|
|
 |
Fiche d'espèce de Copépode |
|
|
Calanoida ( Ordre ) |
|
|
|
Calanoidea ( Superfamille ) |
|
|
|
Paracalanidae ( Famille ) |
|
|
|
Acrocalanus ( Genre ) |
|
|
| |
Acrocalanus longicornis Giesbrecht, 1888 (F,M) | |
| | | | | | | Syn.: | ? Acrocalanus gardineri (M) Wolfenden, 1905 (1906) (p.1004, figs.M); Sewell, 1914 a (p.211); Gurney, 1927 (p.149: Rem.) | | | | Ref.: | | | Giesbrecht, 1892 (p.171, 175, 770, figs.F); Giesbrecht & Schmeil, 1898 (p.25, Rem. F); Thompson & Scott, 1903 (p.233, 243); Wolfenden, 1905 (1906) (p.1000, figs.); A. Scott, 1909 (p.28, Rem.); Sewell, 1912 (p.358, Rem.); Pesta, 1913 (p.31, fg.F); Sewell, 1914 a (p.209); 1929 (p.82, figs.F, Rem. M: p.83, 86); Mori, 1929 (p.172, figs.F); Farran, 1929 (p.208, 222); 1936 a (p.80); Mori, 1937 (1964) (p.31, fig.F); Vervoort, 1946 (p.133, Rem.); Sewell, 1947 (p.53); Tanaka, 1956 c (p.372, Rem.F,M, p.375: Rem.M); Bowman, 1958 (p.119: fig.F, p.121: Rem.); Fish, 1962 (p.11); Grice, 1962 (p.187, figs.F, Rem.); Kasturirangan, 1963 (p.24, figs.F); Chen & Zhang, 1965 (p.46, figs.F); Saraswathy, 1966 (1967) (p.76); Owre & Foyo, 1967 (p.38, figs.F); Corral Estrada, 1970 (p.101, figs.F, Rem.); Chen & Zhang, 1974 (p.106, figs.M); Marques, 1976 (p.989); Greenwood, 1976 (p.19); Björnberg & al., 1981 (p.624, fig.F); Zheng & al., 1982 (p.30, figs.F); Hiromi, 1987 (p.154); Nishida, 1989 (p.173, fig.3, table 1, 2, 3, dorsal hump); Bradford-Grieve, 1994 (p.50, figs.F,M, fig.99); Chihara & Murano, 1997 (p.846, Pl.136: F,M); Bradford-Grieve & al., 1999 (p.877, 909, figs. F,M); Conway & al., 2003 (p.155, figs.F,M, Rem.); Mulyadi, 2004 (p.175, figs.M, Rem.); Vives & Shmeleva, 2007 (p.919, figs.F, Rem.); Phukham, 2008 (p.118, figs.F); Al-Yamani & al., 2011 (p.18, figs.F,M); Soh & al., 2013 (p.52, figs.F) | 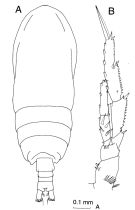 issued from : J.M. Bradford-Grieve in The Marine Fauna of New Zealand: Pelagic Calanoid Copepoda. National Institute of Water and Atmospheric Research (NIWA). New Zealand Oceanographic Institute Memoir, 102, 1994. [p.50, Fig.23]. Female: A, habitus (dorsal); B, P4.
|
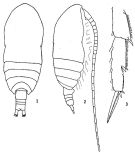 issued from: Q.-c Chen & S.-z. Zhang in Studia Marina Sinica, 1965, 7. [Pl.11, 1-3]. Female: 1, habitus (dorsal); 2, idem (lateral right side); 3, 2nd and 3rd segments of exopod of P4 (posterior).
