|
|
 |
Fiche d'espèce de Copépode |
|
|
Monstrilloida ( Ordre ) |
|
|
|
Monstrillidae ( Famille ) |
|
|
|
Caromiobenella ( Genre ) |
|
|
| |
Caromiobenella helgolandica (Claus, 1863) (F,M) | |
| | | | | | | Syn.: | Monstrilla helgolandica Claus, 1863
Monstrilla canadensis McMurrich, 1917; Fontaine, 1955 (p.890); Tremblay & Anderson, 1984 (p.8); Bernier & al., 2002 (p.651, tab.1);
Monstrilla anglica (M) : Wilson, 1932 a (p.394, figs.M);
Monstrilla serricornis (M) : ? C.B. Wilson, 1950 (p.268);
Non M. helgolandica : Ramirez, 1971 b (p.381, figs.F, Rem.) | | | | Ref.: | | | Claus, 1863 (p.165, figs.F); Malaquin, 1901 (p.111); van Breemen, 1908 a (p.207, figs.F); A. Scott, 1909 (p.238, figs.F); Sars, 1921 (p.18, F); Gallien, 1934 (p.379, figs.F,M, Rem.); Dolgopol'skaya, 1948 (p.178, figs.F); Sewell, 1949 (p.139, fig.F); Fontaine, 1955 (p.890); Park, 1967 (p.149, figs.F); Shih & al., 1971 (p.57); Isaac, 1974 (p.128); 1975 (p.3, 8, non le M); Threlkeld, 1977 (p.226, Rem.); Gardner & Szabo, 1982 (p.84, figs.F,M); McAlice, 1982 (p.45, Rem.); 1985 (p.627, figs.F,M, Rem.); Huys & Boxshall, 1991 (p.163, 464, figs.M); Suarez-Morales, 1994 (p.264: Rem.); Grygier, 1995 a (p.9, 32, 66); Grygier & Ohtsuka, 1995 (Rem.: p.717-718); Suarez-Morales, 2000 (p.115: Rem.); Ferrari & Dahms, 2007 (p.57); Suarez-Morales, 2010 (p.66, Rem.); Vives & Shmeleva, 2010 (p.177, figs.F,M, Rem.); Suarez-Morales, 2011 (p.6: Rem. | 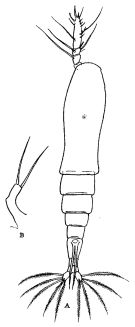 issued from : R.B.S. Sewell in The John Murray Expedition, 1933-34, Scientific Reports, IX (2), 1949. [p.140, Fig.39, A-B]. Female (from Nankauri Harbour, Nicobar Is.): A, habitus (dorsal); B, P5.
|
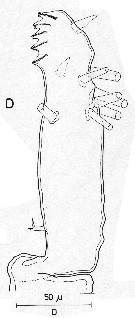 issued from : R. Huys & G.A. Boxshall in Copepod Evolution, The Ray Society, 1991. [p.163, Fig.2.5.6]. Male (from Norway): D, distal segment of A1.
|
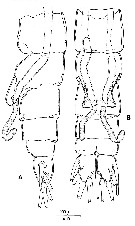 issued from : R. Huys & G.A. Boxshall in Copepod Evolution, The Ray Society, 1991. [p.165, Fig.2.5.8]. Male (from Norway): A, urosome with spermatophore partly discharged (lateral view); B, idem (ventral view).
|
 issued from : R. Huys & G.A. Boxshall in Copepod Evolution, The Ray Society, 1991. [p.167, Fig.2.5.10]. Female: Detail of oral region with mouth cone. Scale bar = 0.030 mm.
|
 issued from : M.J. Grygier & S. Ohtsuka in J. Crustacean Biol., 1995, 15 (4). [p.718, Table 1]. Differences between M. hamatapex and European M. helgolandica
|
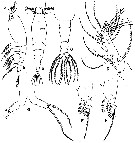 issued from : T.S. Park in Trans. Amer. Microsc. Soc., 1967, 86 (2). [p.147, Fig.3]; Female (from Strait of Georgie): A-B, habitus (lateral and dorsal, respectively); C, posterior portion of body (dorsal); D, A1; E, P1; F, P2; C, P5. Nota: Cephalosome including the 1st metasomal segment about as long as the rest of te body, and its surface is finely rugose. Prominent oral papilla located halfway along the ventral side of the cephalosome. 2 dorsal eyes visible immediately dorsal to A1. Genital segment relatively long being equal to the rest of the urosome., including the caudal rami, and bears ventrally ovigerous spiniform processes. Caudal rami with 6 setae, 2 medial, 2 lateral, 1 terminal and 1 dorsal very short. A1 only 2/5 the length of the fused cephalosome including the 1st metasomal segment; it has only one complete articulation, by which the small proximal segment is separated; none of its setae are dichotomously branched. P1 differs from those of the succeeding legs, which are all alike, in that the 3rd exopodal segment has 4 setae. instead of 5. P5 slender, strongly divergent, bears 1 long terminal seta and 1 subterminal, lateral seta; the inner lobe is absent or at least inconspicuous.
