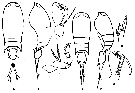|
|
 |
Fiche d'espèce de Copépode |
|
|
Cyclopoida ( Ordre ) |
|
|
|
Corycaeidae ( Famille ) |
|
|
|
Corycaeus ( Genre ) |
|
|
|
Ditrichocorycaeus ( Sous-Genre ) |
|
|
| |
Corycaeus (Ditrichocorycaeus) anglicus Lubbock, 1857 (F,M) | |
| | | | | | | Syn.: | Corycäus anglicus : Giesbrecht, 1892 (p.660, 674);
Ditrichocorycaeus anglicus : Boxshall & Halsey, 2004 (p.495, p.492: figs.F); Valdés & al., 2007 (p.104: tab.1); Cabal & al., 2008 (289, Table 1); Vidjak & Bojanic, 2009 (p.433, Table II, IV, V); Eloire & al., 2010 (p.657, Table II, temporal variability); Vives & Shmeleva, 2010 (p.212, figs.F,M, Rem.); Bode & al., 2012 (p.108, spatial distribution vs time-series, % biomass); Belmonte & al., 2013 (p.222, Table 2, abundance vs stations); El Arraj & al., 2017 (p.272, table 2); Richirt & al., 2019 (p.3, Table 1, fig.2, 3, 4, 5, abundance changes vs years 1998-2014, table 2: diversity index) | | | | Ref.: | | | Bourne, 1889 (p.151); F. Dahl, 1894 (p.71); M. Dahl, 1912 (p.56, figs.F,M); Sars, 1918 (p.196, figs.F,M); Pesta, 1920 (p.646); ? Farran, 1926 (p.298, Rem.F); Rose, 1929 (p.70); Candeias, 1932 (p.7, Rem. M); Rose, 1933 a (p.332, figs.F,M); Dakin & Colefax, 1940 (p.115, figs.M); Cervigon, 1964 (p.192, figs.F,M, Rem.); Vilela, 1965 (p.15, figs.F); 1968 (p.38, figs.F); Razouls, 1972 (p.96, Annexe: p.129, figs.F,M); 1974 c (1975) (p.92, figs.F,M); Dawson & Knatz, 1980 (p.10, figs.F,M); Gophen & Harris, 1981 (p.391, figs. eye structures, visual predation) | 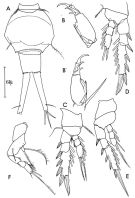 issued from : C. Razouls in Vie Milieu, 1974, 24 (1.A). [p.110, Fig.12]. Female (from W Medit.: Banyuls, France): A, 5th thoracic segment and abdominal segments (dorsal); B-B', A2; C, P1; D, P2; E, P3; F, P4.
|
 issued from : C. Razouls in Vie Milieu, 1974, 24 (1.A). [p.111, Fig.13]. Male: A, 5th thoracic segment and abdominal segments (dorsal); B-B', A2.
|
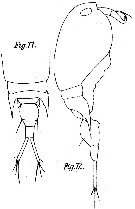 issued from : M. Dahl in Ergebnisse der Plankton-Expedition der Humboldt-Stiftung. Bd II, G. f1. I. Die Corycaeinen 1912. [Taf.IX, Figs.11, 12]. Female: 11, distal part of prosome and urosome (dorsal); 12, habitus (lateral right side).
|
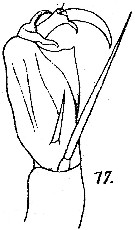 issued from : M. Dahl in Ergebnisse der Plankton-Expedition der Humboldt-Stiftung. Bd II, G. f1. I. Die Corycaeinen 1912. [Taf.IX, Fig.17]. Female: A2.
|
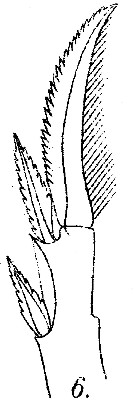 issued from : M. Dahl in Ergebnisse der Plankton-Expedition der Humboldt-Stiftung. Bd II, G. f1. I. Die Corycaeinen 1912. [Taf.IX, Fig.6]. Female: 6, terminal part of exopod of P2.
