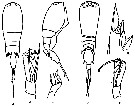|
|
 |
Fiche d'espèce de Copépode |
|
|
Cyclopoida ( Ordre ) |
|
|
|
Corycaeidae ( Famille ) |
|
|
|
Corycaeus ( Genre ) |
|
|
|
Agetus ( Sous-Genre ) |
|
|
| |
Corycaeus (Agetus) typicus (Krøyer, 1849) (F,M) | |
| | | | | | | Syn.: | Agetus typicus Kröyer,1849 (in Damkaer & Damkaer, 1979, p.39, figs.M); Baldina, 1970 (p.507); Böttger-Schnack, 1997 (p.409); Dessier, 1983 (p.89, Tableau 1, 2, Rem., %); 1988 (tabl.1); Boxshall & Halsey, 2004 (p.494); McKinnon & al., 2008 (p.843: Tab.1, p.848: Tab. IV); Vidjak & Bojanic, 2009 (p.432, Table II, IV, V); Lan Y.-C. & al., 2009 (p.1, Table 2, % vs hydrogaphic conditions); Vives & Shmeleva, 2010 (p.200, figs.F,M, Rem.); Belmonte & al., 2013 (p.222, Table 2, abundance vs stations); Wi & al., 2013 (p.400, figs.F,M, Rem. p.415 & following); Zakaria & al., 2016 (p.1, Table 1); Marques-Rojas & Zoppi de Roa, 2017 (p.495, Table 1); El Arraj & al., 2017 (p.272, table 2, spatial distribution); Chaouadi & Hafferssas, 2018 (p.913, Table II: occurrence);
Corycaeus elongatus Claus, 1863 (p.157, figs.F,M); F. Dahl, 1894 (p.70); Thompson, 1900 c (p.292); Wheeler, 1901 (p.192, figs.F,M); Thompson & Scott, 1903 (p.240, 285); ? A. Scott, 1909 (p.247, Rem.); Wolfenden, 1911 (p.360); Brian, 1914 a (p.138); Wilson, 1932 (p.42); 1932 a (p.355, figs.F); Klevenhusen, 1933 a (p.91, carte 42); Wilson, 1936 c (p.93); Oliveira, 1945 (p.191); Carvalho, 1952 a (p.168, figs.F); Krishnaswamy, 1953 (p.70, fig.juv., Rem.); Fish, 1962 (p.28); Uysal & al. (comm. pers. 2001); Wi & al., 2013 (p.400, figs.F, M, Table 2, Rem.);
Corycäus alatus Giesbrecht,1891; 1892 (p.661, 674, figs.F); Thompson, 1900 c (p.292); Corycäus elongatus (M) : Giesbrecht, 1892 (p.659, 674, figs.M, no F);
Corycaeus alatus : F. Dahl, 1894 (p.70); A. Scott, 1909 (p.245, Rem.); Wolfenden, 1911 (p.359);
Corycaeus typicus : Corral Estrada Pereiro Muñoz, 1974 (tab.I); Avancini & al., 2006 (p.150, Pl. 118, figs.F,M, Rem.); | | | | Ref.: | | | M. Dahl, 1912 (p.31, figs.F,M); Pesta, 1920 (p.649, fig.M); Farran, 1929 (p.211, 292); Rose, 1929 (p.68); 1933 a (p.328, figs.F,M); Farran, 1936 a (p.135); Tanaka, 1957 (p.81, figs.F,M); Motoda, 1963 (p.224, figs.F,M); Cervigon, 1964 (p.175, figs.F); Owre & Foyo, 1967 (p.121, figs.F,M); Vilela, 1968 (p.35, figs.F,M); Corral Estrada, 1970 (p.243, figs.F, M, Rem.); Razouls, 1972 (p.96, Annexe: p.130, figs.F,M); 1974 c (1975) (p.87, figs.F,M); Björnberg & al., 1981 (p.675, figs.F,M, Rem.); Scotto di Carlo, 1984 (p.1041); Lakkis & Zeidane, 1987 (p.18, figs. F,M, Rem.); Chihara & Murano, 1997 (p.964, Pl.215: F,M); Boxshall, 1998 (p.222); Bradford-Grieve & al., 1999 (p.887, 974, figs.F,M); Conway & al., 2003 (p.246, figs.F,M, Rem.); | 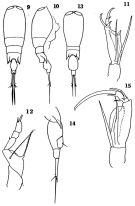 issued from : O. Tanaka in J. Fac. Agricult. Kyushu Univ., 1957, 11 (1). [Pl.4, Figs.9-15]. Female (from Japanese waters): 9, habitus (dorsal); 10, idem (lateral left side); 11, A2; 12, P4. Nota: Head and 1st thoraciv segment separate. Cephalothorax and urosome in the proportional lengths 2:1. Genital segment and furca in the proportional lengths 55:45. Male: 13, habitus (dorsal); 14, idem (lateral right side); 15, A2. Nota: Anterior segment less than 2 times as long as wide (40:23). Cephalothorax and urosome in the proportional lengths 8:5. The abdominal segments and furca in the proportional lengths 52:18:30. Genital segment about 1.5 times as long as wide. Furcal rami more than 6 times as long as it is wide at the proximal (19:3).
