 1 aesthetasc; XXII and XXIII each with with 1 seta; segment XXIV and XXV each with 1 + 1 setae; segments XXVI-XXVIII with 5 setae + 1 aesthetasc.
|
 Issued from : I.Yu Prusova, E.A. Galagovets & E.V. Popova in Arthropoda Selecta, 2019, 28 (4). [p.518, Fig.2]. Female: a, A2; b, Md palp; c, Md gnathobase; d, Mx1; e, Mx2; f, Mxp. Nota: - A2: coxa with 1 long inner seta; basis with 2 long inner setae; endopod 2-segmented, segment 1 with 2 inner setae, segment 2 bilobed with 9 and 7 setae on proximal and distal lobes, respectively, distal lobe armed with row of spinules; exopod with ancestral segments I-II and III-IV fused (fusion line between segments III and IV visible), ancestral segments I-VII each with long plumose seta, terminal segments IX-X with 1+3 setae. - Md: gnathobase with 8 teeth and 1 seta, 3rd and 4th teeth with small spinules at their base; mandibular palp basis with 4 setae; endopod 2-segmented with 4 and 9 setae, respectively; exopod 5-segmented with 1, 1, 1, 1, 2 setae. - Mx1: praecoxal arthrite with 15 9 terminal, 4 posterior and 2 anterior) spines and with line long setules at the base of the spines; coxal endite with 3 setae and coxal epipodite with 9 setae; basal endites 1 and 2 with 4 and 5 setae, respectively; basal exite with 1 seta; endopod with 4 lateral and 5 apical setae; exopod with 8 setae. - Mx2 with long, strong and spinous setae; praecoxal endites 1 and 2 with 5 and 3 setae, respectively; endites 3 and 4 on coxa with 3 setae each; basal endite with 3setae; endopod with 7 setae. - Mxp: syncoxa with 1, 2, 3, 4 setae; basis with 3 setae; endopod segment 1 with 2 setae; endopod segments 2-6 with 2, 2, 2, 2+1, 3+1 setae, respectively.
|
 Issued from : I.Yu Prusova, E.A. Galagovets & E.V. Popova in Arthropoda Selecta, 2019, 28 (4). [p.519, Fig.3]. Female: a, P1 (anterior view); b, P2 (anterior view); c, P3 (anterior view); d, P4 (anterior view); e, P5 (anterior view); f, P1 endopod III; g, P5 ( fused exopod segments I-II) (anterior view). Nota: - P5 biramous, symmetrical; exopod ancestral segments I and II fused (fusion line is faintly visible on anterior surface only, absent in posterior surface), inner distal corner transformed into strong thick and curved projection; endopod 3-segmented, segment 1 inner distal corner with large triangular extension reaching the midlength of endopod segment 2.
|
 Issued from : I.Yu Prusova, E.A. Galagovets & E.V. Popova in Arthropoda Selecta, 2019, 28 (4). [p.520, Table1]. Female & Male: Spine and setal formulae of swimming legs P1 to P5.
|
 Issued from : I.Yu Prusova, E.A. Galagovets & E.V. Popova in Arthropoda Selecta, 2019, 28 (4). [p.520, Table .2]. Variability of spines and setae number in swimming legs P2-P4.
|
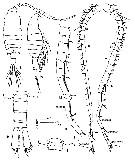 Issued from : I.Yu Prusova, E.A. Galagovets & E.V. Popova in Arthropoda Selecta, 2019, 28 (4). [p.521, Fig.4]. Male: a-b, habitus (dorsal and lateral, respectively); c, left A1; d, right A1; e, posterolateral corners of 5th pedigerous somite and urosome (dorsal); f, posterolateral corners of 5th pediger, a variant (dorsal); g, right A1 segments XVII-XXIII. Nota: - Prosome about 2.3 times as long as urosome. - Cephalosome and pediger 1, pedigers 4 and 5 separate. - Last thoracic segment with 2 caudally produced, symmetrical or slightly asymmetrical, with the left one slightly bigger, pointed projections. - Rostrum extends into 2 thin, ventroposteriorly directed filaments. - Urosome 5-segmented. - Genital somite shorter than urosomite II, genital opening on the left side. - Urosomite V very small (anal somite). - Caudal rami symmetrical, slightly dilated posteriorly, with 6 terminal setae and small setules in the inner border; ancestral seta I absent, seta VII inserted immediately anterior to seta VI; seta V longest being approximately as long as urosome including caudal rami; seta VII shortest. - Left A1 as in female. Righjt A1 geniculated, 21-segmented with main geniculation between segments XX and XXI; ancestral segments II-IV, XXI-XXIII, XXIV-XXV fused
|
 Issued from : I.Yu Prusova, E.A. Galagovets & E.V. Popova in Arthropoda Selecta, 2019, 28 (4). [p.522, Fig.5]. Male: a, A2; b, Md; c, Mx1; d, Mx2; e, Mxp. - A2, Md, Mx1, Mx2 and Mxp well developed, with segmentation and setal formulae as in female.