|
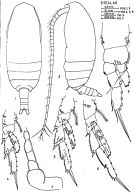 issued from : J. Corral Estrada in Tesis Doct., Univ. Madrid, A-129, Sec. Biologicas, 1970. [Lam.22]. Female (from Canarias Is.): 1, habitus (dorsal); 2, idem (lateral left side); 3, P1; 4, P2; 5, P3; 6, P4; 7, P5. Nota: A1 excceds the caudal rami by the last 5 segments (generally more longer in this species). Exopodal segment 2 of P2 with 7 teeth on outer margin (generally 2-3 teeth in this species).
|
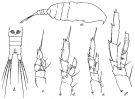 issued from : R.B.S. Sewell in Mem. Indian Mus., 1929, X. [p.82, Fig.33]. Female (from N Indian Ocean): a, habitus (lateral right side); b, urosome (ventral); c, P1; d, P2; e, P3; f, P4.
|
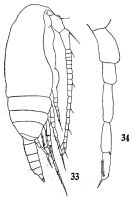 issued from : Q.-c. Chen & S.-z. Zhang in Studia Marina Sinica, 1974, 9. [Pl.3, Figs.33-34]. male (from South China Sea): 33, habitus (lateral right side); 24, P5.
|
 issued from : T.E. Bowman in Bull. mar. Sc. Gulf Caribb., 1958, 8 (2). [p.119, Fig.1, D]. Female (from off Georgia, USA): D, habitus (lateral).
|
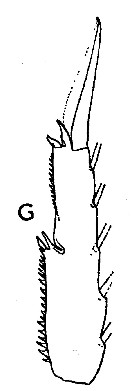 issued from : T.E. Bowman in Bull. mar. Sc. Gulf Caribb., 1958, 8 (2). [p.120, Fig.2, G]. Female: G, exopod segment 3 of P4 (posterior surface).
|
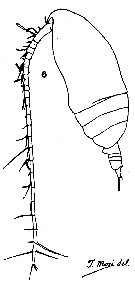 issued from : T. Mori inThe pelagic Copepoda from the neighbouring waters of Japan, 1937 (1964). [Pl.12, Fig.6]. Female: 6, habitus (lateral).
|
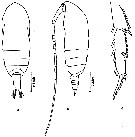 issued from : Z. Zheng, S. Li, S.J. Li & B. Chen inMarine planktonic copepods in Chinese waers. Shanghai Sc. Techn. Press, 1982 [p.30, Fig.17]. Female: a-b, habitus (dorsal and lateral, respectively); c, exopods of P2 and P3. Scale bars in mm.
|
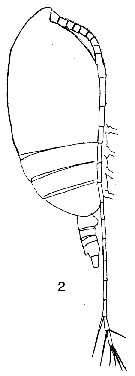 issued from T. Mori in Zool. Mag. Tokyo, 1929, 41 (486-487). [Pl. V, Fig.2]. Female (from Chosen Strait, Korea-Japan): 2, habitus (lateral).
|
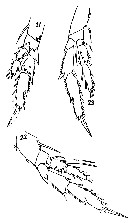 issued from T. Mori in Zool. Mag. Tokyo, 1929, 41 (486-487). [Pl. IV, Figs.21-23]. Female: 21, P2; 22, P3; 23, P4.
|
 issued from : G.D. Grice in Fish. Bull. Fish and Wildl. Ser., 1962, 61. [p.185, Pl.5, Figs.1-16]. Female (from equatorial Pacific): 1-2, habitus (dorsal and lateral, respectively); 3-4, posterior part of thorax and urosome (dorsal and lateral, respectively); 5, P1 (anterior); 6, P1 (posterior); 7, P2 (anterior); 8, P2 (posterior); 9, P3 (anterior; without distal 2 segments of endopod); 10, distal 2 segments of endopod of P3 (anterior); 11, P3 (anterior; without distal 2 segments of endopod); 12, distal 2 segments of endopod of P3 (posterior); 13, P4 (anterior; without 3rd exopodal segment); 14, 3rd exopodal segment of P4 (anterior); 15, P4 (posterior; without 3rd exopodal segment); 16, 3rd exopodal segment of P4 (posterior). Nota: The presence of a partial suture between the head and 1st thoracic segment and the spinulation of the swimming legs, particularly the number of teeth (more than 18) on the distal part of the 3rd exopodal segment of P4, distinguised this species from others in the genus.