|
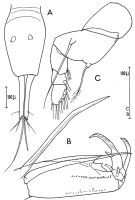 issued from : C. Razouls in Vie Milieu, 1974, 24 (1.A). [p.102, Fig.4]. Female (from W Medit.: Banyuls, France): A, urosome (dorsal); B, A2; C, P4.
|
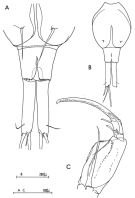 issued from : C. Razouls in Vie Milieu, 1974, 24 (1.A). [p.103, Fig.5]. Male: A-B, urosome (dorsal); C, A2.
|
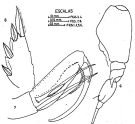 issued from : J. Corral Estrada in Tesis Doct. Univ., Madrid, A-129, Sec. Biologicas, 1970. [Lam.60, figs.5-8]. Male (from Canarias Is.): 5, habitus (dorsal); 6, idem (lateral left side); 7, A2; 8, exopodal segment 3 of P1.
|
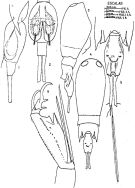 issued from : J. Corral Estrada in Tesis Doct., Univ. Madrid, A-129, Sec. Biologicas, 1970. [Lam.61, figs.1-6]. Male: 1, urosome (lateral left side); 2, idem (ventral). Female: 3, habitus (lateral right side); 4, idem (dorsal); 5, urosome (dorsal); 6, A2.
|
 Issued from : W. Giesbrecht in Systematik und Faunistik der Pelagischen Copepoden des Golfes von Neapel und der angrenzenden Meeres-Abschnitte. – Fauna Flora Golf. Neapel, 1892. Atlas von 54 Tafeln. [Taf.49, Fig.24]; As Corycäus elongatus. Male: 24, A2.
|
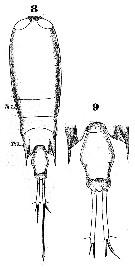 Issued from : W. Giesbrecht in Systematik und Faunistik der Pelagischen Copepoden des Golfes von Neapel und der angrenzenden Meeres-Abschnitte. – Fauna Flora Golf. Neapel, 1892. Atlas von 54 Tafeln. [Taf.51, Figs.8, 9]. As Corycäus alatus. Female: 8, habitus (dorsal); 9, urosome (dorsal).
|
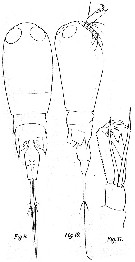 issued from : M. Dahl in Ergebnisse der Plankton-Expedition der Humboldt-Stiftung. Bd II, G. f1. I. Die Corycaeinen 1912. [Taf.IV, Figs.9, 10, 11]. Female: 9, habitus (dorsal); 10, idem (lateral right side); 11, A2.
|
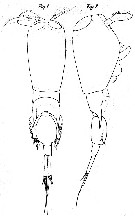 issued from : M. Dahl in Ergebnisse der Plankton-Expedition der Humboldt-Stiftung. Bd II, G. f1. I. Die Corycaeinen 1912. [Taf.V, Figs.1, 2]. Male: 1, habitus (dorsal); 2, idem (lateral right side).