|
 issued from : M. Dahl in Ergebnisse der Plankton-Expedition der Humboldt-Stiftung. Bd II, G. f1. I. Die Corycaeinen 1912. [Taf.IX, Fig.9. Female: 9, P4
|
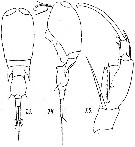 issued from : M. Dahl in Ergebnisse der Plankton-Expedition der Humboldt-Stiftung. Bd II, G. f1. I. Die Corycaeinen 1912. [Taf.IX, Figs.13, 14, 15]. Male: 13, habitus (dorsal); 14, idem (lateral left side); 15, A2.
|
 issued from : M. Dahl in Ergebnisse der Plankton-Expedition der Humboldt-Stiftung. Bd II, G. f1. I. Die Corycaeinen 1912. [Taf.IX, Fig.30]. Male: 30, terminal part of exopod of P1.
|
 issued from : F. Cervigon iin Mem. Soc. Cienc. nat. La Salle, 1964, 24 (68). [p.195, Lam.22]. As Ditrichocorycaeus anglicus. Female (from Venezuela): 1, habitus (dorsal); 2, abdomen (lateral, right side); 3, A2; 4, exopod 3 of P2; 5, exopod 3 of P3; 6, P4. Nota: length prosome: 0.56; length urosome: 0.25. Lengths ratio genital , anal segments and caudal rami 44:16:40 and 43.4:17.3:39.1.
|
 issued from : F. Cervigon iin Mem. Soc. Cienc. nat. La Salle, 1964, 24 (68). [p.196, Lam.23]. As Ditrichocorycaeus anglicus. Male: 1-2, habitus (dorsal and lateral, respectively); 3, A2; 4, P4. Nota: Length prosome: 0.44; length urosome: 0.25. Lengths ratio genital , anal segments and caudal rami 60:16:24.
|
 issued from : G.O. Sars in An Account of the Crustacea o Norway, 1918, VI. [Pl. CX]. Female (from W coast of Norway, Christiania Fjord). m = Md + Mx1; m.exp = Mx1; mp1 = Mx2; mp2 = Mxp; F = caudal ramus
|
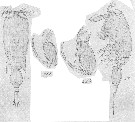 issued from : G.O. Sars in An Account of the Crustacea o Norway, 1918, VI. [Pl. CIX, 2]. Male. mp2 = Mxp.
|
 [B & H] Female: Caudal rami at most as long as genital double-somite. Anal somite a little longer than width at base. Outer distal margin of first endopodal segment of A2 with 1 tooth. [V & S] Female: Posterior points of thoracic segment 3, in dorsal view, scarcely reaching half genital segment. Basipodite 2 of P4 with the two setae divergent. Spine of basipodite 2 of A2 reaching half of spine of basipodite 1. Male: Posterior points of thoracic segment 3 shorter than 2/3 genital segment. Genital segment length equal to anal segment plus caudal rami.
|
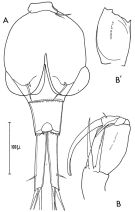
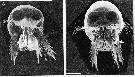 issued from : M. Gophen & R.P. Harris in J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K., 1981, 61. [p.393, Fig.1]. Scanning electron micrographs of anterior view of male (A) and female (B) Corycaeus anglicus (from off Plymouth) showing the paired eyes. Scale bar = 0.100 mm. Nota: For the authors, Corycaeus is considered to be an unspecialized raptorial carnivore (cf. Wickstead, 1962)
|
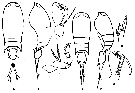 Issued from : F. Vives & A.A. Shmeleva in Fauna Iberica, 2010, 33. [p.213, Fig.95]. After G.O. Sars, 1925. Female: A-B, habitus (dorsal and lateral, respectively); C, A2; D, P4. Male: E-F, habitus (dorsal and lateral, respectively); G, A2; H, distal segment of P1 exopodite .
