|
|
 |
Fiche d'espèce de Copépode |
|
|
Cyclopoida ( Ordre ) |
|
|
|
Corycaeidae ( Famille ) |
|
|
|
Farranula ( Genre ) |
|
|
| |
Farranula rostrata (Claus, 1863) (F,M) | |
| | | | | | | Syn.: | Corycaeus rostratus Claus, 1863 (p.157); Thompson, 1900 c (p.291); Thompson & Scott, 1903 (p.239, 285); Wolfenden, 1911 (p.360); Chatton, 1920 (p.18, parasited); Rose, 1925 (p.153); Wilson, 1932 (p.42); Tanaka, 1964 (p.17); 1965 a (p.21); Senô & al., 1966 (p.5); Halim, 1969 (tab.24); Kim & al., 1993 (p.271); Park & Choi, 1997 (Appendix); Noda & al., 1998 (p.55, Table 3, occurrence); Vukanic & Vukanic, 2004 (p.9, tab. 2, 3); Skovgaard & Salomonsen, 2009 (p.425, Table 2); Maiphae & Sa-ardrit, 2011 (p.641, Table 2, 3, Rem.)
C. pellucidus : Brady, 1883 (part., p.112, Pl. 52, figs.15-18);
Corycäus rostratus : Giesbrecht, 1892 (p.660, 674, 772, figs.F,M); Brian, 1914 a (p.139); Sewell, 1948 (p.357);
Corycella rostrata : Farran, 1929 (p.211, 297); Rose, 1929 (p.72); 1933 a (p.336, figs.F,M); Klevenhusen, 1933 a (p.84, carte 35); Dakin & Colefax, 1940 (p.110, figs.F,M); Massuti Alzamora, 1942 (p.107, Rem.); Moore, 1949 (p.64); Zavodnik, 1961 (p.69, figs.); 1961 a (p.203); Giron-Reguer, 1963 (p.61); V.N. Greze, 1963 a (tabl.2); Shmeleva, 1963 (p.141); Björnberg, 1963 (p.86, Rem.); Unterüberbacher, 1964 (p.36); De Decker, 1964 (p.15); De Decker & Mombeck, 1964 (p.12); Shmeleva, 1965 b (p.1350, lengths-volume -weight relation); El-Maghraby, 1965 (p.58, Appendix); Pavlova, 1966 (p.45); Mazza, 1966 (p.74); 1967 (p.367, 377); Ehrhardt, 1967 (p.744, geographic distribution, Rem.); Evans, 1968 (p.12); Delalo, 1968 (p.139); Vinogradov, 1968 (1970) (p.268); Dowidar & El-Maghraby, 1970 (p.268); Jillett, 1971 (p.30, 32, 57); Apostolopoulou, 1972 (p.329, 389); Binet & al., 1972 (p.71); Desgouille, 1973 (p.1, 131, Rem.: p.134); Vaissière & Séguin, 1980 (p.23, tab.2); Kovalev & Shmeleva, 1982 (p.86); Sazhina, 1985 a (p.491, tab.3); Moraitou-Apostolopoulou, 1985 (p.303, occurrence/abundance in E Mediterranean Sea, Rem.: p.310); Regner, 1985 (p.11, Rem.: p.44); Jansa, 1985 (p.108, Tabl.I, II, III, IV, V); Pancucci-Papadopoulou & al., 1990 (p.199); Zerouali & Melhaoui, 2002 (p.91, Tableau I, fig.5); Hidalgo & al., 2010 §p.2089, fig.4, cluster analysis); Selifonova, 2011 a (p.77, Table 1, alien species in Black Sea); Gubanova & al., 2013 (in press, p.4, Table 2);Zaafa & al., 2014 (p.67, Table I, occurrence);