|
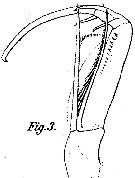 issued from : M. Dahl in Ergebnisse der Plankton-Expedition der Humboldt-Stiftung. Bd II, G. f1. I. Die Corycaeinen 1912. [TafV, Fig.3]. Male: 3, A2.
|
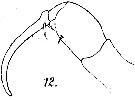 issued from : M. Dahl in Ergebnisse der Plankton-Expedition der Humboldt-Stiftung. Bd II, G. f1. I. Die Corycaeinen 1912. [Taf.IV, Fig.12]. Male: 12, Mxp.
|
 issued from : M. Dahl in Ergebnisse der Plankton-Expedition der Humboldt-Stiftung. Bd II, G. f1. I. Die Corycaeinen 1912. [Taf.IV, Figs.13, 14]. Male: 13, terminal portion of exopod of P1; 14, P4.
|
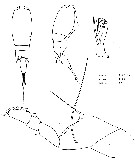 issued from : F. Cervigon iin Mem. Soc. Cienc. nat. La Salle, 1964, 24 (68). [p.176, Lam.8]. As Agetus typicus. Female (from Venezuela): 1-2, habitus (dorsal and lateral, respectively); 3, A2; 4, P4. Nota: Lengths ratio abdomen and caudal rami 56:44 and 60:40
|
 [O & F] Female: Caudal rami more than 1/2 the length of the urosome. Urosome conical in dorsal view. External edge of basipodite 2 of A2 serrated. Thoracic segment 4 very prominent in lateral view. Male: Eyes separated. Genital segment as long as the anal segment + caudal rami. [B & H] Female: Caudal ramus more than half length of urosome in dorsal view. Urosome slender, dorsal hump flattened (in lateral view). First endopodal segment of A2 toothed on outer margin. Male: Eyes clearly separated on frontal margin. Anal somite slightly longer than wide (in dorsal view) and combined with caudal rami, about equal in length to genital somite. [V & S] Female: Eyes clearly separated. Abdomen conical , not swollen foreward. Angles of the thoracic segment 4 (in lateral view) pointed toward dorsally. Basipodite 2 of A2 serrated on the outer margin. Male: Eyes separated. Anal segment (in dorsal view) scarcely longer than wide, and as maximum of length equal to caudal rami + genital segment. In lateral view, the genital segment shows salients dorsally and ventrally.
|
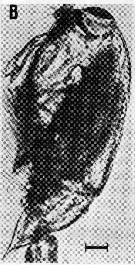 issued from : A. Ianora, B. Scotto di Carlo, M.G. Mazzocchi & P. Mascellaro in J. Plankton Res., 1990, 12 (2). [p.253, Fig.4, B]. Corycaeus typicus female (from Gulf of Naples, Italy) parasitized by the dinoflagellate Blastodinium, occasionally observed with infection rates of 1 % or less throughout the year.