|
 Issued from : I.Yu Prusova, E.A. Galagovets & E.V. Popova in Arthropoda Selecta, 2019, 28 (4). [p.523, Fig.6]. Male: a, P1 (anterior view); b, P2 (anterior view); c, P3 (anterior view); d, P4 (anterior view); e, P5 (anterior view); f, right P5 (exopod segments II-III , posterior view); g, P4 right exopod segments I-II; h, P5 left ramus (anterior view); i, P5 right ramus (anterior view). Nota: - P5 biramous, asymmetrical, modified. Left leg: exopod 2-segmented with ancestral segments I and II fused, terminal segment with a small terminal spine; endopod 3-segmented, segment 1 outer distal corner with a small swelling, segment 2 outer distal corner with a large swelling. Right leg: exopod 3-segmented, with 2 terminal segments forming a chela: segment 2 inner distal corner modified into a claw-like extension, outer distal corner with thin and relatively long spine directed posteeriorly; segment 3 elongated and curved, with a medium-sized inner spine and very small outer spine.
|
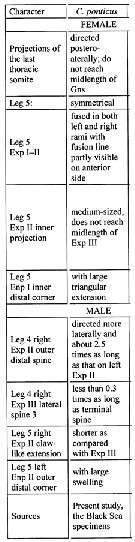 Issued from : I.Yu Prusova, E.A. Galagovets & E.V. Popova in Arthropoda Selecta, 2019, 28 (4). [p.518, Fig.2]. Centropages ponticus: Characters for distinguishing between species of the hamatus group of the genus Centropages. Compare with the species C. hamatus, C. kroyeri, C. tenuiremis, and C. abdominalis.
| | | | | Compl. Ref.: | | | Delalo, 1968 (p.138); Greze & al., 1968 (p.1066, annual variation); Sazhina, 1968 (p.1554, resting eggs); Kovalev, 1968 a (p.441, fig.1); 1969 a (p.168); Porumb, 1976 (p.91); Porumb, 1980 (p.167); Grice & Marcus, 1981 (p.125, Dormant eggs, Rem.: p.134); Kovalev & Shmeleva, 1982 (p.84); Lakkis, 1984 (p.299); Moraitou-Apostolopoulou, 1985 (p.303, occurrence/abundance in E Mediterranean Sea, Rem.: p.313); Jansa, 1985 (p.108, tab.I, II, III, IV, V); Garcia-Rodriguez, 1985 (p.37); 1985 a (p.41, 42); Lam Hoi & al., 1985 (p.451, 462); Jouffre & al., 1991 (p.489, lagoon); Ragosta & al., 1995 (p. 490, Appendix A); Madhupratap & al., 1996 (p.77, Table 2: resting eggs); Marcus, 1996 (p.143); Hure & Krsinic, 1998 (p.101); Mauchline, 1998 (tab.40, 46); Omori & Norman, 1998 (p.279, Rem.: anthropogenic short-term effects); Siokou-Frangou, 1999 (p.476); Riccardi & Mariotto, 2000 (p.243); El-Serehy & al., 2001 (p.116, Table 1: abundance vs transect in Suez Canal); Bressan & Moro, 2002 (tab.2); Kovalev, 2003 (p.47); Zagorodnyaya & al., 2003 (p.52); Isari & al., 2006 (p.241, tab.II); Mageed, 2006 (p.168, Table 4); Camatti & al., 2006 (p.46, fig.5); Busatto, 2007 (p.26, Tab.3); Isinibilir & al., 2008 (p.745: Tab.1); Selifonova & al., 2008 (p.305, Tabl. 2); Mazzocchi & Di Capua, 2010 (p.424); Isinibilir, 2010 (p.233, abundance %); Mazzocchi & al., 2011 (p.1163, Table II, fig.6, long-term time-series 1984-2006); Isari & al., 2011 (p.51, Table 2, abundance vs distribution); Uysal & Shmeleva, 2012 (p.909, Table I); Stefanova & al., 2012 (p.403, Table 