|
|
 |
Fiche d'espèce de Copépode |
|
|
Calanoida ( Ordre ) |
|
|
|
Clausocalanoidea ( Superfamille ) |
|
|
|
Clausocalanidae ( Famille ) |
|
|
|
Ctenocalanus ( Genre ) |
|
|
| |
Ctenocalanus heronae Vega-Perez & Bowman, 1992 (F) | |
| | | | | | | Ref.: | | | Vega-Perez & Bowman, 1992 (p.98, Descr.F, figs.F, Rem.); Suarez-Morales & Leon-Oropeza, 2000 (p.39, tab.1, Rem.); Andronov, 2014 (p.36, fig.: A2) |  issued from : L.A. Vega-Pérez & T.E. Bowman in Proc. Biol. Soc. Wash., 1992, 105 (1). [p.99, Figs.1-4, 16-18]. Female (from Ubatuba region, Brazil): 1, forehead and rostral filaments (ventral); 2, habitus (lateral); 3, urosome (lateral; 4, idem (ventral); 16, genital segment (dorsal); 17, idem (lateral, right side); 18, anal segment and caudal rami (dorsal). Nota: Genital segment more expanded on left than right side. A1 24-segmented (segments 9 and 10 separated by complete suture). P4 exopod segment 1 with ctenospine with 0-4 teeth, segment 2 with ctenospine with 7 teeth, segment 3 ctenospines with 6-7 (proximal and 7-9 (distal) teeth directed at angles of about 50° and 54° respectively to axis of segment.
|
 issued from : L.A. Vega-Pérez & T.E. Bowman in Proc. Biol. Soc. Wash., 1992, 105 (1). [p.99, Figs.5-10]. Female: 5, A1; 6, A2; 6', A2 (distal segment of endopod); 7, Md; 8, Mx1; 9, Mx2; 10, Mxp.
|
 issued from : L.A. Vega-Pérez & T.E. Bowman in Proc. Biol. Soc. Wash., 1992, 105 (1). [p.99, Figs.11-15]. Female: 11, P1; 12, P2; 13, P3; 14, P4; 15, P5 (from 3 different specimens).
|
 issued from : E. Suarez M. & A. Leon-Oropeza in Gulf and Caribbean Researc, 2000, 12. [p.38, Fig.1]. Female (from Campeche Sound, G. of Mexico): A, habitus (dorsal); B, idem (latral); C, urosome (lateral); D, idem (dorsal); E, right A1; F, P3; G, detail of P3 ctenospines; H, exopodite of P2; I, P1; J, head (lateral); K, P5. Scales in mm.
|
 issued from : E. Suarez M. & A. Leon-Oropeza in Gulf and Caribbean Researc, 2000, 12. [p.39, Table I]. Characters used to separate the known species of Ctenocalanus. c/u ratio = cephalosome/urosome length ratio.
|
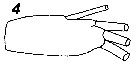 Issued from : V.N. Andronov in Russian Acad. Sci. P.P. Shirshov Inst. Oceanol. Atlantic Branch, Kaliningrad, 2014. [p.36, Fig.9, 4]. Ctenocalanus heronae after Vega-Perez & Bowman, 1992, 1970. 4, distal segment of exopod of A2.
| | | | | Ref. compl.: | | | Miyashita & al., 2009 (p.815, Tabl.II) | | | | NZ: | 2 | | |
|
Carte de distribution de Ctenocalanus heronae par zones géographiques
|
| | | | Loc: | | | Brazil (Sao Paulo), Caribbean | | | | N: | 3 | | | | Lg.: | | | (372) F: 1,32-1,23; (912) F: 1,17; {F: 1,17-1,32} | | | | Rem.: | Pour A. Prado-Por (1984) les épines cténoides pourraient être articulées à leur base, ainsi leur angle avec l'axe de l'exopode ne constitue pas un bon critère taxonimique. Vega-Pérez & Bowman (1992, p.100) n'observent aucun muscles attachés à la base des épines cténoides. le seul mouvement possible pourrait résulter de la flexion antero-posterieur de la patte. Pour ces derniers auteurs, la position des épines cténoides constitue un caractère valide.
Voir aussi les remarques en anglais | | | Dernière mise à jour : 19/04/2016 | |
|
|
 Toute utilisation de ce site pour une publication sera mentionnée avec la référence suivante : Toute utilisation de ce site pour une publication sera mentionnée avec la référence suivante :
Razouls C., Desreumaux N., Kouwenberg J. et de Bovée F., 2005-2026. - Biodiversité des Copépodes planctoniques marins (morphologie, répartition géographique et données biologiques). Sorbonne Université, CNRS. Disponible sur http://copepodes.obs-banyuls.fr [Accédé le 07 janvier 2026] © copyright 2005-2026 Sorbonne Université, CNRS
|
|
 |
 |