|
 Issued from J.H. Wi, D.H. Kim & H.Y. Soh in Ocean Sci. J., 2013, 48 (4). [p.401, Fig.2]. As Agetus typicus. Female (from Jeju Island, S Korea): a, habitus (dorsal); B, urosome (lateral), C, caudal ramus (right side; caudal setae nulbering using Roman numerals); D, A1; E, A2; G, P5. Scale bars in µm. Nota : Prosome 4-segmented ; 1.9 times longer than urosome (including caudal ramus), 3.3 times urosome (excluding caudal ramus). - Frontal margin rounded, with 2 large separate cuticular lenses. - Cephalosome completely fused with 1st pedigerous somite. - 4th pedigerous somite consisting of long extended outer area and inner margin 1.2 times shorter than outer margin, with folds in dorsal view, and dorsally swollen in lateral view (indicated by arrow) . - Urosome 2-segmented. 1st urosomal somite bearing P5 ventrolaterally. Proportional lengths (%) of urosomites and caudal rami 5.2 : 50.9 : 43.9. 2nd urosomal somite rounded to anterior 2/3, widest and distal part irregular, showing folds in dorsal view (indicated by arrows), about twice as long as maximum width, dorsal margin protruded in mid-region and constricted in posterior quarter (indicated by arrow). - Genital double-somite and anal somite combined. - Caudal ramus sharply narrowed in anterior part in lateral view, about 1.2 times shorter than 2nd urosomal somite, 4.3 times longer than maximum width at base. Each ramus parallel, with slight space, armed with 6 setae : slender anterolateral seta II, outer posterolateral seta III short and robust and spiniform, outer terminal seta IV reduced and long inner terminal seta V, terminal accessoty seta VI short, and dorsal seta VII located on small pedestal, 1.5 times longer than seta III. - A1 short, 6-segmented. Proportional lengths (%) of segments measurd along posterior non-setigerous margin 15.7 : 10.9 : 15.0 : 28.1 : 18.7 : 10.9. - A2 4-segmented, coxa and basis fused and bearing 3 endopodal segments. Coxobasis 1.7 times longer than wide, with strong, naked seta at inner distal margin, and dorsal surface with row of minute spinules medially and laterally. Endopod 3-segmented, unequal in length : 1st segment robust, much longer than remander, 4.2 times as long as wide at base, bearing long unipinnate seta on inner proximal margin, 1.2 times shorter than coxobasal seta, inner distal margin formed into 2 stout teeth in different size, outer lateral margin an douter margin ornamented row of denticles and small teeth ; 2nd segment short, bearing 3 elements : curved stout pine arising from outer distal margin, small spine near its base, and blunt, curved spine arising from inner margin ; 3rd segment cylindrical, twice as long as wide at base, armed with curved terminal claw and 2 elements, short spine arising from outer distal margin and small blunt spine at inner base. - P5 consisting of 2 unequal simple setae, located ventrolaterally (fig.2G). - P6 represented by operculum closing off each genital aperture (fig.2A, B)
|
 Issued from J.H. Wi, D.H. Kim & H.Y. Soh in Ocean Sci. J., 2013, 48 (4). [p.403, Fig.3]. As Agetus typicus. Female: A, Md; B, Mx1; C, Mx2; D, Mx2 (medial element on allobasis); E, Mxp (arrow indicating protrusion on basis); F, P1; G, P2; H, P3; I, P4. Scale bars in µm. Md with 2 elements on gnathobase : 1 spine and 1 blade. Sine broad and robust, bicuspid, ventral side with 2 spines on proximal margin and ornamented with minute denticles on distal margin. Blade forming spinous process, surronded by patch of spinules around base. - Mx1 reduced, praecoxal arthrite bearing 4 articulated spinous elements : innermost one (A) at some distance of other elements, distal area pointed and fringed with fine spinules, element (B) longest and stout and distal margin with spinous process ; element (C) short, with spinous process on distal margin, and element (D) short and naked and almost equal to length of element (C) ; length ratios of elements about 64.7 : 100.0 : 55.9 : 41.2. - Mx2 2-segmented, syncoxa unarmed ; allobasis produced distally into strong spine, with naked 4 setae bilaterally, inner margin bearing 2 elements in different shape : 1 branched into comb-like spine and naked spine, other one forming long unipectinate spine, distally tapering. - Mxp 3-segmented : syncoxa unarmed ; basis robust and expanded, 1.8 times as long as width at base, with element ornamented with spinules along inner margin, located at anterior 2/3 of inner margin, 2.1 times shorter than width at base, with 2 rows of fine spinules along inner margin between element and anterior margin, and mid-lateral margin forming protrusion (indicated by arrow) ; endopodal segment drawn out into long curved claw, unornamented and longer than basis, accessory armature consisting of slender, unipinnate spines on inner proximal margin and lateral proximal margin of claw laterally, lateral one longer than inner one. - Exopods of P1 to P3 : inner margin of proximal segments fringed with long setules, relative length ratios of terminal spine to distal outer spine and distal segment of P1-P3 different : in P1 2 : 1 and 2.1 : 1 ; in P2 2.6 : 1 and 1.7 : 1 ; and in P3 4.1 : 1 and 1.2 : 1. - Endopods of P1 to P3 : outer margin of segment fringed with long setules ; distal segment of P2 longest and that of P3 shortest ; length ratio of distal segments of P1-P3 about 89.0 : 100.0 : 51.1. - P4 with transversally extended intercoxal sclerite narrow, coxa unarmed, basis with outer basal seta arising from the posterior surface ; exopod well developed, 3-segmented, bearing spinules along inner margin of proximal segment, bearing short spine on outer distal corner, 1.7 times shorter than spine on outer distal corner of distal segment, proportional length ratio of each segment 39.5 : 25.6 : 34.9, distal segment 1.9 times longer than terminal spine. Endopod reduced to knob-like segment, with long plumose terminal seta, 1/3 times shorter than basal seta.
