|
|
 |
Fiche d'espèce de Copépode |
|
|
Calanoida ( Ordre ) |
|
|
|
Arietelloidea ( Superfamille ) |
|
|
|
Augaptilidae ( Famille ) |
|
|
|
Haloptilus ( Genre ) |
|
|
| |
Haloptilus acutifrons (Giesbrecht, 1892) (F,M) | |
| | | | | | | Syn.: | Hemicalanus acutifrons Giesbrecht, 1892 (p.384, 398, Descr.F, figs.F);
Hemicalanus spinifrons Sars, 1900 (p.95, figs.F);
Haloptilus spinifrons : Mrazek, 1902 (p.523); Dessier, 1979 (p.206); 1983 (p.89, Tableau 1, Rem., %);
? Haloptilus acutifrons : Grice, 1962 (p.223, figs.F, Rem.) | | | | Ref.: | | | Giesbrecht & Schmeil, 1898 (p.119, Rem. F, fig.F); Sars, 1902 (1903) (p.122, figs.F); Farran, 1908 b (p.68); T. Scott, 1912 (1913) (p.536); Sars, 1925 (p.250, figs.F); Farran, 1926 (p.285); 1929 (p.209, 267); Rose, 1933 a (p.214, figs.F); Jespersen, 1934 (p.110, fig.28); 1940 (p.56); ? Farran, 1936 a (p.113, juv.5F); Mori, 1937 (1964) (p.77, figs.F); Sewell, 1947 (p.190); Brodsky, 1950 (1967) (p.364, figs.F); Vervoort, 1957 (p.135, Rem.); Chiba & al., 1957 (p.308); 1957 a (p.11); Tanaka, 1964 b (p.42); Owre & Foyo, 1967 (p.81, figs.F); Bradford, 1970 a (p.359: Rem.) Corral Estrada, 1970 (p.193, Rem.); Paiva, 1971 (p.26, figs.F, Rem.); Vidal, 1971 a (p.10, 114, fig.F); Matthews, 1972 (p.47); Björnberg & al., 1981 (p.654, figs.F); Roe, 1984 (p.358); Park, 1988 (p.2); Mazzocchi & al., 1995 (p.31, figs.F, Rem.); Chihara & Murano, 1997 (p.728, Pl.61: F); Bradford-Grieve & al., 1999 (p.882, 941, figs.F,M); Bradford-Grieve,1999 b (p.59, figs.F,M, Rem., figs. 172, 190); Vives & Shmeleva, 2007 (p.236, figs.F,M, Rem.) | 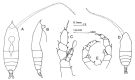 issued from : J.M. Bradford-Grieve in The Marine Fauna of New Zealand: Pelagic Calanoid Copepoda. National Institute of Water and Atmospheric Research (NIWA). NIWA Biodiversity Memoir, 111, 1999. [p.59, Fig.30]. Female: A, habitus (dorsal); B, idem (right lateral side); C, P5. Male: D, habitus (dorsal); E, P5 (endopods: incomplete).
|
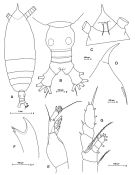 Issued from: M.G. Mazzocchi, G. Zagami, A. Ianora, L. Guglielmo & J. Hure in Atlas of Marine Zooplankton Straits of Magellan. Copepods. L. Guglielmo & A. Ianora (Eds.), 1995. [p.32, Fig.3.2.1]. Female: A, habitus (dorsal); B, urosome (dorsal); C, forehead (ventral); D, idem (lateral right side); E, Md (mandibular palp); F, Md (cutting edge of mandibular blade). Nota: Forehead produced into long, strong spine, slightly bent downward, with subtle filamentous rostrum. A1 exceeds end of body by 5-7 distal segments. Proportional lengths of urosomites and furca 39:11:9:14:27 = 100.
|
 Issued from : G.O. Sars in Résult. Camp. Scient. Prince Albert I, 69, pls.1-127 (1924). [Pl.LXXIV, figs.1-11]. Female: 1, habitus (dorsal); 2, idem (lateral left side); 3, forehead (lateral); 4, A2; 5, Md; 6, Mx1; 7, Mx2; 8, Mxp; 9, P1; 10, P3; 11, P5.