|
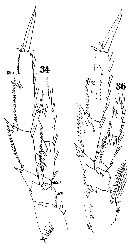 Issued from : W. Giesbrecht in Systematik und Faunistik der Pelagischen Copepoden des Golfes von Neapel und der angrenzenden Meeres-Abschnitte. – Fauna Flora Golf. Neapel, 1892, 19 , Atlas von 54 Tafeln. [Taf. 10, Figs. 34, 36]. Female: 34, P1 (posterior view); 36 P3 (posterior view). B, basipodite (B2 = basis); Ri = endopodite; Re = exopodite
|
 Issued from : W. Giesbrecht in Systematik und Faunistik der Pelagischen Copepoden des Golfes von Neapel und der angrenzenden Meeres-Abschnitte. – Fauna Flora Golf. Neapel, 1892, 19 , Atlas von 54 Tafeln. [Taf. 10, Fig.39]. Female: 39, Md.
|
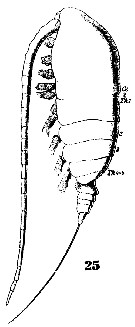 Issued from : W. Giesbrecht in Systematik und Faunistik der Pelagischen Copepoden des Golfes von Neapel und der angrenzenden Meeres-Abschnitte. – Fauna Flora Golf. Neapel, 1892, 19 , Atlas von 54 Tafeln. [Taf. 6, Fig.25]. Female: 25, habitus (lateral).
|
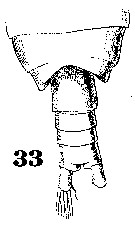 Issued from : W. Giesbrecht in Systematik und Faunistik der Pelagischen Copepoden des Golfes von Neapel und der angrenzenden Meeres-Abschnitte. – Fauna Flora Golf. Neapel, 1892, 19 , Atlas von 54 Tafeln. [Taf. 6, Fig.33]. Female: 33, thoracic somites 4 +5 and urosome (dorsal)
|
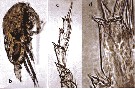 issued from : Y. Al-Yamani, V. Skryabin, A. Gubanova, S. khvorov & I. Prusova in Marine Zooplankton Practical Guide for the Northwestern Arabian Gulf, 2, 2011. [p.19, Fig.126, b-d]. Female (from Kuwait): b, habitus (lateral); c, exopod of P4; d, distal part of P4 exopod.
|
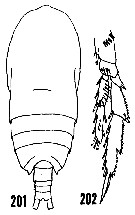 issued from : H.B. Owre & M. Foyo in Fauna Caribaea, 1, Crustacea, 1: Copepoda. Copepods of the Florida Current. [p.38, Figs.201, 202]. Female: 201, habitus (dorsal); 202, P4.
|
 issued from : N. Phukham in Species diversity of calanoid copepods in Thai waters, Andaman Sea (Master of Science, Univ. Bangkok). 2008. [p.200, Fig.74]. Female (from W Malay Peninsula): a-b, habitus (dorsal and lateral, respectively); c, P4. Body length after the drawing: F = 1.298 mm.
|
 issued from : Mulyadi in Published by Res. Center Biol., Indonesia Inst. Sci. Bogor, 2004. [p.175, Fig.98]. Male (from 03°40'S, 128°10'E): a, habitus (dorsal); b, P3; c, P4; d, P5. Nota: Dorsal separation between cephalon and metasome segments incomplete. P4, outer margin of exopod segment 3 with the large number (>18) of denticles.
|
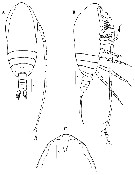 Issued from : H.Y. Soh, S.Y. Moon & J.H. Wi in Invertebrate Fauna of Korea (eds) Incheon: NIBR, 2013, 21 (28). [p.53, Fig.30]. Female (Korean waters): A-B, habitus (dorsal and lateral, respectively); C, forehead (ventral). Scale bars: A, B = 200 µm; C = 100 µm.