|
 Issued from J.H. Wi, D.H. Kim & H.Y. Soh in Ocean Sci. J., 2013, 48 (4). [p.405, Fig.4]. As Agetus typicus. Male: A, habitus (dorsal); B, urosome (lateral); C, A2 (arrow indicating the rearmost denticle on lateral margin of 1st endopodal segment); D, Mxp; E, P1 (exopodal segment 3); F, P2 (exopodal segment 3); G, P3 (exopodal segment 3); H, P4 (intercoxal sclerite and coxa omitted); I, P6 and genital flap (arrow indicating small process at base of seta). Scale bars in µm. Nota : Prosome 3-segmented, cephalosome fused with 1st pedigerous somite, 3rs and 4th pzdigerus somites fused to one somite ; prosome about 1. 4 times as long as urosome including caudal ramus, about 2.1 times as long as urosome excluding caudal ramus - 3rd prosomal somite with outer and inner epimeral extensions : outer one extended and pointed distally, reaching to 2/5 from anterior margin of genital somite and inner one much shorter than outer one, with folds. - Frontal part of prosome round, with 2 large contiguous cuticular lenses located some distance of each other. - Genital somite oval, 1.7 times as long as maximum width at anterior mid-region. Genital area formed into flaps (derived from P6). - Anal somite rectangular-shaped, with 2 secretory pores at anterior surface, about 1.2 times as long as wide at base, distal margin ornamented with minute spinules ventrolaterally, and large opening dorsally placed, 3. 6 times shorter as long as genital somite. Caudal ramus 7 times longer than wide at base, aboit 1.8 times shorter as long as genital somite . Armature of caudal rami similar to that of female. - A1 with segmentation and armature similar to that of female. A2 sexually dimorphic, 4-segmented : coxobasis with long strong seta on inner distal margin, with cleft on tip ; endopod 3-segmented ; 1st segment about 3 times as long as width at bazse, with unipectinate seta on ventral proximal margin, with cleft on tip slightly shorter than coxobasal seta, inner distal margin ornamented with minute spinules, mid-ventral surface vertically ornamented with row of coarse teeth gradually increasing in length towards distal margin, distal teeth longest (indicated by arrow), outer lateral margin randomly ornamented with small denticles ; 2nd segment short, bearing 3 elements : curved stout spine arising from outer distal margin, with small spine at base, and spine arising from inner distal corner ; 3rd segment cylindrical, twice as long as wide at base, armed with 3 elements : slender naked seta on outer distal margin, spine arising from inner distal margin delimited to segment, 1.5 times longer than inner spine on 2nd segment, and terminal spine drawn out as long as claw, much linger than that of female. - Md, Mx1, Mx2 similar tothose of female. - Mxp sexually dimorphic. 4-segmented, comprising of syncoxa, basis and 2-segmented subchela. Syncoxa without surface ornamentation, unarmed ; basis robust, oval-shaped, 1.8 times as long as wide at base, inner margin fringed with 2 rows of spinules longitudinally, with naked spiniform seta located at anterior 45%, mid-lateral margin forming protrusion. Subchela comprising unarmed proximal endopodal segment and distal endopodal segment drawns out into long curved claw, with accessory armature consisted of slender, unipinnate spines on outer proximal and lateral margin, lateral one slightly longer than proximal one, distal endopodal segment extended over inner margin of syncoxa. - P5- P6 male represented by genital flap closing off each genital aperture; armed with long plumose seta, with small process at base (indicated by arrows in fig.4I), anterior surface irregularly ornamented with several rows of different sized spinules, with 2 secretory pores on mid-region.
