|
|
 |
Fiche d'espèce de Copépode |
|
|
Calanoida ( Ordre ) |
|
|
|
Arietelloidea ( Superfamille ) |
|
|
|
Heterorhabdidae ( Famille ) |
|
|
|
Heterorhabdus ( Genre ) |
|
|
| |
Heterorhabdus spinifrons (Claus, 1863) (F,M) | |
| | | | | | | Syn.: | Heterochaeta spinifrons Claus, 1863 (p.182, figs.F); Brady, 1883 (p.49, figs.F,M);
Heterochäta spinifrons (M) : Giesbrecht, 1892 (p.372, 382, 773, figs.M, non F);
Heterorhabdus (Heterorhabdus) spinifrons : Vervoort, 1965 (p.119, Rem.); Bradford-Grieve,1999 b (p.87, figs.F,M, Rem., figs.175, 191); | | | | Ref.: | | | Giesbrecht & Schmeil, 1898 (p.114); Thompson & Scott, 1903 (p.235, 249); Esterly, 1905 (p.183, figs.F); 1906 a (p.77, fig.M); Farran, 1908 b (p.65); A. Scott, 1909 (p.130, Rem.); Wolfenden, 1911 (p.302); Pesta, 1920 (p.531); Lysholm & Nordgaard, 1921 (p.25); Sars, 1925 (p.227, figs.F, M); Farran, 1926 (p.282); 1929 (p.209, 264); Sewell, 1932 (p.300); Wilson, 1932 a (p.133, figs.F,M); Rose, 1933 a (p.202, figs.F,M); Farran, 1936 a (p.112); Jespersen, 1940 (p.55); Sewell, 1947 (p.179, fig.44, Rem.F); Farran, 1948 e (n°16, p.3, figs.F,M); Brodsky, 1950 (1967) (p.351, figs.F,M); Chiba & al., 1957 (p.308); 1957 a (p.11); Vervoort, 1957 (p.133, Rem.); Grice, 1962 (p.222, figs.F); Paiva, 1963 (p.59, figs.M); Tanaka, 1964 a (p.13, figs.F,M); Mazza, 1965 a (p.314, figs.F,M, juv.); Owre & Foyo, 1967 (p.79, figs.F,M); Mazza, 1967 (p.191, 202, figs.F,M, juv.); Shih & al., 1971 (p.40); Bowman, 1971 b (p.40, figs.F, Rem.); Razouls, 1972 (p.95, Annexe: p.76); Arcos, 1974 (p.223, figs.F,M); 1975 (p.22, figs.F,M); Björnberg & al., 1981 (p.648, figs.F,M); Gardner & Szabo, 1982 (p.372, figs.F,M); Roe, 1984 (p.358); Mazzocchi & al., 1995 (p.35, figs.F,M, Rem.); Nishida & Ohtsuka, 1996 (p.620, figs.); Chihara & Murano, 1997 (p.819, Pl.118,120: F,M); Ohtsuka & al., 1997 (p.579, figs.F); Bradford-Grieve & al., 1999 (p.883, 944, figs.F,M); Park, 2000 (p.92, figs.F,M, Rem.); G. Harding, 2004 (p.4, figs.F,M); Vives & Shmeleva, 2007 (p.308, figs.F,M, Rem.) | 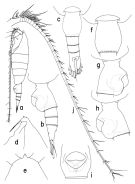 issued from : T. Park in Bull. Scripps Inst. Oceanogr. Univ. California, San Diego, 2000, 31. [p.211, Fig.59]. Female (Atlantic specimen): a, habitus (left side); b, c, urosome (left, dorsal, respectively); d, e, forehead (left, dorsal, respectively); f, g, h, i, genital somite (dorsal, right, left, ventral, respectively); j, left A1 (ventral). Nota: - Prosome about 7/10 length of body and about 2.2 times length of urosome. - Midanterior tubercular process of forehead produced into a spiniform process: laterally rostral lobe poorly developed with 2 slender filaments. - Length ratios of 4 urosomal somites and left caudal ramus 37.0 : 17.3 : 13.6 : 9.9 : 22.2 = 100. - Genital prpminence extending to posterior end of somite; ventrally, genital operculum typically with a length-width ratio of 77 : 100 and about 7/10 as wide as somite; genital field with a row of about 15 pores on each side. - Caudal ramus extending beyond posterior end of right by 1/6 its length as measured along medial margin. - Dorsal appendicular seta of left ramus nearly as long as ramus itself and about twice as long as corresponding seta on right ramus; 4th marginal seta of left ramus unarmed and much longer than body. - A1 extending beyond posterior end of caudal ramus by its 3 segments; segments 2-19 with 1 middle and 2 distal setae/aesthetes.