|
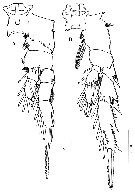 Issued from : H.Y. Soh, S.Y. Moon & J.H. Wi in Invertebrate Fauna of Korea (eds) Incheon: NIBR, 2013, 21 (28). [p.54, Fig.31]. Female: A, P1; B, P2. Scale bars: 50 µm.
|
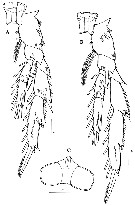 Issued from : H.Y. Soh, S.Y. Moon & J.H. Wi in Invertebrate Fauna of Korea (eds) Incheon: NIBR, 2013, 21 (28). [p.55, Fig.32]. Female: A, P3; B, P4; C, P5. Scale bars: A, B = 100 µm; C = 25 µm.
| | | | | Ref. compl.: | | | Carl, 1907 (p.16); Wilson, 1942 a (p.170); Oliveira, 1945 (p.191); Sewell, 1948 (p.390, 395, 407, 412, 414, 433, 436, 442, 450, 459); C.B. Wilson, 1950 (p.157); Krishnaswamy, 1953 (p.114); Chiba & al., 1957 (p.306); Yamazi, 1958 (p.148, Rem.); Heinrich, 1961 (tab.2); Fagetti, 1962 (p.13); Ganapati & Shanthakumari, 1962 (p.7, 15); Gaudy, 1963 (p.21, Rem.); Björnberg, 1963 (p.31, Rem.); De Decker & Mombeck, 1964 (p.11); Grice & Hulsemann, 1967 (p.14); Fleminger, 1967 a (tabl.1); Vinogradov, 1968 (1970) (p.78); Delalo, 1968 (p.137); Park, 1970 (p.475); Timonin, 1971 (p.281, trophic group); Binet & al., 1972 (p.55); Bainbridge, 1972 (p.61, Appendix Table I: vertical distribution vs day/night, Table II: %, Table IV: seasonal abundance); Björnberg, 1973 (p.384); Corral Estrada & Pereiro Muñoz, 1974 (tab.I); Patel, 1975 (p.659); Deevey & Brooks, 1977 (p.256, tab.2, Station "S"); Carter, 1977 (1978) (p.35); Dessier, 1979 (p.204); Star & Mullin, 1981 (p.1322, abundance); Vives, 1982 (p.290); Dessier, 1983 (p.89, Tableau 1, 2, Rem., %); Guangshan & Honglin, 1984 (p.118, tab.); Stephen, 1984 (p.161, Rem.: 168); Almeida Prado Por, 1985 (p.250); Brinton & al., 1986 (p.228, Table 1); Madhupratap & Haridas, 1986 (p.105, tab.1); Lozano Soldevilla & al., 1988 (p.57); Dessier, 1988 (tabl.1); Yoo, 1991 (tab.1); Jimenez-Perez & Lara-Lara, 1988; Mitra & al., 1990 (fig.3); Othman & al., 1990 (p.561, 563, Table 1); Godhantaraman, 1994 (tab. 6, 7); Gouda & Panigrahy, 1995 (p.206); Shih & Young, 1995 (p.71); Webber & al., 1996 (tab.1); Kotani & al., 1996 (tab.2); Go & al., 1997 (tab.1); Suarez-Morales & Gasca, 1997 (p.1525); Alvarez-Cadena & al., 1998 (tab.1,2,3,4); Noda & al., 1998 (p.55, Table 3, occurrence); Suarez-Morales & Gasca, 1998 a (p.110); Smith S. & al., 1998 (p.2369, Table 6, moonsoon effects); Lavaniegos & Gonzalez-Navarro, 1999 (p.239, Appx.1); Lopes & al., 1999 (p.215, tab.1); Neumann-Leitao & al., 1999 (p.153, tab.2); Fernandez-Alamo & al., 2000 (p.1139, Appendix); Suarez-Morales & Gasca, 2000 (1247, tab.1); Lopez-Salgado & al., 2000 (tab.1); Shimode & Shirayama, 2004 (tab.2); Hsiao & al., 2004 (p.326, tab.1); Rezai al., 2004 (p.489, tab.2); Chang & Fang, 