|
 Issued from J.H. Wi, D.H. Kim & H.Y. Soh in Ocean Sci. J., 2013, 48 (4). [p.404, Table I]. As Agetus typicus. Female & Male: Armature formula of swimming legs P1 to P4. Nota: P1 to P3 in segmentation and armature similar , except in male for respective length ratios of terminal spine to distal segment and distal outer spine: in P1 1 : 1.19 and 1.6 : 1; in P2 1 : 1.7 and 2.3 : 1; and in P3 1 : 1.3 and 3 : 1. P4 similar, except length ratios in male of distal segment to terminal spine (2.7 : 1) and terminal spine to proximal outer spine (3 : 1) larger than those of female (1.7 : 1).
|
 Issued from J.H. Wi, D.H. Kim & H.Y. Soh in Ocean Sci. J., 2013, 48 (4). [p.406, Table 2]. As Agetus typicus. Female & Male: morphological characters. PR: prosome; UR: urosome; -CR: including CR; +CR: excluding CR: SUS/GS: 2nd urosomal somite/genital somite. Nota: Compare with Agetusflaccus and Agetus limbatus.
|
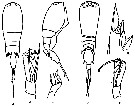 Issued from : F. Vives & A.A. Shmeleva in Fauna Iberica, 2010, 33. [p.202, Fig.189]. After Giesbrecht, 1892; Cervigon, 1964. Female: A-B, habitus (dorsal and lateral, respectively); C, A2; Male: D, habitus (dorsal); E, P5; F, A2; G, distal segment of P1 exopodite..
|
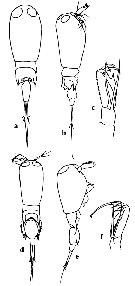 Issued from : M.G. Mazzocchi in Guida al Riconoscimento del plancton dei Mari Italiani, Vol. II, 2006. [p.126, Tav. 118]. Redrawn after Dahl, 1912. Female: a-b, habitus (dorsal and lateral, respectively); c, A2. Male: d-e, habitus (dorsal and lateral, respectively); f, A2.
| | | | | Ref. compl.: | | | Wilson, 1942 a (p.182); Massuti Alzamora, 1942 (p.16, Rem.); Sewell, 1948 (p.393, 434, 461); C.B. Wilson, 1950 (p.196); Fagetti, 1962 (p.54); V.N. Greze, 1963 a (tabl.2); Shmeleva, 1963 (p.141); Duran, 1963 (p.26); Björnberg, 1963 (p.85, Rem.); Unterüberbacher, 1964 (p.35); De Decker & Mombeck, 1964 (p.12); Pavlova, 1964 (p.1711); Shmeleva, 1965 b (p.1350, lengths-volume -weight relation); Furuhashi, 1966 a (p.295, vertical distribution in Kuroshio region, Table 9);Mazza, 1966 (p.74); Pavlova, 1966 (p.45); Ehrhardt, 1967 (p.744, geographic distribution, Rem.); Evans, 1968 (p.12); Dowidar & El-Maghraby, 1970 (p.268); Deevey, 1971 (p.224); Nival & al., 1972 (p.63, respiration); Apostolopoulou, 1972 (p.329, 382, fig.11); Vives & al., 1975 (tab.II); Boxshall, 1977 b (p.556); Vaissière & Séguin, 1980 (p.23, tab.1); Star & Mullin, 1981 (p.1322, abundance); Vives, 1982 (p.296); Kovalev & Shmeleva, 1982 (p.86); Guangshan & Honglin, 1984 (p.118, tab.); Scotto di Carlo & al., 1984 (p.1041); Tremblay & Anderson, 1984 (p.7: Rem.); Regner, 1985 (p.11, Rem.: p.42); Jansa, 1985 (p.108, Tabl.V); Lozano Soldevilla & al., 1988 (p.61); Ianora & al., 1990 (p.249, fig., parsitism effects); Hernandez- Trujillo, 1991 (1993) (tab.I); Webber & Roff, 1995 (tab.1); Shih & Young, 1995 (p.76); Hure & Krsinic, 1998 (p.94, 105); Alvarez-Cadena & al., 1998 (t.1,2); Suarez-Morales & Gasca, 1998 a (p.112); Lapernat, 1999 (p.32); Siokou-Frangou, 1999 (p.479); Escribano & Hidalgo, 2000 (p.283, tab.2); El-Sherif & Aboul Ezz, 2000 (p.61, Table 3: occurrence); Seridji & Hafferssas, 2000 (tab.1); Lopez-Salgado & al., 2000 (tab.1); Hidalgo & Escribano, 2001 (p.159, tab.2); Hidalgo & Escribano, 2001 (p.157, fig.4); Lapernat & Razouls, 2001 (tab.1); Vukanic, 2003 (p.139, tab.1); Lo & al., 2004 (p.89, tab.1); Vukanic & Vukanic, 2004 (p.9, tab.3); Isari & al., 2006 (p.241, tab.II); Escribano, 2006 (p.20, Table 1); Khelifi-Touhami & al., 2007 (p.327, Table 1); Zakaria, 2007 (p.238, Table 2, spatial distribution); Zakaria & al., 2007 (p.52, Table 1, vs Salinity); McKinnon & al., 2008 (p.648: Tble IV); Fernandes, 2008 (p.465, Tabl.2); Raybaud & al., 2008 (p.1765, Table A1); Lan Y.-C. & al., 2008 (p.61, Table 1, % vs stations); C.-Y. Lee & al., 2009 (p.151, Tab.2); Escribano & al., 2009 (p.1083, Table 1, figs.6, 10); C.E. Morales & al., 2010 (p.158, Table 1); Brugnano & al., 2010 (p.312, Table 2, 3, fig.8); Hernandez-Trujillo & al., 2010 (p.913, Table 2); Hidalgo & al., 2010 (p.2089, fig.2, , 4, Table 2, cluster analysis); Mazzocchi & Di Capua, 2010 (p.428); Hsiao S.H. & al., 2011 (p.475, Appendix I); Hsiao & al., 2011 (p.317, Table 2, indicator of seasonal change); Isari & al., 2011 (p.51, Table 2, abundance vs distribution); Andersen N.G. & al., 2011 (p.71, Fig.3: abundance); Selifonova, 2011 a (p.77, Table 1, alien species in Black Sea); Shiganova & al., 2012 (p.61, Table 4); Uysal & Shmeleva, 2012 (p.909, Table I); Salah S. & al., 2012 (p.155, Tableau 1); Zizah & al., 2012 (p.79, Tableau I, Rem.: p.86); in CalCOFI regional list (MDO, Nov. 2013; M. Ohman, pers. comm.); Lidvinov & al., 2013 (p.290, Table 2, % composition); Bonecker & a., 2014 (p.445, Table II: frequency, horizontal & vertical distributions); Mazzocchi & al., 2014 (p.64, Table 3, 4, occurrence); Fierro Gonzalvez, 2014 (p.1, Tab. 3, 4, 5, occurrence, abundance); Marquez-Rojas & al., 2014 (p.4, Rem.); Zakaria, 2014 (p.3, Table 1, abundance vs. 1960-2000); Zaafa & al., 2014 (p.67, Table I, occurrence); Dias & al., 2015 (p.483, Table 2, abundance, biomass, production); Rojas-Herrera & al., 2016 (p.40, Table 2: temporal abundance); Benedetti & al., 2016 (p.159, Table I, fig.1, functional characters); Benedetti & al., 2018 (p.1, Fig.2: ecological functional group); Palomares-Garcia & al., 2018 (p.178, Table 1: occurrence) | | | | NZ: | 16 + 1 douteuse | | |
|
Carte de distribution de Corycaeus (Agetus) typicus par zones géographiques
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | 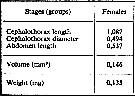 issued from : A.A. Shmeleva in Bull. Inst. Oceanogr., Monaco, 1965, 65 (n°1351). [Table 6: 45]. Corycaeus typicus (from South Adriatic). issued from : A.A. Shmeleva in Bull. Inst. Oceanogr., Monaco, 1965, 65 (n°1351). [Table 6: 45]. Corycaeus typicus (from South Adriatic).