Corycaeus (Corycella) rostratus : M. Dahl, 1912 (p.111, figs.F,M); Pesta, 1920 (p.648, fig.F); Dakin & Colefax, 1933 (p.209); Sewell, 1948 (p.393, 435, 461); Tanaka, 1957 (p.96, figs.M, Rem.); 1960 (p.90, figs.F,M); Vilela, 1965 (p.16); Vukanic, 2003 (p.139, tab.1); Drira & al., 2010 (p.145, Tabl.2);
Non Corycaeus (Corycella) rostratus : Chen & al., 1974 (p.65, figs.F,M); ? Guangshan & Honglin, 1984 (p.118, tab.); ? Shih & Young, 1995 (p.76);
Corycaeus (Farranula) rostrata : Böttger-Schnack, 1988 (p.313, 315); 1989 (p.1093, 1094);
Corycaeus rostrata : Scotto di Carlo & al., 1984 (p.1041) | | | | Ref.: | | | Owre & Foyo, 1967 (p.124, figs.F,M); Vilela, 1968 (p.41); Corral Estrada, 1970 (p.249); Björnberg, 1972 (p.95, fig.N, Rem.N); Razouls, 1972 (p.96, Annexe: p.137); Björnberg, 1973 (p.368, 386); Razouls, 1974 c (1975) (p.94); Björnberg & al., 1981 (p.677, figs.F,M); Lakkis & Zeidane, 1987 (p.15, figs.F,M, Rem.); Chihara & Murano, 1997 (p.967, Pl.219: F,M); Boxshall, 1998 (p.224); Bradford-Grieve & al., 1999 (p.888, 975, figs.F,M); Boxshall & Halsey, 2004 (p.493); Avancini & al., 2006 (p.151, Pl. 119, figs.F,M, Rem.); Vives & Shmeleva, 2010 (p.228, figs.F,M, Rem.); Wi & Soh, 2013 (p.1, Rem., p.22, Table 1) | 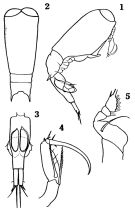 issued from : O. Tanaka in J. Fac. Agricult. Kyushu Univ., 1957, 11 (1). [Pl.10, Figs.1-5]. As Corycaeus (Corycella) rostratus. Male (from Pacific coast of Japan): 1, habitus (lateral right side); 2, cephalothorax (dorsal); 3, urosome (ventral); 4, A2; 5, P4. Nota: Furcal rami 3 times as long as wide.
|
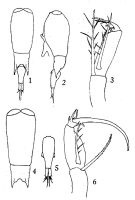 issued from : Q.-c Chen & S.-z. Zhang & C.-s. Zhu in Studia Marina Sinica, 1974, 9. [Pl.22, Figs.1-6]. As Corycaeus (Corycella) rostratus; Female (from China Seas): 1, habitus (dorsal); 2, idem (lateral left side); 3, A2. Male: 4, prosome (dorsal); 5, urosome; 6, A2. Non = F. orbisa after Wi & Soh, 2013 (p.1814)
|
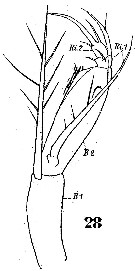 Issued from : W. Giesbrecht in Systematik und Faunistik der Pelagischen Copepoden des Golfes von Neapel und der angrenzenden Meeres-Abschnitte. – Fauna Flora Golf. Neapel, 1892. Atlas von 54 Tafeln. [Taf.49, Fig.28]. As Corycäus rostratus. Female: 28, A2. B = basipod; Ri = endopod.
|
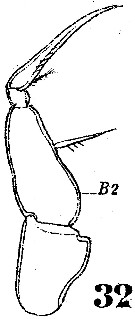 Issued from : W. Giesbrecht in Systematik und Faunistik der Pelagischen Copepoden des Golfes von Neapel und der angrenzenden Meeres-Abschnitte. – Fauna Flora Golf. Neapel, 1892. Atlas von 54 Tafeln. [Taf.49, Fig.32]. As Corycäus rostratus. Male: 32, Mxp.