| | | | | Ref. compl.: | | | Pearson, 1906 (p.33); Wilson, 1942 a (p.180); Sewell, 1948 (p.393, 406); Fleury, 1950 (p.47, fig.2); Bodo & al., 1965 (p.219, annual cycle); Mazza, 1966 (p.74); 1967 (p.326); Harder, 1968 (p156, Table 1, behaviour vs. density discontinuity); Shih & al., 1971 (p.155, 214); Paulmier, 1971 (p.168); Frolander & al., 1973 (p.277, annual cycles); Laval, 1974 (p.57, Rem.: p.78, avoidance); Peterson & Miller, 1975 (p.642, 650, Table 3, interannual abundance); Vives & al., 1975 (p.58, tab.II, IV); Peterson & Miller, 1976 (p.14, Table 1, 2, 3, abundance vs interannual variations); 1977 (p.717, Table 1, seasonal occurrence); Pipe & Coombs, 1980 (p.223, Table II, vertical occurrence); Star & Mullin, 1981 (p.1322, abundance); Gophen, 1981 (p.391, visual predation); Gallo, 1981 (p.847); Vives, 1982 (p.296); Kovalev & Shmeleva, 1982 (p.86); Castel & Courties, 1982 (p./417, Table II, fig.4, spatial & monthly distribution); Tremblay & Anderson, 1984 (p.7, Rem.); Kleppel & Pieper, 1984 (p.193, gut contents); Regner, 1985 (p.11, Rem.: p.43); Landry al., 1985 (p.163); Brinton & al., 1986 (p.228, Table 1); Lewis & Thomas, 1986 (p.1079, tidal transport); Brylinski, 1986 (p.457, spatial variations); Quisthoudt & al., 1987 (p.995, spatial distribution); Dey & al., 1988 (p.321, 323, UV-B effect); Lozano Soldevilla & al., 1988 (p.61); Landry & Fagerness, 1988 (p.509, Table 1, 3, 5, 6, fig.1, 4, 5, 7, 9, grazing vs behaviour & morphology); Fransz & al., 1991 (p.11); Hays & al., 1994 (tab.1); Krause & al., 1995 (p.81, Fig.36, abundance, Rem.: p.141); Suarez-Morales & Gasca, 1998 a (p.112); Hure & Krsinic, 1998 (p.105); Gomez-Gutiérrez & Peterson, 1999 (p.637, Table II, abundance); Logerwell & Ohman, 1999 (p.428, tab.1); El-Sherif & Aboul Ezz, 2000 (p.61, Table 3: occurrence); d'Elbée, 2001 (tabl. 1); Peterson & al. 2002 (p.381, Table 2, fig.6, interannual abundance); Peterson & Keister, 2003 (p.2499, interannual variability); Keister & Peterson, 2003 (p.341, Table 1, 2, abundance, cluster species vs hydrological events); Bonnet & Frid, 2004 (p.485, fig.5); Zamon & Welch, 2005 (p.133, 139, fig.5); Lavaniegos & Jiménez-Pérez, 2006 (p.140, tab.2, Rem.); Hooff & Peterson, 2006 (p.2610); Knotz & al., 2006 (p.406, enzymology); Humphrey, 2008 (p.84: Appendix A); Galbraith, 2009 (pers. comm.); Brylinski, 2009 (p.253: Tab.1, p.257: Rem.); Mazzocchi & Di Capua, 2010 (p.428); Bollens & al., 2011 (p.1358, Table III); S.C. Marques & al., 2011 (p.59, Table 1); Fileman & al., 2011 (p.403, abundance vs bloom condition); Keister & al., 2011 (p.2498, interannual variation); Van Ginderdeuren & al., 2012 (p.3, Table 1); DiBacco & al., 2012 (p.483, Table S1, ballast water transport); Takahashi M. & al., 2012 (p.393, Table 2, water type index); Gusmao & al., 2013 (p.279, Table 3, sex-specific predation by fish); in CalCOFI regional list (MDO, Nov. 2013; M. Ohman, comm. pers.); Sobrinho-Gonçalves & al., 2013 (p.713, Table 2, fig.8, seasonal abundance vs environmental conditions); Lidvanov & al., 2013 (p.290, Table 2, % composition); Benedetti & al., 2016 (p.159, Table I, fig.1, functional characters); Palomares-Garcia & al., 2018 (p.178, Table 1: occurrence); | | | | NZ: | 13 | | |
|
Carte de distribution de Corycaeus (Ditrichocorycaeus) anglicus par zones géographiques
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | 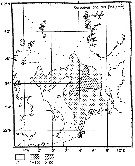 Issued from : M. Krause, J.W. Dippner & J. Beil in Prog. Oceanogr., 1995, 35. [p.123, Fig.36]. Issued from : M. Krause, J.W. Dippner & J. Beil in Prog. Oceanogr., 1995, 35. [p.123, Fig.36].