|
 issued from : T. Mori in The pelagic Copepoda from the neighbouring waters of Japan, 1937 (2nd edit., 1964). [Pl.39, Figs.1-4]. Female: 1, P5; 2, habitus (dorsal); 3, Mx1; 4, Mx2.
|
 Issued from : W. Giesbrecht in Systematik und Faunistik der Pelagischen Copepoden des Golfes von Neapel und der angrenzenden Meeres-Abschnitte. – Fauna Flora Golf. Neapel, 1892. Atlas von 54 Tafeln. [Taf.27 , Fig.4 ]. Hemicalanus acutifrons. Female: 4, rostrum and sements 1 to 14 of A1 (ventral view). Aes = aesthetasc
|
 Issued from : W. Giesbrecht in Systematik und Faunistik der Pelagischen Copepoden des Golfes von Neapel und der angrenzenden Meeres-Abschnitte. – Fauna Flora Golf. Neapel, 1892. Atlas von 54 Tafeln. [Taf.27 , Fig.4 ]. Hemicalanus acutifrons. Female: 4, segments 14 to 25 of A1 (ventral view).:
|
 Issued from : W. Giesbrecht in Systematik und Faunistik der Pelagischen Copepoden des Golfes von Neapel und der angrenzenden Meeres-Abschnitte. – Fauna Flora Golf. Neapel, 1892. Atlas von 54 Tafeln. [Taf.27 , Figs.12, 18]. Hemicalanus acutifrons. Female: 12, Mx1 (posterior view); 18, Md (biting edge of mandibular blade). Li = inner lobe; Le = outer lobe; B = basipodite; Re = exopodite; Ri = endopodite
|
 Issued from : W. Giesbrecht in Systematik und Faunistik der Pelagischen Copepoden des Golfes von Neapel und der angrenzenden Meeres-Abschnitte. – Fauna Flora Golf. Neapel, 1892. Atlas von 54 Tafeln. [Taf.27 , Fig.26]. Hemicalanus acutifrons. Female: 26, exopodite 3 of P2.
|
 issued from : G.D. Grice in Fish. Bull. Fish and Wildl. Ser., 1962, 61. [p.224, Pl.25, Figs.1-8]. Female (from equatorial Pacific): 1habitus (dorsal); 2, Md (mandibular palpus); 3, Md (biting edge); 4, P1; 5, P2; 6, P3; 7, P4; 8, P5.
|
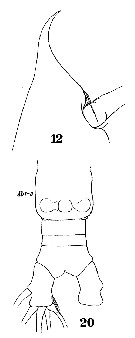 Issued from : W. Giesbrecht in Systematik und Faunistik der Pelagischen Copepoden des Golfes von Neapel und der angrenzenden Meeres-Abschnitte. – Fauna Flora Golf. Neapel, 1892. Atlas von 54 Tafeln. [Taf.42, Fig.12, 20]. As Hemicalanus oxycephalus. Female: 12, forehead (lateral); 20, urosome (ventral).
|
 issued from : J.M. Bradford-Grieve, E.L. Markhaseva & C.E.F. Rocha & B. Abiahy in South Atlantic Zooplankton, Edit. D. Boltovskoy. 1999. Vol.2. Copepoda. [p.1041, Fig. 7.265]. Female: Mx1. Exopodite of Mx1 with 11 setae; outer lobe 1 with 10 setae.