|
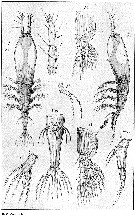 issued from : G.O. Sars in An Account of the Crustacea of Norway, with short descriptions and figures of all the species, 1921a, 8. [Pl. IX]. Female (from West coast of Norway: Christiansund): Urs, urosome (ventral and lateral, respectively). Nota: Body comparatively short and stout, and somewhat dilated in its anterior part. Cephalic segment occupying half the length of the body. Eye easily observable, and having all 3 lenses developed. A1 4-segmented. Oral tubule well marked, located in the middle of the cephalic segment. Swimming legs without any denticle inside the 2nd basal segment (Basis). P5 , each forming a narrow cylindrical stem, angularly bent in the middle and tipped with 2 subequal setae. Genital segment being rather large and gradually narrowed behind. Ovigerous spines of moderate length. Caudal rami considerably divergent, narrow oblong in shape, each with 6 setae of somewhat unequal length, one of them, attached somewhat dorsally, being very small, that next to it on the outer side somewhat shorter than the 4 remaining ones.
|
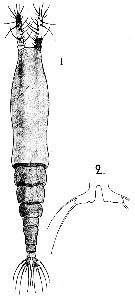 Issued from : A. Scott in The Copepoda of the Siboga Expedition Part I. Siboga-Expeditie XXIX a., 1909. [Pl. LVIII, Figs.1-2]. Female (from off North Ubian, Sulu Islands): 1, habitus (dorsal); 2, P5. Nota: Abdomen 3-segmented. Genital segment sub-cylindrical in shape; it is contracted in the middle but without trace of suture; Segment one and half times longer than the combined length of the next two segments; it is as long as the united length of the next two segments and caudal rami. Anal segment slightly shorter than the 2nd segment. Caudal rami as long as the anal segment; each ramus is furnished with 1outer marginal seta and 5 apical setae, the middle apical seta much shorter than the others. A1 3-segmented and equal to one-third of the lenhth of the cephalic segment. P5 very small and divergent. The apex is directed at right angles to the body and furnished with 2 setae.
| | | | | Ref. compl.: | | | Rose, 1926 a (p.61); Tremblay & Anderson, 1984 (p.8); Holmes, 2001 (p.62); Bernier & al., 2002 (p.651, tab.1); Kovalev, 2003 (p.47); Dias & Bonecker, 2007 (p.270, fig.3, tab.II); Brylinski, 2009 (p.253: Tab.1, p.258: Rem.); Suarez-Morales, 2010 a (p.3); W.-B. Chang & al., 2010 (p.735, Table 2, abundance); Zaafa & al., 2014 (p.67, Table I, occurrence); El Arraj & al., 2017 (p.272, table 2, spatial distribution); | | | | NZ: | 10 + 1 douteuse | | |
|
Carte de distribution de Caromiobenella helgolandica par zones géographiques
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | Loc: | | | Gulf of Maine, Woods Hole, Bay of Fundy, Ungava Bay, Norway, North Sea, Maroccan coast, Helgoland, Ireland, English Channel, N Bay of Biscay (Loire Estuary), off W Tangier, Medit. (Algiers, Black Sea), Nicobar Is., Indonesia-Malaysia, ? Japan, Taiwan (south), Gilbert Is., Georgia Strait | | | | N: | 20 ? | | | | Lg.: | | | (5) F: 2,07; (45) M: 2-1,4; (277) F: 1,55-1,47; (663) F: ? 1,4; (746) F: 2,31; (747) F: 5,3-1,4; M: 2-1,1; (749) F: 2; M: 1,15-1; {F: 1,40-5,30; M: 1,00-2,00} | | | | Rem.: | Pour Jeon & al. (2018, p.47) cette espèce appartient au nouveau genre Caromiobenella.
Voir aussi les remarques en anglais | | | Dernière mise à jour : 07/01/2025 | |
|
|
 Toute utilisation de ce site pour une publication sera mentionnée avec la référence suivante : Toute utilisation de ce site pour une publication sera mentionnée avec la référence suivante :
Razouls C., Desreumaux N., Kouwenberg J. et de Bovée F., 2005-2026. - Biodiversité des Copépodes planctoniques marins (morphologie, répartition géographique et données biologiques). Sorbonne Université, CNRS. Disponible sur http://copepodes.obs-banyuls.fr [Accédé le 20 février 2026] © copyright 2005-2026 Sorbonne Université, CNRS
|
|
 |
 |