|
|
 |
Fiche d'espèce de Copépode |
|
|
Calanoida ( Ordre ) |
|
|
|
Diaptomoidea ( Superfamille ) |
|
|
|
Centropagidae ( Famille ) |
|
|
|
Centropages ( Genre ) |
|
|
| |
Centropages trispinosus Sewell, 1914 (F,M) | |
| | | | | | | Ref.: | | | Sewell, 1914 a (p.223, Descr.F, figs.F); Kasturirangan, 1963 (p.32, figs.M); Vervoort, 1964 b (p.309); Saraswathy, 1966 (1967) (p.78, Rem.F); Silas, 1972 (p.648); Ohtsuka, McKinnon & al., 2003 (p.75: Rem.) | 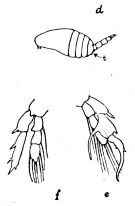 issued from : Kasturirangan L.R. in Publs Counc. Scient. Indust. Res. India, 2. [Fig.27, p.33]. Male: d, habitus (lateral view, left side) (t: three small teeth-like); e, P5 (right, posterior face).
|
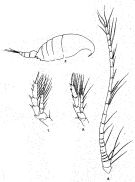 Issued from : R.B.S. Sewell in Spolia Zeylanica, 1914, 9. [Pl.XVIII, Figs.5-8]. Female (from Gulf of Mannar): 5, habitus (lateral right side); 6, A1; 7, P2; 7, P5. Nota: Proportional lengths of cephalothorax and abdomen 3:1. Head and 1st thoracic segment separate, 4th and 5th separate. Posterior thoracic margin rounded, armed 3 short spines situated rather towards the ventral side. Rostrum consists of 2 slender processes. Proportional lengths of urosomites and furca 4:3:2:2. Genital segment somewhat barrel-shaped, and has a rounded swelling on the dorsal aspect. A1 21-segmented (segments 2-4, 8-9, 24-25 fused). P5: both rami 3-segmented; exopod 1 bears a marginal spine, but has no internal seta; exopod 2, in addition to the single external marginal spine, bears the usual spine on its inner border, this spine is long and has somewhat swollen base; it tapers gradually to a fine point and bears no teeth on its surface; exopod 3 has 2 marginal spines and a finely serrated end-spine; the endopodite reaches to the level of the joint between exopods 2 and 3; endopod 1 presents a well-marked rounded swelling at its distal external angle. The remaining appendages appear similar to those of C. alcocki but the serrations on the terminal spines of the swimming feet are not so coarse and are less widely separated.
| | | | | Ref. compl.: | | | Sewell, 1932 (p.232); 1948 (p.323); Krishnaswamy, 1953 (p.121); Ganapati & Shanthakumari, 1962 (p.8, 15); Goswami & al., 1977 (tab.3); Goswami & Selvakumar, 1977 (tab.1, 2); Madhupratap & Haridas, 1986 (p.105, tab.1); Dalal & Goswami, 2001 (p.22, fig.2); Rakhesh & al., 2006 (p.93, Table 2, spatial distribution); | | | | NZ: | 1 | | |
|
Carte de distribution de Centropages trispinosus par zones géographiques
|
| | | | | | | Loc: | | | India (S, W), G. de Mannar, Lawson's Bay, Madras, Bay of Bengal | | | | N: | 7 (Indian: 7) | | | | Lg.: | | | (82) F: 1,4; (334) F: 1,2-1; M: 1; (530) F: 1,5; M: 1,5; (795) F: 1,6-1,4; M: 1,025; {F: 1,00-1,60; M: 1,00-1,50} | | | | Rem.: | Saumâtre.
peut-être synonyme de Centropages brevifurcus.
Voir aussi les remarques en anglais | | | Dernière mise à jour : 31/12/2014 | |
|
|
 Toute utilisation de ce site pour une publication sera mentionnée avec la référence suivante : Toute utilisation de ce site pour une publication sera mentionnée avec la référence suivante :
Razouls C., Desreumaux N., Kouwenberg J. et de Bovée F., 2005-2025. - Biodiversité des Copépodes planctoniques marins (morphologie, répartition géographique et données biologiques). Sorbonne Université, CNRS. Disponible sur http://copepodes.obs-banyuls.fr [Accédé le 01 janvier 2026] © copyright 2005-2025 Sorbonne Université, CNRS
|
|
 |
 |