| | | | | Ref. compl.: | | | Pearson, 1906 (p.28); Rose, 1924 d (p.481); Wilson, 1942 a (p.188); Massuti Alzamora, 1942 (p.111); Lysholm & al., 1945 (p.37); Sewell, 1948 (p.330, 496, 504, 509, 522, 534, 538, 547, 558, 559, 567); C.B. Wilson, 1950 (p.235); Hoenigman, 1955 (p.49); Yamazi, 1958 (p.150, Rem.); Fagetti, 1962 (p.31); Grice & Hart, 1962 (p.287, 293: Rem.); V.N. Greze, 1963 a (tabl.2); Duran, 1963 (p.23); Grice, 1963 a (p.496); Ahlstrom & Thrailkill, 1963 (p.57, Table 5, abundance); Gaudy, 1963 (p.27, Rem.); M.W. Johnson, 1963 (p.89, Table 1, 2); Björnberg, 1963 (p.54, Rem.); De Decker & Mombeck, 1964 (p.12); Grice & Hulsemann, 1965 (p.224); Mazza, 1966 (p.72); Pavlova, 1966 (p.44); Harding, 1966 (p.17, 65, 71); Fleminger, 1967 a (tabl.1); Grice & Hulsemann, 1967 (p.19); Dunbar & Harding, 1968 (p.319); Delalo, 1968 (p.138); Park, 1970 (p.478); Deevey, 1971 (p.224); Roe, 1972 (p.277, tabl.1, tabl.2); 1972 c (p.1033); Apostolopoulou, 1972 (p.328, 362); Bainbridge, 1972 (p.61, Appendix Table II, vertical distribution %); Björnberg, 1973 (p.347, 386); Corral Estrada & Pereiro Muñoz, 1974 (tab.I); Vives & al., 1975 (p.50, tab.II, III); Deevey & Brooks, 1977 (p.156, tab.2, Station "S"); Carter, 1977 (1978) (p.36); Vaissière & Séguin, 1980 (p.23, tab.1); Buchanan & Sekerak, 1982 (p.41, vertical distribution); Vives, 1982 (p.293); Kovalev & Shmeleva, 1982 (p.84); Greze & al., 1983 (p.17); Scotto di Carlo & al., 1984 (p.1044); Cummings, 1984 (p.163, Table 2); Longhurst, 1985 (tab.2); Brenning, 1985 a (p.28, Table 2); 1986 (p.14, Rem.); Brinton & al., 1986 (p.228, Table 1); Madhupratap & Haridas, 1986 (p.105, tab.1); Lozano Soldevilla & al., 1988 (p.60); Kosobokova, 1989 (p.26); Heinrich, 1990 (p.18); Suarez & al., 1990 (tab.2); Hattori, 1991 (tab.1, Appendix); Scotto di Carlo & al., 1991 (p.271); Suarez & Gasca, 1991 (tab.2); Suarez, 1992 (App.1); Mumm, 1993 (tab.1, fig.2); Seguin & al., 1993 (p.23); Richter, 1994 (tab.4.1a); Shih & Young,1995 (p.68); Hanssen, 1997 (tab.3.1); Hure & Krsinic, 1998 (p.102); Padmavati & al., 1998 (p.347); Gilabert & Moreno, 1998 (tab.1, 2); Suarez-Morales & Gasca, 1998 a (p108); Kosobokova & al., 1998 (tab.2); Voronina & Kolosova, 1999 (p.71); Razouls & al., 2000 (p.343, tab. 5, Appendix); Lopez-Salgado & al., 2000 (tab.1); Fernandez-Alamo & al., 2000 (p.1139, Appendix); Kosobokova & Hirche, 2000 (p. 2029, tab. 2); Holmes, 2001 (p.12, Rem.); Auel & Hagen, 2002 (p.1013, tab.2); Vukanic, 2003 (139, tab.1); Hsiao & al., 2004 (p.325, tab.1); Isari & al., 2006 (p.241, tab.II); Dur & al., 2007 (p.197, Table IV); Khelifi-Touhami & al., 2007 (p.327, Table 1); McKinnon & al., 2008 (p.843: Tab.1); Ayon & al., 2008 (p.238, Table 4: Peruvian samples); Neumann-Leitao & al., 2008 (p.799: Tab.II, fig.6); Morales-Ramirez & Suarez-Morales, 2008 (p.517); Fernandes, 2008 (p.465, Tabl.2); Raybaud & al., 2008 (p.1765, Table A1); Galbraith, 2009 (pers. comm.); C.E. Morales & al., 2010 (p.158, Table 1); Kosobokova & Hopcroft, 2010 (p.96, Table 1, fig.7); Mazzocchi & Di Capua, 2010 (p.424); Medellin-Mora & Navas S., 2010 (p.265, Tab. 2); Dvoretsky & Dvoretsky, 2010 (p.991, Table 2); Kosobokova & al., 2011 (p.29, Table 2, Rem.: Arctic Basins); Hsiao S.H. & al., 2011 (p.475, Appendix I); Tutasi & al., 2011 (p.791, Table 2, abundance distribution vs La Niña event); Pillai H.U.K. & al., 2011 (p.239, Table 3, vertical distribution); Andersen N.G. & al., 2011 (p.71, Fig.3: abundance); Uysal & Shmeleva, 2012 (p.909, Table I); Miloslavic & al., 2012 (p.165, Table 2, transect distribution); in CalCOFI regional list (MDO, Nov. 2013; M. Ohman, comm. pers.); Lidvanov & al., 2013 (p.290, Table 2, % composition); Mazzocchi & al., 2014 (p.64, Table 4, abundance); Benedetti & al., 2016 (p.159, Table I, fig.1, functional characters); Benedetti & al., 2018 (p.1, Fig.2: ecological functional group); Belmonte, 2018 (p.273, Table I: Italian zones); Acha & al., 2020 (p.p.1, Table 3: occurrence % vs ecoregions). | | | | NZ: | 21 | | |
|
Carte de distribution de Haloptilus acutifrons par zones géographiques
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Loc: | | | Antarct. (Weddell Sea, SE Atlant.), sub-Antarct. (S Tasmania, SE Pacif., Straits of Magellan: Pacific area), South Africa (E), Congo, off Lagos, Cape Verde Is., off Morocco-Mauritania, Canary Is., off Madeira, off W Cape Finisterre, Azores, S Brazil, off Amazon, Caribbean Colombia, Caribbean Sea, G. of Mexico, Cuba, Florida, Sargasso Sea, off Bermuda: Station ‘’ S’’ (32°10’N, 64°30’W), Baffin Bay, W Greenland, Greenland Sea, S Iceland, Arctic (all polar Basins), Arctic. (central, Fletcher's Ice Is.), Nansen Basin, Lomonosov Ridge, Barents Sea, Laptev Sea, Canadian abyssal plain, Canada Basin, Chukchi Sea, E Beaufort Sea, off W Ireland, Porcupine bank, Norway, North Sea, Bay of Biscay, Baie Ibéro-marocaine, Medit. (Alboran Sea, Gulf of Annaba, Castellon, Baleares, Ligurian Sea, Tyrrhenian Sea, Strait of Messina, Adriatic Sea, Mljet Is., Ionian Sea, Aegean Sea, Johnston Bank, Lebanon Basin), Red Sea, G. of Aden, G. of Oman, Arabian Sea, Natal, Indian, Bay of Bengal, Andaman Sea (Batten Island); Australia (North West Cape), Philippines, China Seas (East China Sea, South China Sea), Taiwan (SW, E), Japan (Izu, Tanabe Bay, off Sanriku), Bikini Is., Pacif. (tropical), ? Australia (Great Barrier), New Zealand (North Island: NE & NW, SE South Island), N Tasman Sea, Hawaii, Vancouver Is., California, W Baja California, Gulf of California, G. of Tehuantepec, off W Guatemala, W Costa Rica, off W Costa Rica, off SW Panama, Pacif. (SE tropical), SE Easter Is., Galapagos-Ecuador, Peru, Chile (., Concepcion) | | | | N: | 158 | | | | Lg.: | | | (1) F: 3,3; (22) F: 3,2-2,6; (35) F: 3,9-3,5; (36) F: 4,66-4,35; (38) F: 3,5-3,2; (46) F: 2,9-2,6; (65) F: 3,2; (69) F: 2,99; (91) F: 3-2,5; ? (101) F: 3,8; (134) F: ± 4; (199) F: 3,95-3,12; M: 3,19; (237) F: 2,0; (310) F: 3,86-3,64; (765) F: 3-2,6; M: 2,4-2,1; (1108) F: 3,8; {F: 2,00-4,66; M: 2,1-3,19} | | | | Rem.: | épi-bathypélagique.
Sampling depth (Antarct., sub-Antarct.): 100-250 m.
La description originale du mâle ne nous est pas connue, mais indiquée in Bradford-Grieve & al. (1999) et Bradford-Grieve (1999 b, p.59, Fig.30 et remarques p.60).
Voir aussi les remarques en anglais | | | Dernière mise à jour : 07/12/2020 | |
|
|
 Toute utilisation de ce site pour une publication sera mentionnée avec la référence suivante : Toute utilisation de ce site pour une publication sera mentionnée avec la référence suivante :
Razouls C., Desreumaux N., Kouwenberg J. et de Bovée F., 2005-2026. - Biodiversité des Copépodes planctoniques marins (morphologie, répartition géographique et données biologiques). Sorbonne Université, CNRS. Disponible sur http://copepodes.obs-banyuls.fr [Accédé le 10 mars 2026] © copyright 2005-2026 Sorbonne Université, CNRS
|
|
 |
 |