2004 (p.456, tab.1); Lo & al., 2004 (p.89, tab.1); Kazmi, 2004 (p.230); Alvarez-Silva & al., 2005 (p.39); Smith & Madhupratap, 2005 (p.214, tab.4,6) ; Rezai & al., 2005 (p.157, Table 2: spatial & temporal variations); Prusova & Smith, 2005 (p.75); Dias & Araujo, 2006 (p.58, Rem., chart); Lavaniegos & Jiménez-Pérez, 2006 (tab.2, 4, Rem.); Dur & al., 2007 (p.197, Table IV); Jitlang & al., 2008 (p.65, Table 1); Neumann-Leitao & al., 2008 (p.799: Tab.II, fig.6); Morales-Ramirez & Suarez-Morales, 2008 (p.514, 521); Fernandes, 2008 (p.465, Tabl.2); Ohtsuka & al., 2008 (p.115, Table 5); C.-Y. Lee & al., 2009 (p.151, Tab.2); Miyashita & al., 2009 (p.815, Tabl.II); Cornils & al., 2010 (p.2076, Table 3); Schnack-Schiel & al., 2010 (p.2064, Table 2: E Atlantic subtropical/tropical); Dias & al., 2010 (p.230, Table 1); Medellin-Mora & Navas S., 2010 (p.265, Tab. 2); Fazeli & al., 2010 (p.153, Table 1); Tutasi & al., 2011 (p.791, Table 2, abundance distribution vs La Niña event); Guo & al., 2011 (p.567, table 2, indicator); Hsiao S.H. & al., 2011 (p.475, Appendix I); Pillai H.U.K. & al., 2011 (p.239, Table 3, vertical distribution); Maiphae & Sa-ardrit, 2011 (p.641, Table 2); Beltrao & al., 2011 (p.47, Table 1, density vs time); Johan & al., 2012 (p.647, Table 1, fig.2, salinity range); Johan & al., 2012 (2013) (p.1, Table 1); Uysal & Shmeleva, 2012 (p.909, Table I); Lavaniegos & al., 2012 (p. 11, Table 1, fig.3, seasonal abundance, Appendix); Naz & al., 2012 (p.61, Table 4, relative abundance); Cornils & Blanco-Bercial, 2013 (p.861, Table 1, molecular analysis, figs.3, 4, 5); Palomares-Garcia & al., 2013 (p.1009, Table I, abundance vs. environmental factors); in CalCOFI regional list (MDO, Nov. 2013; M. Ohman, pers. comm.); Tseng & al., 2013 (p.507, seasonal abundance); Lidvanov & al., 2013 (p.290, Table 2, % composition); Bonecker & a., 2014 (p.445, Table II: frequency, horizontal & vertical distributions); Dias & al., 2015 (p.483, Table 2, abundance, biomass, production, Table 4: % vs. season); Marques-Rojas & Zoppi de Roa, 2017 (p.495, Table 1); Dias & al., 2018 (p.1, Tables 2, 4, 5: vertical distribution, abundance vs. season); Palomares-Garcia & al., 2018 (p.178, fig.3: relative frequency, Table 1); Hirai & al., 2020 (p.1, Fig. 5: cluster analysis (OTU), spatial distribution). | | | | NZ: | 15 | | |
|
Carte de distribution de Acrocalanus longicornis par zones géographiques
