|
|
 |
Fiche d'espèce de Copépode |
|
|
Calanoida ( Ordre ) |
|
|
|
Eucalanoidea ( Superfamille ) |
|
|
|
Eucalanidae ( Famille ) |
|
|
|
Pareucalanus ( Genre ) |
|
|
| |
Pareucalanus smithae Prusova, 2007 (F,M) | |
| | | | | | | Ref.: | | | Prusova, 2007 (p.61, figs.F,M) |  issued from : I. Yu. Prusova in Mar. Ecol. J., 2007, 6 (3). [p.62, Fig.1]. Female (from 16°77'N, 55°47'E): 1-2, habitus (dorsal and lateral, respectively); 3, urosome (right lateral); 4, Md (mandibular palp); 5, Md (mandible gnthobase; 6, integumental pores pattern on dorsal surface of pedigerous somites 3-5 and urosome. Nota: Ratio of prosome to urosome length about 7 : 1. Rostrum well developed, ending in 2 fine filaments. Pedigerous somite 1 and Head fused, 4th and 5th partly fused. Urosome of 3 segments; anal segment and caudal rami fused; left caudal ramus slightly larger than the right; right caudal ramus with fascicle of hairs; 2nd medial terminal seta on left caudal ramus markedly stouter and much longer than others. Md exopod-5 segmented, setal formula 1, 1, 1, 1, 2; endopod 2-segmeted, endopod 1 without setae, endopod 2 with 4 setae. Male: 7-8, habitus (dorsal and lateral, respectively); 9, Md (mandibular palp); 10, Md (mandible gnathobase); 11, P5; 12, integumental pores pattern on dorsal surface of pedigerous somites 3-5 and urosome. Nota: Ratio of prosome to urosome length about 6 : 1. Forehead in dorsal view almost triangular with apex smoothly rounded and less produced than in female. Rostrum elongated, ending in 2 fine filaments. Head and pedigerous segment 1 fused, 4th and 5th partly fused. Urosme 5-segmented, anal segment and caudal rami fused; genital segment slightly produced on left side, with distinct genital operculum; left caudal ramus larger than the right. A2, Md palp, Mx1, Mx2 and Mxp slightly reduced, much smaller than in female, but resemble the latter in details of arrangement. Ganthobase of Md degenerated, with single spinelike tooth. P5 both left and right uniramous, 4-segmented; left ramus long, distal segment tipped with hook-like spine; right ramus short, 3rd and 4th incompletely separated, distal segment tipped with seta. On anal segment, 4 pores were revealed in 4 specimens, 5 pores in 1 specimen, localization of the 5th pore is indicated by open circle.
|
 issued from : I. Yu. Prusova in Mar. Ecol. J., 2007, 6 (3). [p.63, Fig.2]. Female: 1, A2; 2, Mx1; 3, Mx2; 4, Mxp; 5, P1; 6, P2; 7, P3; 8, P4; 9, urosome (dorsal). Nota: A2 biramous, coxa and basis with 1 and 2 setae on distomedial angle, respectively; exopod 8-segmented with 2, 2, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 3 setae; endopod 2-segmented with 2 medial setae on endopod 1, with 9 medial and 7 terminal setae on endopod 2. Mx1 with the 1st praecoxal arthrite carrying 15 spines, praecoxal arthrites 2-3 with 4, 4 setae, respectively; coxal endite 1 with 9 stout setae; coxal endite 2 is not pronounced, with 1 medium-sized seta; basis with 5 setae, exopod with 5 setae, endopod with 13 setae. Mx2 with well developed endites, endite 1 with 6 setae and 1 spine, endites 2-6 with 3, 3, 3, 4, 1 setae, respectively; endopod 4-segmented, setal formula 1, 1, 1, 2. Outer margin of coxa has round swelling with hairs and long plumose seta. Mxp 7-segmented; coxa with 1, 2, 3, 3, setae on medial margin; basis partly fused with endopodite 1, with 3 medial and 2 distal setae, free endopod 2-6 setal formula 3, 4, 3, 3 +1 and 2+2. P1 coxa with hairs on inner margin, basis with curved plumose seta at internal apex. P5 lacking.
|
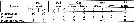 issued from : I. Yu. Prusova in Mar. Ecol. J., 2007, 6 (3). [p.64, Table.1]. Integumental pores pattern in different species of the genus Pareucalanus in the analysed material. Pd = pedigerous segment; Gns = genital segment; Ans = anal segment; Ur = urosomal segment.
| | | | | Ref. compl.: | | | Goetze & Ohman, 2010 (p.2110, Table 1) | | | | NZ: | 1 | | |
|
Carte de distribution de Pareucalanus smithae par zones géographiques
|
| | | | | | 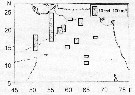 issued from : I. Yu. Prusova in Mar. Ecol. J., 2007, 6 (3). [p.65]. issued from : I. Yu. Prusova in Mar. Ecol. J., 2007, 6 (3). [p.65].
Spatial distribution of P. smithae in the Arabian Sea.
Nota: The species is found in all investigated area (in 14 of 19 sampled stations) in the depth range 0-1300 m. The highest abundance values (38.9 and 22.4 ind. per 100 m3) in the water column were recorded nearshore in the upwelling area.
In general 60 % of the P. smithae population in the investagated layers were found deeper than 100 m. |
| | | | Loc: | | | NW Indian (Arabian Sea) | | | | N: | 1 | | | | Lg.: | | | (990) F: 5,0-5,6; M: 3,8-4,3; {F: 5,0-5,6; M: 3,8-4,3} | | | | Rem.: | Depth range: 0-1300 m. For Prusova (2007, p.65) , nearly 60 % of the P. smithae population in the investigated layers were found deeper than 100 m (i.e. , within the oxygen minimum zone that occurs in the Arabian Sea in the depth range from 50-100 m to 1000-1250 m and is characterized by extremely low dissolved oxygen concentrations, far less than 1 ml/l). On the basis of vertical distribution patterns, a wide range of tolerance to oxygen concentrations in P. smithae can be assumed.
P. smithae is similar to P. attenuatus and P. sewelli in setation of Mxp with 2 setae on the basis, whereas other species of this genus (P. langae and P. parki have 4 setae.P. smithae can be distinguished from P. attenuatus and P. sewelli by more expressed anteriorly and not curved forhead, more narrow and elongated shape of seminal receptacles in lateral view,, and proportional lengths of setae on Mxp endopodal segment 2, the ratio of these setae length in P. smithae 1 : 1.2 : 1.5 : 1.7 ; in P. attenuarus 1 : 1.7 : 2.7 : 4.1; in P. sewelli 1 : 1.8 : 3.5 : 4.5. Additionally, P. smithae differs from P. attenuatus and P. sewelli in pore pattern according to the Fleminger's (1973) method (Table 1). | | | Dernière mise à jour : 13/05/2016 | |
|
|
 Toute utilisation de ce site pour une publication sera mentionnée avec la référence suivante : Toute utilisation de ce site pour une publication sera mentionnée avec la référence suivante :
Razouls C., Desreumaux N., Kouwenberg J. et de Bovée F., 2005-2026. - Biodiversité des Copépodes planctoniques marins (morphologie, répartition géographique et données biologiques). Sorbonne Université, CNRS. Disponible sur http://copepodes.obs-banyuls.fr [Accédé le 03 février 2026] © copyright 2005-2026 Sorbonne Université, CNRS
|
|
 |
 |