|
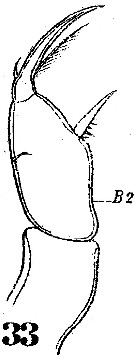 Issued from : W. Giesbrecht in Systematik und Faunistik der Pelagischen Copepoden des Golfes von Neapel und der angrenzenden Meeres-Abschnitte. – Fauna Flora Golf. Neapel, 1892. Atlas von 54 Tafeln. [Taf.49, Fig.33]. As Corycäus rostratus. Female: 33, Mxp.
|
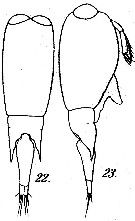 issued from : M. Dahl in Ergebnisse der Plankton-Expedition der Humboldt-Stiftung. Bd II, G. f1. I. Die Corycaeinen 1912. [Taf.XIV, Figs.22, 23]. As Corycaeus (Corycella) rostratus. Female; 22, habitus (dorsal); 23, idem (lateral right side).
|
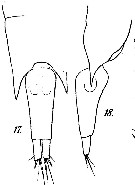 issued from : M. Dahl in Ergebnisse der Plankton-Expedition der Humboldt-Stiftung. Bd II, G. f1. I. Die Corycaeinen 1912. [Taf.XV, Figs.17, 18]. As Corycaeus (Corycella) rostratus. Female: 17, posterior part of metasome and urosome (dorsal); 18, idem (lateral left side).
|
 Female: Urosome about 4 times as long as the caudal rami and, in lateral view, it tapers posteriorly rather regularly from its broad base. Male: Urosome over 3 times as long as the caudal rami; rami at most only 2 times as long as broad.
|
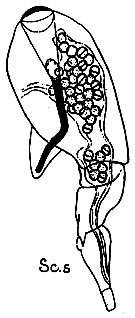 issued from : G. Trégouboff & M. Rose in Manuel de planctonologie méditerranéenne, 1957, CNRS, Paris. [Pl. 125]. As Corycella rostrata (from Meditrerranean Sea). Schizodinium aparsum (Sc.s) in the copepod's gut.
|
 Issued from : J.H. Wi & H.Y. Soh in J. Nat. Hist., 2013. [p.3, Table I]. Length and width proportions of body segments of Farranula rostrata. Nota: Compare with other species of Farranula (on line: http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/00222933.2012.708454).
|
 Issued from : O. Tanaka in Spec. Publs. Seto mar. biol. Lab., 10, 1960 [Pl. XXXIX, 5-7]. As Corycaeus (Corycella) rostratus. Female (from Indian Ocean): 5, habitus (lateral); 6, abdomen (dorsal); 7, same (lateral). Nota: Cephalothorax and abdomen in the proportional lengths 70 to 30. Abdominal segment and caudal rami in the proportional lengths 73 to 27. Genital segment 2 times as long as broad; ventral pad setose. Caudal rami 3 times as long as broad.
|
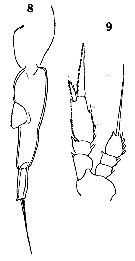 Issued from : O. Tanaka in Spec. Publs. Seto mar. biol. Lab., 10, 1960 [Pl. XXXIX, 8-9]. As Corycaeus (Corycella) rostratus. Male: 8, abdomen (lateral); 9, P1. Nota: Cephalothorax and abdomen in the proportional lengths 65 to 35. Abdominal segment and caudal rami in the proportional lengths 75 to 25. The distal 1/3 of the genital segment narrow, about half as broad as it is broad at the middle section. Caudal rami 3.5 times as long as broad.
|
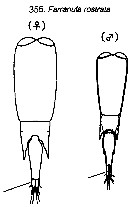 Issued from : M. Chihara & M. Murano (eds) inAn illustrated Guide to the Marine Plankton in Japan, 1997. [p.977, Pl. 219, fig.355]. Female (After Dahl, 1912): habitus (dorsal). Male: habitus (dorsal). Note the length of caudal rami (very short by comparison with the other species of farranula).