Dimensions, volume and Weight wet. Means for 50-60 specimens. Volume and weight calculated by geometrical method. Assumed that the specific gravity of the Copepod body is equal to 1, then the volume will correspond to the weight. |
| | | | Loc: | | | South Africa (E), Namibia, off SE St. Helena Is., off Trinidade Is., Cape Verde Is., Canary Is., Mauritania-Morocco, Moroccan coast, Cap Ghir, off Madeira, Brazil (Campos Basin, ...), Barbada Is., Caribbean Sea, Bahia de Mochima (Venezuela), Jamaica, Yucatan, Venezuela, Cariaco Gulf, Caribbean, G. of Mexico, Sargasso Sea, off Bermuda, off Woods Hole, off SE Nova Scotia, Flemish Cap, Portugal, Ibero-moroccan Bay, off W Tangier, Medit. (Alboran Sea, Habibas Is., Gulf of Annaba, El Kala shelf, Baleares, Algiers, Banyuls, G. of Lion, Marseille, Ligurian Sea, Napoli, Tyrrhenian Sea, Strait of Messina, Gulf of Taranto, Malta, Adriatic Sea, Ionian Sea, Aegean Sea, Thracian Sea, Black Sea, Lebanon Basin, Lebanon, W Egyptian coast, Alexandria), Sharm El-Sheikh, Taba, Hurgada, Safaga, Red Sea, Indian, Madagascar, Rodrigues Is., Bay of Bengal, Indonesia-Malaysia, Philippines, Viet-Nam, China Seas (East China Sea, South China Sea), Luzon Strait, Taiwan Strait, Taiwan (E, NW), Mienhua Canyon, S Korea (Jeju Is.); Japan, Bering Sea (in C.B. Wilson, 1950), Pacif. (W equatorial), Australia (Great Barrier, North West Cape), New Caledonia, Pacif. (equatorial), Pacif. (N Central Gyre), Fidji Is., off N Hawaii, off W California, W & S Baja California (Bahia Magdalena, La Paz), Acapulco Bay, Chile (N, Concepcion), off Chile | | | | N: | 171 | | | | Lg.: | | | (34) F: 1,59-1,57; M: 1,49-1,41; (35) F: 1,37; (45) F: 1,65-1,45; M: 1,4-1,3; (46) F: 1,55-1,45; (107) F: 1,61-1,5; M: 1,54-1,5; (180) F: 1,7-1,62; M: 1,53-1,44; (237) M: 1,5; (327) F: 1,8-1,75; M: 1,56-1,27; (340) F: 1,6; M: 1,5; (432) F: 1,62-1,55; (449) F: 1,65-1,62; M: 1,62-1,27; (531) F: 1,3; (666) F: 1,65-1,62; M: 1,42; (667) F: 1,8-1,57; M: 1,6-1,55; (668) F: 1,64-1,57; (670) F: 1,78-1,63; M: 1,55-1,48; (991) F: 1,45-1,65; M: 1,3-1,54; (1150)* F: 1,59-1,60; M: 1,56-1,57; {F: 1,30-1,80; M: 1,27-1,62}
* Total body length in lateral view | | | | Rem.: | épi-mésopélagique, 2000-3000 m (off Malte).
Cette espèce essentiellement tropicale ne semble pas dépasser les 40 ème degrés de latitude nord et sud.
The occurrence in the Bering sea is surprising.
Voir aussi les remarques en anglais | | | Dernière mise à jour : 25/10/2022 | |
|
|
 Toute utilisation de ce site pour une publication sera mentionnée avec la référence suivante : Toute utilisation de ce site pour une publication sera mentionnée avec la référence suivante :
Razouls C., Desreumaux N., Kouwenberg J. et de Bovée F., 2005-2026. - Biodiversité des Copépodes planctoniques marins (morphologie, répartition géographique et données biologiques). Sorbonne Université, CNRS. Disponible sur http://copepodes.obs-banyuls.fr [Accédé le 06 janvier 2026] © copyright 2005-2026 Sorbonne Université, CNRS
|
|
 |
 |