Horizontal distribution pattern of Corycaeus anglicus (individuals per m2) in the winter North Sea.
Collected by WP2-net. Numbers (ind/m3) depth-integrated, extrapoled to the bottom (but at a maximum to a depth of 500 m) and expressed as ind per m2 of water surface. |
 Issued from : W.T. Peterson, J.E. Keister & L.R. Feinberg in Prog. Oceanogr., 2002, 54. [p.393, Fig.8]. Issued from : W.T. Peterson, J.E. Keister & L.R. Feinberg in Prog. Oceanogr., 2002, 54. [p.393, Fig.8].
Abundance (number per cubic meter) of Corycaeus anglicus at the station NH5 (off Newport, Oregon, at depth 30 m) from May 1996 through September 1999.
Compare with Calanus marshallae and Pseudocalanus mimus at the same station during El Niño event in 1997-98, the largest of the century. |
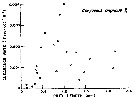 Issued from : M.R. Landry & V.L. Fagerness in Bull. Mar. Sc., 1988, 43 (3) [p.512, Fig.2]. Issued from : M.R. Landry & V.L. Fagerness in Bull. Mar. Sc., 1988, 43 (3) [p.512, Fig.2].
Clearance rates of Corycaeus anglicus feeding on naupliar (closed circles) and copepodid stages (open circles).
Data from Landry & al. (1985). |
 Issued from : M.R. Landry & V.L. Fagerness in Bull. Mar. Sc., 1988, 43 (3) [p.514, Table 3]. Issued from : M.R. Landry & V.L. Fagerness in Bull. Mar. Sc., 1988, 43 (3) [p.514, Table 3].
Comparison of size of body and appendages for seven species of marine copepods. Relationships among predation rates, selection patterns, swimming speed and orientation, and morphology of prey sensory and capture appendages. |
 Issued from : M.R. Landry & V.L. Fagerness in Bull. Mar. Sc., 1988, 43 (3) [p.520, Fig. 9]. Issued from : M.R. Landry & V.L. Fagerness in Bull. Mar. Sc., 1988, 43 (3) [p.520, Fig. 9].
Swimming speeds and directions of the copepods Tortanus discaudatus, Corycaeus anglicus, Oithona spinifera (= Oithona setigera). See also to Neocalanus cristatus, Euchaeta elongata (= Paraeuchaeta elongata), Calanus pacificus.
Swimming speeds measured as displacement over 2-s time intervals. 0° is up.
Study of the relationships among predation rates, selection patterns, swimming speed and orientation, and morphology of prey sensory and capture appendages.
The mean relative swimming speeds (S) of the predatory copepods and their preferred prey were calculated by the equation (Gerritsen, 1980).
S = [u + v)3 - [u - v)3 / 6uv.
u and v are respectively, the mean swimming speeds (mm/s) of the prey and the predator. |
 Issued from : M.R. Landry & V.L. Fagerness in Bull. Mar. Sc., 1988, 43 (3) [p.522-523, Table 5]. Issued from : M.R. Landry & V.L. Fagerness in Bull. Mar. Sc., 1988, 43 (3) [p.522-523, Table 5].
