|
|
 |
|
Calanoida ( Order ) |
|
|
|
Diaptomoidea ( Superfamily ) |
|
|
|
Centropagidae ( Family ) |
|
|
|
Isias ( Genus ) |
|
|
| |
Isias clavipes Boeck, 1864 (F,M) | |
| | | | | | | Syn.: | Isias bonnieri Canu, 1888 b (p.228) | | | | Ref.: | | | Brady, 1878 (p.62, figs.F,M); Giesbrecht, 1892 (p.323, 776, figs.F,M); Thompson, 1888 d (p.142); Giesbrecht & Schmeil, 1898 (p.62); Sars, 1902 (1903) (p.79, figs.F,M); Thompson & Scott, 1903 (p.234, 248); Pesta, 1920 (p.524); Sars, 1925 (p.207); Rose, 1929 (p.33); 1933 a (p.189, figs.F,M); Massuti Alzamora, 1942 (p.94); Lysholm & al., 1945 (p.34); Bayly, 1964 b (p.243, Table 1, p.244: Table 2 ); Marques, 1966 (p.8, figs.F,M); Vilela, 1968 (p.22, figs.F,M); Corral Estrada, 1970 (p.184, figs.F,M, Rem.); Shih & al., 1971 (p.39); Razouls, 1972 (p.94, Annexe: p.65); Pillai P., 1975 a (p.320, 325, Table 1); G. Harding, 2004 (p.35, figs.F,M); Boxshall & Halsey, 2004 (p.89: figs.M); Avancini & al., 2006 (p.98, Pl. 67, figs.F,M, Rem.); Vives & Shmeleva, 2007 (p.482, figs.F,M, Rem.); Laakmann & al., 2013 (p.862, figs.1, 2, 3, 4, 5, Table 1, 2, 3, mol. Biol.) | 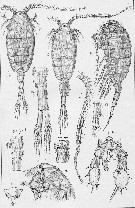 issued from : Sars G.O. in An Account of the Crustacea of Norway, with short descriptions and figures of all species. Vol. IV. Copepoda Calanoida. Publ. by The Bergen Museum. 1903. [Pl. LIII]. Female & Male. C = head (lateral); L = labrum; gen. sgn = genital segment (ventral and lateral); Urs = urosome.
|
 issued from : Sars G.O. in An Account of the Crustacea of Norway, with short descriptions and figures of all species. Vol. IV. Copepoda Calanoida. Publ. by The Bergen Museum. 1903. [Pl. LIV]. Female. M = Md; m = Mx1; mp1 = Mx2; mp2 = Mxp.
|
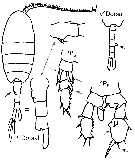 issued from : G. Harding in Key to the adullt pelagic calanoid copepods found over the continental shelf of the Canadian Atlantic coast. Bedford Inst. Oceanogr., Dartmouth, Nova Scotia, 2004. [p.35]. Female & Male.
|
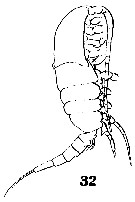 Issued from : W. Giesbrecht in Systematik und Faunistik der Pelagischen Copepoden des Golfes von Neapel und der angrenzenden Meeres-Abschnitte. – Fauna Flora Golf. Neapel, 1892, 19 , Atlas von 54 Tafeln. [Taf.38, Fig.32]. Female: 32, habitus (lateral).
|
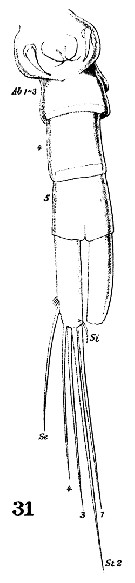 Issued from : W. Giesbrecht in Systematik und Faunistik der Pelagischen Copepoden des Golfes von Neapel und der angrenzenden Meeres-Abschnitte. – Fauna Flora Golf. Neapel, 1892, 19 , Atlas von 54 Tafeln. [Taf.38, Fig.31]. Female: 31, urosome (ventral).
|
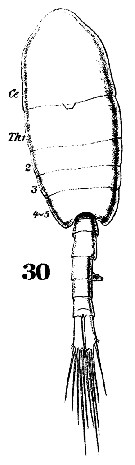 Issued from : W. Giesbrecht in Systematik und Faunistik der Pelagischen Copepoden des Golfes von Neapel und der angrenzenden Meeres-Abschnitte. – Fauna Flora Golf. Neapel, 1892, 19 , Atlas von 54 Tafeln. [Taf.38, Fig.30]. Male: 30, habitus (dorsal).
|
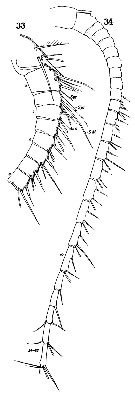 Issued from : W. Giesbrecht in Systematik und Faunistik der Pelagischen Copepoden des Golfes von Neapel und der angrenzenden Meeres-Abschnitte. – Fauna Flora Golf. Neapel, 1892, 19 , Atlas von 54 Tafeln. [Taf.19, Figs.33, 34]. Female: 33, segments 1 to 9 of A1 (ventral view); ; 34, A1 (ventral view).