|
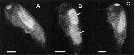 Issued from : C. Alves-da-Souza, C. Cornet, A. Nowaczyk, S. Gasparini, A. Skovgaard & L. Guillou in Biogeosciences, 2011, 8. [p.2130, Fig.2 A-C]. Observation of Blastodinium spp. located inside the gut of their host: Farranula rostrata. At least two individuals (arrows) of an unknown Blastodinium with a globular shape.
|
 Issued from : E. Chatton in Arch. Zool. Exp. & Gen., 1920, 59, [Pl. IV, 40]. As Corycaeus rostratus. Farranula rostrata female (from Banyuls), with stomach filled in by numerous sporocytes of Schizodinium sparsum (Peridiniens). t.d;: gut; Sch. s: Schizodinium sparsum.
|
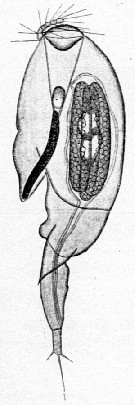 Issued from : E. Chatton in Arch. Zool. Exp. & Gen., 1920, 59, [p.162, Fig.61]. As Corycaeus rostratus. Farranula rostrata female (from Banyuls) parasited by Blastodinium mangini (Dinoflagellate) inside the copepod's gut. Nota: maximum number of parasitism in the species: 10%. B. mangini appears located only into F. rostrata among the copepod community at Banyuls The parasite is generally gregarious. Here , there is a group of three.
|
 Issued from : M.G. Mazzocchi in Guida al Riconoscimento del plancton dei Mari Italiani, Vol. II, 2006. [p.127, Tav. 119]. Redrawn after Dahl, 1912; Rose, 1933. Female: a, habitus (lateral); b, urosome (ventral); c, A2; d, distal segment of P1. Male: e, urosome (ventral); f, A2; g, Mxp.
| | | | | Ref. compl.: | | | Wilson, 1942 a (p.187); Sewell, 1948 (p.484, Rem.); C.B. Wilson, 1950 (p.228); Fagetti, 1962 (p.50); Duran, 1963 (p.26); Neto & Paiva, 1966 (p.34, Table III); Deevey, 1971 (p.224); Corral Estrada & Pereiro Muñoz, 1974 (tab.I); Vives & al., 1975 (tab.II, IV); Deevey & Brooks, 1977 (p.156, tab.2, Station "S"); Dessier, 1979 (p.187, 202, 208); Vives, 1982 (p.296); Brinton & al., 1986 (p.228, Table 1); Lozano Soldevilla & al., 1988 (p.61); Böttger-Schnack, 1995 (p.92); 1996 (p.1087); 1997 (p.409); Hure & Krsinic, 1998 (p.96, 105); Suarez-Morales & Gasca, 1998 a (p.112); Lapernat, 1999 (p.34); Siokou-Frangou, 1999 (p.479); Siokou-Frangou & al., 1999 (p.205, Table 5); Lavaniegos & Gonzalez-Navarro, 1999 (p.239, Appx.1); Seridji & Hafferssas, 2000 (tab.1); Moraitou-Apostolopoulou & al., 2000 (tab.I, fig.8); Lapernat & Razouls, 2001 (tab.1); Hsieh & al., 2004 (p.398, tab.1); Rezai & al., 2004 (p.490, tab.2, p.495, tab.8); Lo & al., 2004 (p.468, tab.2); Fernandez de Puelles & al., 2004 (p.654, fig.7); Lo & al., 2004 (p.89, tab.1); Lakkis & al., 2005 (p.152); Choi & al., 2005 (p.710: Tab.III); Isari & al., 2006 (p.241, tab.II); Zervoudaki & al., 2006 (p.149, Table I); Fernandez de Puelles & al., 2007 (p.338, 348, fig.7): Khelifi-Touhami & al., 2007 (p.327, Table 1); Vidjak & Bojanic, 2009 (p.435, Table II, IV,V); Lidvanov & al., 2010 (p.356, Table 3); Mazzocchi & Di Capua, 2010 (p.428); Tutasi & al., 2011 (p.791, Table 2, abundance distribution vs La Niña event); Mazzocchi & al., 2011 (p.1163, Table II, fig.6, long-term time-series 1984-2006); Isari & al., 2011 (p.51, Table 2, abundance vs distribution); Alves-de-Souza & al., 2011 (p.2125, Blastodinium infestation); Mazzocchi & al., 2012 (p.135, annual abundance 1984-2006); Shiganova & al., 2012 (p.61, Table 4); Uysal & Shmeleva, 2012 (p.909, Table I); Vidjak & al., 2012 (p.243, Rem.: p.254); Belmonte & al., 2013 (p.222, Table 2, abundance vs stations); Terbiyik Kurt & Polat, 2013 (p.1163, Table 2, seasonal distribution); Lidvanov & al., 2013 (p.290, Table 2, % composition); Siokou & al., 2013 (p.1313, fig.4, 8, biomass, vertical distribution); Fernandez de Puelles & al., 2014 (p.82, Table 3, seasonal abundance); Bonecker & a., 2014 (p.445, Table II: frequency, horizontal & vertical distributions); Pansera & al., 2014 (p.221, Table 2, abundance); Marquez-Rojas & al., 2014 (p.12, Rem., %); Zakaria, 2014 (p.3, Table 1, abundance vs 1960-2000); Zakaria & al., 2016 (p.1, Table 1, 3) ; Benedetti & al., 2016 (p.159, Table I, fig.1, functional characters); Ben Ltaief & al., 2017 (p.1, Table III, Summer relative abundance); Marques-Rojas & Zoppi de Roa, 2017 (p.495, Table 1); El Arraj & al., 2017 (p.272, table 2); Benedetti & al., 2018 (p.1, Fig.2: ecological functional group); Palomares-Garcia & al., 2018 (p.178, Table 1: occurrence) | | | | NZ: | 18 | | |
|
Carte de distribution de Farranula rostrata par zones géographiques
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | 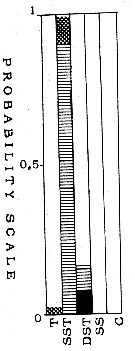 issued from : T.S.K. Björnberg in Bol. Inst. Oceanogr., Sao Paulo, 1963, XIII (1). [p.87, Fig.48]. issued from : T.S.K. Björnberg in Bol. Inst. Oceanogr., Sao Paulo, 1963, XIII (1). [p.87, Fig.48].
Probability of occurrence of Corycella (= Farranul ropstrata in different environments.
T: Tropical waters (above 36.00 p.1000 salinity and above 20°C temperature); SST: Surface subtropical waters (salinity around 36 p.1000 and temperature 18°C or less); DST: Deeper shelf waters (salinity between 34 and 36, temperature under 20°C p.1000); SS: Surface shelf waters (same salinity and temperature above 20°C);
C: coastal waters with low salinity and variable temperature.
In each column no shading means no probability of finding the species in the samples from this environment; horizontal shading indicates the probability of finding the sepecies in percentages less than one in samples from this environment; cross shading indicates the probability of finding it in percentages higher than one and black shading represents the probability of finding it in the largest percentages of the total number of copepods. |
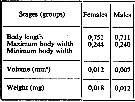 issued from : A.A. Shmeleva in Bull. Inst. Oceanogr., Monaco, 1965, 65 (n°1351). [Table 6: 46]. As Corycella rostrata (from South Adriatic). issued from : A.A. Shmeleva in Bull. Inst. Oceanogr., Monaco, 1965, 65 (n°1351). [Table 6: 46]. As Corycella rostrata (from South Adriatic).