Comparison of the predatory characteristics of seven planktonic marine copepods.
F max is the mean, maximum clearance rate measured for the predator feeding on its preferred prey. Prey are developmental stages of common species of planktonic copepods.
F = female, M = male, C5 = stage 5. |
 Issued from : M.R. Landry & V.L. Fagerness in Bull. Mar. Sc., 1988, 43 (3) [p.524, Figs.10-11]. Issued from : M.R. Landry & V.L. Fagerness in Bull. Mar. Sc., 1988, 43 (3) [p.524, Figs.10-11].
Fig. 10: Relationship between optimal prey length and length of the second maxillae (Mx2) of predatory marine copepods.
Fig 11: Relationships between maximum clearance rate (F max = liters/day) and mean predator swimming speed (S = mm/s) for predatory marine copepods. |
 Issued from : M.R. Landry & V.L. Fagerness in Bull. Mar. Sc., 1988, 43 (3) [p.525, Table 6]. Issued from : M.R. Landry & V.L. Fagerness in Bull. Mar. Sc., 1988, 43 (3) [p.525, Table 6].
Relationships between swimming speeds of predators and their preferred prey and ratios of maximum clearance rates for seven species of marine copepods. |
| | | | Loc: | | | off Morocco-Mauritania, Canary Is., off Madeira, Portugal, Mondego estuary), NW Spain, Ibero-moroccan Bay, Medit. (Alboran Sea, Castellon, Banyuls, Ligurian Sea, Tyrrhenian Sea, Gulf of Taranto, Taranto Harbour, Adriatic Sea, Lebanon Basin), N Red Sea (Sharm El-Sheikh, Safaga), Caribbean Sea, N Hudson Bay (in Wilson, 1936 d), Flemish Cap, off S Newfoundland, Bay of Biscay, Arcachon Bay, Gironde estuary, La Pallice roadstead, Belon estuary, W Ireland, off SW Ireland, Celtic Sea, English Channel, Roscoff, Pas de Calais, North Sea, Norway, Wyville Thomson Ridge, E Siberia, S Kuril Is. (in Kos, 1960), Puget Sound, Vancouver Is., Friday Harbor, off Washington coast, Oregon (Yaquina Bay, off Newport), California (San Francisco Estuary, San Pedro Bay), W BaJa California, La Paz, Gulf of California, W Mexico, Pacif. (central), China Seas (East China Sea: inW. Zhang & al., 2010), Australia (New South Wales) | | | | N: | 90 | | | | Lg.: | | | ? (38) F: 1,1; M: 0,88; (104) M: 0,9; (133) F: 1; (327) F: 1,19-1,04; M: 1,02-0,87; (373) F: 1,13-0,91; M: 0,97-0,76; (666) F: 1,147; M: 0,95-0,87; (668) F: 0,81; M: 0,69; (1259) M: 0,8; (1302) F: 0,633-0,686; M: 0,535-0,550; {F: 0,633-1,190; M: 0,540-1,020}.
(1259) M: 0,8 (total length), 0,53 (prosome length) ; A1 = 0,12 mm. (total length). | | | | Rem.: | épipélagique.
Gardner & Szabo, 1982 (p.98) considèrent C. affinis comme synonyme junior de cette espèce.
Voir aussi les remarques en anglais | | | Dernière mise à jour : 21/10/2022 | |
|
|
 Toute utilisation de ce site pour une publication sera mentionnée avec la référence suivante : Toute utilisation de ce site pour une publication sera mentionnée avec la référence suivante :
Razouls C., Desreumaux N., Kouwenberg J. et de Bovée F., 2005-2026. - Biodiversité des Copépodes planctoniques marins (morphologie, répartition géographique et données biologiques). Sorbonne Université, CNRS. Disponible sur http://copepodes.obs-banyuls.fr [Accédé le 01 février 2026] © copyright 2005-2026 Sorbonne Université, CNRS
|
|
 |
 |