2, interannual abundance); Neffati & al., 2012 (p.80, egg production & nauplii survival vs environmental factors); Belmonte & al., 2013 (p.222, Table 2, abundance vs stations); El-Serehy & al., 2013 (p.2099, Rem.: p.2101); Pansera & al., 2014 (p.221, Table 2, abundance); Benedetti & al., 2016 (p.159, Table I, fig.1, functional characters); , Ben Ltaief & al., 2017 (p.1, Table III, Summer relative abundance) ; Belmonte, 2018 (p.273, Table I: Italian zones) Camatti & al., 2019 (p.1, fig.6, Table 3, 5) | | | | NZ: | 2 | | |
|
Distribution map of Centropages ponticus by geographical zones
|
| | | | | | | Loc: | | | Medit. (Marmara Sea, Black Sea, Sebastopol, Agigea (coast), off Valencia: Alicante & Castellon, Cullera Bay, Malaga, Mar Menor, Baleares, Gulf of Lion (Thau lagoon), Ligurian Sea, Lake Faro (Sicily), Tyrrhenian Sea, Napoli, Bizerte Channel, G. of Gabes, Taranto, Venezzia, Pô delta, S Adriatic Sea, Aegean Sea, Thracian Sea, N Lebanon Basin, Bardawill Lagoon, Marmara Sea, W Black Sea, Sebastopol), Suez Canal (Le Cap: Km. 35 from Port Said), Red Sea, ? [Indonesia] | | | | N: | 44 ? (Medit. & Black Sea: 37; Suez Canal: 3; Red Sea: 1 + 2 ?; Indonesia: 1 ?) | | | | Lg.: | | | (178) M: 1,05; (357) F: 0,973-0,772; M: 0,843-0,657; {F: 0,704-1,040; M: 0,544-1,05}.
issued : C. Razouls (1987, from Thau lagoon, Gulf of Lion, NW Mediterranean Sea) : Female: 1,040-0,704; M: 0,912-0,544. (1244) F: 1,07-1,22; M: 0,92-1,08. | | | | Rem.: | Neritic and in lagoons, ports.
Example of an "antilesseptian" form, probably original from the Mediterranean Sea having penetrated the Red Sea.
A genetic analysis of the three species C. hamatus, C. kröyeri and C. ponticus would permit to specify the distinction between these three forms.
After Prusova & al; (2019, p.526) this species can be distinguished from the other species of the 'hamatus' Group by details of morphology of P5, (1) by having exopod segments I-II fused in both right and left rami in female, (2) by having a large swelling on outer distal corner of the left endopod segment II in male. Additionally, from its closest congener, C. kroyeri, C. ponticus is distinguished by relative length of the male P5 right exopod segment II claw-like extension: in C. ponticus this element is shorter as compared to exopod segment 3, whereas in C. kriyeri this element is longer as compared to exopod segment 3. | | | Last update : 31/10/2020 | |
|
|
 Any use of this site for a publication will be mentioned with the following reference : Any use of this site for a publication will be mentioned with the following reference :
Razouls C., Desreumaux N., Kouwenberg J. and de Bovée F., 2005-2025. - Biodiversity of Marine Planktonic Copepods (morphology, geographical distribution and biological data). Sorbonne University, CNRS. Available at http://copepodes.obs-banyuls.fr/en [Accessed July 03, 2025] © copyright 2005-2025 Sorbonne University, CNRS
|
|
 |
 |