Dimensions, volume and Weight wet. Means for 50-60 specimens. Volume and weight calculated by geometrical method. Assumed that the specific gravity of the Copepod body is equal to 1, then the volume will correspond to the weight. |
| | | | Loc: | | | off S South Africa, off Cape of Good Hope, Namibia, Angola, Baia Farta, Congo, Ivorian shelf, off S Cape Verde Is., Canary Is., off Morocco-Mauritania, off Madeira, off E Trindade Is., off N St. Helena Is., S Brazil, off Rio de Janeiro, Venezuela, Cariaco Gulf, Bahia de Mochima, Caribbean Sea, Cuba, G. of Mexico, Florida, Sargasso Sea, off Bermuda (Station "S"), Chesapeake Bay, off W Azores, Portugal, Ibero-moroccan Bay, off W Tangier, Medit. (Alboran Sea, Baleares, Algiers, Gulf of Annaba, El Kala shelf, Banyuls, Marseille, Toulon harbour, Ligurian Sea, Tyrrhenian Sea, G. of Napoli, Lake Faro (Sicily), Messina, Gulf of Taranto, Taranto Harbour, G. of Gabès, Malta, Adriatic Sea, Island of Pag, Ionian Sea, Aegean Sea, Thracian Sea, Iskenderoun Bay, Black Sea, Iskenderun Bay, Lebanon Basin, Egyptian coast, Alexandria), Red Sea, Arabian Sea, off S Madagascar, Indian, Straits of Malacca, G. of Thailand, Sulu Sea, Philippines, China Seas (East China Sea, South China Sea), Taiwan (W, Tapong Bay, N: Mienhua Canyon), S Korea, S Japan Sea, Japan , Kuchinoerabu Is., Bering Sea, Aleutian Is., Pacif. (W equatorial), Australia (New South Wales), New Zealand, S Baja California (La Paz), Gulf of California, W Mexico, off Washington, Fiji Is., off Hawaii, Galapagos-Ecuador, N Chile | | | | N: | 166 ? | | | | Lg.: | | | (35) F: 0,8-0,78; M: 0,7-0,66; (46) F: 0,8; M: 0,78-0,72; (66) F: 0,85-0,77; M: 0,78-0,68; (104) F: 0,77; M: 0,8; (107) M: 0,69; (114) F: 0,82; M: 0,76-0,71; (180) F: 0,74-0,7; M: 0,66-0,61; (237) F: 0,75-0,9; M: 0,7-0,8; (327) F: 0,87-0,74; (340) F: 1,7; (373) F: 0,86-0,81; M: 0,78-0,7; (432) F: 0,85-0,78; (449) F: 0,72; M: 0,73; (670) F: 0,8-0,77; M: 0,72-0,67; (864) F: 0,9; (920) F: 0,78; {F: 0,70-0,90; M: 0,61-0,80}
The female size furnished by Lapernat (1999): 1,70 mm appears very high. | | | | Rem.: | Sub-superficielle, (off Malte: sample at 2000 m).
Cette espèce apparaît essentiellement de l'Atlantique tropical et en Méditerranée, les citations en Indien ne concernent que le SW, elles sont encore plus rares dans les eaux sino-japonaises.
Les signalisations dans le Pacifique concernent l’Australie SE, la Nouvelle-Zélande Farran (1929) et Jillett (1971), les autres signalisations dans l'Indo-Pacifique sont dues à C.B. Wilson (1942 a, 1950).
Une confusion est possible entre cette espèce et F. orbisa décrite par Wi & Soh (2013, p.1814, Table 1).
Voir aussi les remarques en anglais | | | Dernière mise à jour : 21/10/2022 | |
|
|
 Toute utilisation de ce site pour une publication sera mentionnée avec la référence suivante : Toute utilisation de ce site pour une publication sera mentionnée avec la référence suivante :
Razouls C., Desreumaux N., Kouwenberg J. et de Bovée F., 2005-2026. - Biodiversité des Copépodes planctoniques marins (morphologie, répartition géographique et données biologiques). Sorbonne Université, CNRS. Disponible sur http://copepodes.obs-banyuls.fr [Accédé le 06 janvier 2026] © copyright 2005-2026 Sorbonne Université, CNRS
|
|
 |
 |