|
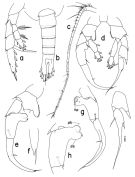
 issued from : T. Park in Bull. Scripps Inst. Oceanogr. Univ. California, San Diego, 2000, 31. [p.212, Fig.60]. Female: a, left A2 (posterior); b, first endopodal segment of left A2 (anterior); c, left Md (posterior); d, masticatory edge of left Md (posterior); e, masticatory edge of right Md (posterior); f, left Mx1 (posterior); g, left Mx2 (posterior); h, right Mxp (anterior); i, P1 (anterior); j, basipod of P1 (posterior); k, P2 (anterior); l, P3 (anterior); m, P4 (anterior). Nota: - A2: Basipod a little shorter than 1st endopodal segment; inner marginal setae of coxa and basis only moderately developed; endopod and exopod of similar length; 1st endopodal segment with rather poorly developed inner marginal setae abd a row of furcate spinules on anterior surface; first 2 exopodal segments each with a small conical process at distomedial corner, without marginal setae; inner marginal seta of last exopodal segment normally developed. - Md: Mandibular palp with small endopod reaching about distal end of exopod. Basis well developed, with 1 relatively small seta. 1st endopodal segment with 1 small and 2 long setae; 2nd with 8 terminal setae plus 1 anterior appendicular seta. Mandibular blade 1.2 times length of palp; Two dorsal teeth of left Md tricuspid (Fig.60-d); 1st dorsal tooth of right Md bicuspid (Fig.60-e), 2nd tricuspid, and 3rd single-pointed. Masticatory edge between dorsal teeth and ventral falcate tooth more or less straight. - Mx1: 1st inner lobe with 12 setae; 2nd inner lobe and basis each with 1 seta; endopod with 3 setae; all of these setae are rather poorly developed; outer lobe with 5 well-developed setae plus 2 tiny setae. - Mx2: 1st segment nearly as long as rest of appendage. Long seta of 1st lobe about twice length of short seta. Spine of 2nd lobe stout, about as long as short seta of 1st lobe. Spine of 3rd lobe a little longer than segment itself and about 5/9 length of longest spine of 4th lobe; seta of 3rd lobe very fine and short. 1st saberlike spine of 4th lobe only slightly shorter than 2nd and about 4/5 length of large, falcate spine of 5th lobe; small spine of 4th lobe about as long as spine of 2nd lobe and about 1/5 length of longest spine of same lobe. 5th lobe a little shorter than segment; falcate spine a little longer than longest spine of 4th lobe and proximal half of its medial margin fringed with extremely fine spinules (visible only under a high magnification); saberlike spine of 5th lobe about 2/3 length of falcate spine. 6th lobe reaching about halfway to distal end of 5th; falcate spine of 6th lobe a little longer but thinner than falcate spine of 5th lobe; proximal 4/7 serrated along medial margin; seta of 6th lobe very fine and short. Endopod very small, with 7 delicate setae barely reaching distal end of 5th lobe. - Mxp: Distal half of saberlike spine thickly armed with spinules; anterior distal spine of coxa well developed, about 1/2 length of segment and reaching 2/5 way to distal end of basis; 2 posterior distal spines greatly reduced, less than 1/2 length of anterior distal spine and very fine. Basis with a long band of spinules on anterior surface and about 1.4 times length of coxa as measured along medial margins; 3 middle marginal setae poorly developed and the first arising about 5/9 length of segment from proximal end. Endopod about as long as coxa.
