|
|
 |
Fiche d'espèce de Copépode |
|
|
Calanoida ( Ordre ) |
|
|
|
Calanoidea ( Superfamille ) |
|
|
|
Paracalanidae ( Famille ) |
|
|
|
Acrocalanus ( Genre ) |
|
|
| |
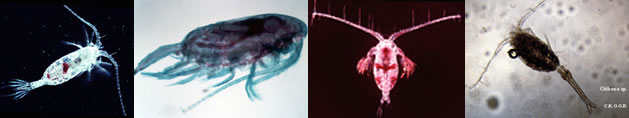
Acrocalanus sp. Ardania, Wardiatno & Kamal, 2017 (F) | |
| | | | | | | Ref.: | | | Issued from :D. Ardiana, Y. Wardiatno & M. M. Kamal in AACL Bioflux, 2017 (739, fig., blue pigment).. | | | | NZ: | 1 | | |
|
Carte de distribution de Acrocalanus sp. par zones géographiques
|
| | | | Loc: | | | Indonesia (Cendrawasih Bay, Papua) | | | | N: | 1 | | | | Lg.: | | | (1237) F: 1,054-1,131; {F: 1,054-1,131} | | | | Rem.: | After several authors (Zagalsky & Herring, 1972; Mojib & al., 2014) blue pigment in copepod (like Pontella fera, Labidocera glauca, Labidocera acutifrons, Corycaeus amazonicus, Acartia erythraea), appear because of carotenoprotein containing astaxanthin as the protect group found that in the tropical marine ecosystem, mesozooplankton are commonly discovered to be blue pigmented, since the ecosystem are depicted by great transparency and annual solar radiation; Several environmental factors may influence carotenoid metabolism (Byron, 1982). Copepods take the risk to staying on the surface for food because there is an increase-risk of biological stressor such as ultraviolet radiation (UVR) and predation (Johnsen & Jakobsen, 1987). To adapt with that, one of their physiological adaptation is accumulation of either UVR absorbing compound such as mycosporine like amino acids or carotenoid pigments such as astaxanthion which give red or blue color depending on the bound or free form (Persaud & al., 2007). The red color was caused by carotenoud astaxanthin and its esters (Hairston, 1976), while blue color was developeed from union with protein (Zagalsky, 1976) | | | Dernière mise à jour : 19/06/2023 |
|
|
 Toute utilisation de ce site pour une publication sera mentionnée avec la référence suivante : Toute utilisation de ce site pour une publication sera mentionnée avec la référence suivante :
Razouls C., Desreumaux N., Kouwenberg J. et de Bovée F., 2005-2026. - Biodiversité des Copépodes planctoniques marins (morphologie, répartition géographique et données biologiques). Sorbonne Université, CNRS. Disponible sur http://copepodes.obs-banyuls.fr [Accédé le 11 février 2026] © copyright 2005-2026 Sorbonne Université, CNRS
|
|
 |
 |