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | Loc: | | | South Africa (E), Congo, G. of Guinea, off Lagos, Ivorian shelf, Dakar, off S Cape Verde Is., off Morocco-Mauritania, Canary Is., Brazil (S, Campos Basin, off Macaé, Cabo Frio, off Vitoria-Cabo de Sao Tomé, off Natal, Tocantins Estuary), off Amazon, Venezuela, Barbada Is., Caribbean Colombia, Caribbean Sea, Bahia de Mochima (Venezuela), Jamaica, Yucatan, E Costa Rica, G. of Mexico, Cuba, Florida, off Bermuda, Sargasso Sea, Station "S" (32°10'N, 64°30'W), Medit. (N Lebanon Basin), Red Sea, Gulf of Oman, G. of Aden, Arabian Sea, Arabian Gulf (Kuwait), Maldive Is., Madagascar, G. of Mannar, Sri Lanka, Natal, Indian, India (Karashi coast, Saurashtra coast, S, Madras, Rushikulya estuary, Lawson's Bay, Mandarmani), G. of Bengal, Nicobar Is., Barren Island, S Burma, W Malay Peninsula (Andaman Sea), Perai River estyary (Penang), Straits of Malacca, Indonesia-Malaysia, Bintulu coast, SW Celebes, Ambon Bay (SW Ceram Is.), Philippines, Viet-Nam (Cauda Bay), China Seas (Yellow Sea, East China Sea, South China Sea), Taiwan Strait, Taiwan (SW, E, Kaohsiung Harbor, N: Mienhua Canyon, NW, NE), Okinawa, S Korea, Japan, Ariake Bay, Kucginoerabu Is., off SE Japan, Pacif. (W equatorial), Australia (G. of Carpentaria, Great Barrier, Moreton Bay), New Caledonia, off NW New Zealand, Pacif. (equatorial), Pacif. (N Central Gyre), Hawaii, California, W Baja California, G. of California (rare, Bahia de los Angeles), Zihuatanejo Bay, La Paz, SW Mexico, G. of Tehuantepec, W Costa Rica, Galapagos-Ecuador, N Chile
Data from Cornils & Blanco-Bercial (2013): 01°00S; 09°00'W. | | | | N: | 174 | | | | Lg.: | | | (28) F: 1,24-1,02; (29) F: 1; M: 1-0,95; (34) F: 1,44-1,24; (35) F: 1,18-1,13; (47) F: 1,2-1; (55) F: 1,28-1,14; M: 0,955; (101) F: 1,27-1,17; (237) F: 1,1; M: 0,95-0,8; (290) F: 1,55-1,46; (333) F: 1,12; (334) F: 1,2-1,14; (338) M: 1,4-1,35; (530) F: 1,2; M: 1,1; (785) F: 1,14-0,94; (795) F: 1,2; (991) F: 1-1,26; M: 0,9-1,25; (1023) F: 1,16-1,41; (1085) F: 1,0-1,26; M: 0,95-1,25; (1122) M: 1,1; (1174) F: 1,42; {F: 0,94-1,55; M: 0,80-1,40} | | | | Rem.: | épipélagique, parfois plus profond.
Acrocalanus longicornis plumulosus Sewell,1912
Ref.: Sewell, 1912 (p.359); Früchtl, 1923 (p.456); Silas, 1972 (p.646)
Loc.: NE Gulf of Bengal
Voir aussi les remarques en anglais | | | Dernière mise à jour : 03/12/2020 | |
|
|
 Toute utilisation de ce site pour une publication sera mentionnée avec la référence suivante : Toute utilisation de ce site pour une publication sera mentionnée avec la référence suivante :
Razouls C., Desreumaux N., Kouwenberg J. et de Bovée F., 2005-2026. - Biodiversité des Copépodes planctoniques marins (morphologie, répartition géographique et données biologiques). Sorbonne Université, CNRS. Disponible sur http://copepodes.obs-banyuls.fr [Accédé le 06 février 2026] © copyright 2005-2026 Sorbonne Université, CNRS
|
|
 |
 |