|
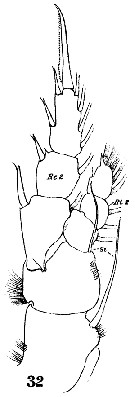 Issued from : W. Giesbrecht in Systematik und Faunistik der Pelagischen Copepoden des Golfes von Neapel und der angrenzenden Meeres-Abschnitte. – Fauna Flora Golf. Neapel, 1892, 19 , Atlas von 54 Tafeln. [Taf.19, Fig.32]. Female: 32, P1 (anterior view).
|
 Issued from : W. Giesbrecht in Systematik und Faunistik der Pelagischen Copepoden des Golfes von Neapel und der angrenzenden Meeres-Abschnitte. – Fauna Flora Golf. Neapel, 1892, 19 , Atlas von 54 Tafeln. [Taf.19, Figs.35, 36]. Female: 35, P3 (anterior view); 36, P5 (postrior view).
|
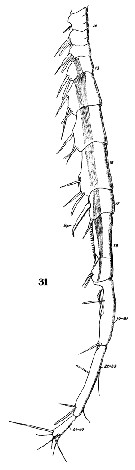 Issued from : W. Giesbrecht in Systematik und Faunistik der Pelagischen Copepoden des Golfes von Neapel und der angrenzenden Meeres-Abschnitte. – Fauna Flora Golf. Neapel, 1892, 19 , Atlas von 54 Tafeln. [Taf.19, Fig.31. Male: segments 10 to 24-25 of A1 (ventral view).
|
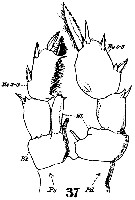 Issued from : W. Giesbrecht in Systematik und Faunistik der Pelagischen Copepoden des Golfes von Neapel und der angrenzenden Meeres-Abschnitte. – Fauna Flora Golf. Neapel, 1892, 19 , Atlas von 54 Tafeln. [Taf.19, Fig.37]. Male: P5 (anterior view). Ps = left leg; Pd = right leg; B2 = basis; Ri = endopod; Re = exopod.
|
 Issued from : P.P. Pillai in Bull. Dept. Mar. Sci. Univ. Cochin, 1975, VII (2). [p.326, Table I]. Setal formulae of certain appendages in Isias clavipes. Spines = Roman numerals; setae = Arabic numerals.
| | | | | Compl. Ref.: | | | Gadeau de Kerville, 1894 (p.81); Pearson (1906, p.22); Rose, 1924 d (p.479); 1925 (p.152); Massuti Alzamora, 1942 (p.94, Rem.); Gaudy, 1962 (p.93, 99, Rem.: p.110) ; Duran, 1963 (p.22); Giron-Reguer, 1963 (p.48); Pavlova, 1966 (p.44); Mazza, 1966 (p.71); 1967 (p.329, 367); Matthews, 1967 (p.159, Table 1, Rem.); Champalbert, 1969 a (p.620); El-Maghraby & Dowidar, 1970 (p.81); Dowidar & El-Maghraby, 1970 (p.268); Carli, 1971 (p.372, tab.1); Paulmier, 1971 (p.168); Lefèvre-Lehoërff, 1972 (p.1681); Della Croce & al., 1972 (p.1, Rem.); Apostolopoulou, 1972 (p.328, 359); Corral Estrada & Pereiro Muñoz, 1974 (tab.I); Vives & al., 1975 (p.48, tab.IV); Andronov & Maigret, 1980 (p.65, Table 2, 3); Castel & Courties, 1982 (p.417, Table II, spatial distribution); Vives, 1982 (p.292); Kovalev & Shmeleva, 1982 (p.84); Tremblay & Anderson, 1984 (p.4); Regner, 1985 (p.11, Rem.: p.34); Jansa, 1985 (p.108, Tabl. I, II, III, IV, V); Garcia-Rodriguez, 1985 (p.37); 1985 a (p.41, 42); Williams & Collins, 1985 (p.28); Moraitou-Apostolopoulou, 1985 (p.303, occurrence/abundance in E Mediterranean Sea); Comaschi Scaramuzza, 1987 (tab.1); Lozano Soldevilla & al., 1988 (p.59); Valdes & al., 1990 (tab.2); Krsinic, 1990 (p.337, Table I-II, vertical distribution); Fransz & al., 1991 (p.11); Kouwenberg, 1994 (tab.1); Ragosta & al., 1995 (Appendix A); Lakkis, 1998 (p.236, Rem.); Hure & Krsinic, 1998 (p.53, 101); Gilabert & Moreno, 1998 (tab.1, 2); Siokou-Frangou, 1999 (p.476); d'Elbée, 2001(tabl. 1); Fransz & Gonzalez, 2001 (p.255, tab.1); Holmes, 2001 (p.23, Rem.); Zerouali & Melhaoui, 2002 (p.91, Tableau I); Beaugrand & al., 2002 (p.179, figs.5, 6); Vukanic, 2003 (139, tab.1); Bode & al., 2003 (p.85, Table 1, abundance); Daly Yahia & al., 2004 (p.366, fig.4); CPR, 2004 (p.55, fig.159); Licandro & al., 2005 (p.153); Isari & al., 2006 (p.241, tab.II); Marques & al., 2006 (p.297, tab.III) ; Mageed, 2006 (p.168, Table 4); Zervoudaki & al., 2006 (p.149, Table I); Valdés & al., 2007 (p.104: tab.1); Khelifi-Touhami & al., 2007 (p.327, Table 1); Cabal & al., 2008 (289, Table 1); Rossi, 2008 (p.90: Tableau XII); Brylinski, 2009 (p.253: Tab.1, p.255: Rem.); Brugnano & al., 2010 (p.312, Table 2, 3); Eloire & al., 2010 (p.657, Table II, temporal variability); Mazzocchi & Di Capua, 2010 (p.424); Mazzocchi & al., 2011 (p.1163, Table II, fig.6, long-term time-series 1984-2006); S.C. Marques & al., 2011 (p.59, Table 1); Mazzocchi & al., 2012 (p.135, annual abundance 1984-2006); Alvarez-Fernandez & al., 2012 (p.21, Rem.: Table 1); Van Ginderdeuren & al., 2012 (p.3, Table 1); Miloslavic & al., 2012 (p.165, Table 2, transect distribution); Sobrinho-Gonçalves & al., 2013 (p.713, Table 2, seasonal abundance vs environmental conditions); Lidvanov & al., 2013 (p.290, Table 2, % composition); Pansera & al., 2014 (p.221, Table 2, abundance); Zakaria, 2014 (p.3, Table 1, abundance vs 1960-2000); Zakaria & al., 2016 (p.1, Table 1); Benedetti & al., 2016 (p.159, Table I, fig.1, functional characters); El Arraj & al., 2017 (p.272, table 2, seasonal composition); Benedetti & al., 2018 (p.1, Fig.2: ecological functional group); Belmonte, 2018 (p.273, Table I: Italian zones); Richirt & al., 2019 (p.3, Table 1, fig.2, 3, 4, 5, abundance changes vs years 1998-2014, table 2: diversity index) | | | | NZ: | 5 | | |
|
Distribution map of Isias clavipes by geographical zones
|
| | | | | | | | | | Loc: | | | Congo, Morocco-Mauritania, Canary Is., off W Madeira, G. of St. Lawtrnce, Lisbon, S Porto, Galicia (coast), Arcachon Basin, Brest Roadstead, Morlaix estuary, Belon estuary, Ireland, Mouth of Shannon, Bristol Channel, English Channel, Granville, Pas de Calais, North Sea, W Norway, Raunefjorden, Portugal (Mondego estuary), off Coruña, Iberian Shelf, Ibero-moroccan Bay, Gibraltar, Medit. (Alboran Sea, Algiers, El Kala shelf, laguna Mar Menor, Baleares, Banyuls, Marseille, Toulon Harbour, Monaco, Genova, Ligurian Sea, Tyrrhenian Sea, G. of Naples, Lake Faro (Sicily), Strait of Messina, Malta, Adriatic Sea, Mljet Is., Venezzia, Aegean Sea, W Egyptian coast, Alexandria) | | | | N: | 141 (SE Atlant.: 1; N Atlant.: 71; Medit.: 69) | | | | Lg.: | | | (46) F: 1,3-1,25; M: 1,25; (65) F: 1,35; M: 1,35; (327) F: 1,66-1,31; M: 1,59-1,26; (449) F: 1,35-1,25; M: 1,35-1,25; (920) F: 1,49; M: 1,45; {F: 1,25-1,66; M: 1,25-1,35}; | | | | Rem.: | coastal. Mainly in surface
According to Lakkis (1998, p.2,6) this species is rare in the Levant Sea (E Mediterranean Sea) and should be an indicator of the Atlantic current in the Mediterranean Sea.
Zakaria (2014, p.17) shows in Table 1 the paucity of this species during the period 1960-2008, excepted in the 1960s.
After Benedetti & al. (2018, p.1, Fig.2) this species belonging to the functional group 6 corresponding to small ambush feeding omnivorous. | | | Last update : 24/10/2022 | |
|
|
 Any use of this site for a publication will be mentioned with the following reference : Any use of this site for a publication will be mentioned with the following reference :
Razouls C., Desreumaux N., Kouwenberg J. and de Bovée F., 2005-2025. - Biodiversity of Marine Planktonic Copepods (morphology, geographical distribution and biological data). Sorbonne University, CNRS. Available at http://copepodes.obs-banyuls.fr/en [Accessed July 01, 2025] © copyright 2005-2025 Sorbonne University, CNRS
|
|
 |
 |