|
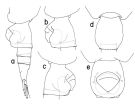
 issued from : T. Park in Bull. Scripps Inst. Oceanogr. Univ. California, San Diego, 2000, 31. [p.213, Fig.61]. Female: a, P5 (anterior). Male: b, urosome (dorsal); c, left A1 (dorsal); d, P5 (anterior); e, right P5 (endopod omitted), anterior; f, distal end of exopod of right P5 (lateral); g, exopod of right P5 (posterior); h, second exopodal segment of right P5 (anterior); i, distal exopodal segments of left P5 (anterior). dlb = distal lobe; plb = proximal lobe; tsp = terminal spiniform process. Nota: - Left geniculate A1 with segments 1 and 2 fused, segments 19-21 fused to form 1st postgeniculate segment; segments 22 and 23 also fused. - Other cephalosomal appendages and P1 to P4 as in female.
|
 issued from : T. Park in Bull. Scripps Inst. Oceanogr. Univ. California, San Diego, 2000, 31. [p.214, Fig.62]. Female (specimen from off west coast of North America): a, urosome (left side); b, c, d, e, genital somite (left, right, dorsal, ventral, respectively).
|
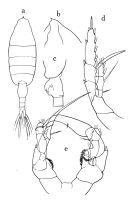 issued from : O. Tanaka in Publs Seto Mar. Biol. Lab., 1964, XII (1). [p.14, Fig.179]. Female: a, habitus (dorsal); b, forehead (left lateral side); c, last thoracic segment and genital somite (left lateral side); d, P5. Nota: A1 exceeds the end of the furca by distal 2 segments. Male: e, P5.
|
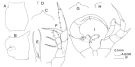 issued from : J.M. Bradford-Grieve in The Marine Fauna of New Zealand: Pelagic Calanoid Copepoda. National Institute of Water and Atmospheric Research (NIWA). NIWA Biodiversity Memoir, 111, 1999. [p.87, Fig.55]. Female: A, genital somite (dorsal); B, idem (left lateral side); C, forehead (dorsal); D, anterior part of the head (left lateral side); E, Mx2 (lobe 4); F, P5. Nota: remark a short 3rd seta on lobe 4of Mx2. Male: G, forehead (dorsal); H, idem (left lateral side); I, P5.
|
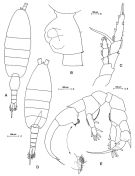 Issued from: M.G. Mazzocchi, G. Zagami, A. Ianora, L. Guglielmo & J. Hure in Atlas of Marine Zooplankton Straits of Magellan. Copepods. L. Guglielmo & A. Ianora (Eds.), 1995. [p.37, Fig.3.3.1]. Female: A, habitus (dorsal); B, genital somite (lateral left side); C, P5. Nota: A1 exceeds caudal rami by about 2 segments. Proportional lengths of urosomites and furca 42:15:12:12:19 = 100. Caudal rami asymmetrical; left ramus longer, bearing very long strong inner marginal seta. Male: D, habitus (dorsal); E, P5. Nota: Proportional lengths of urosomites and furca 23 : 19 : 16 : 11 : 8: 23 = 100
|
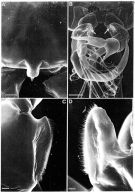
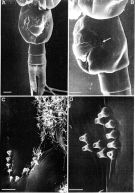 Issued from: M.G. Mazzocchi, G. Zagami, A. Ianora, L. Guglielmo & J. Hure in Atlas of Marine Zooplankton Straits of Magellan. Copepods. L. Guglielmo & A. Ianora (Eds.), 1995. [p.39, Fig.3.3.3]. Female (SEM preparation): A, urosome (ventral); B, genital somite (lateral left side); C and D, detail of integumental cone-like pores on either side of genital aperture (arrow in B). Bars: A-B 0.100 mm; C 0.010 mm; D 0.005 mm.
|
 Issued from: M.G. Mazzocchi, G. Zagami, A. Ianora, L. Guglielmo & J. Hure in Atlas of Marine Zooplankton Straits of Magellan. Copepods. L. Guglielmo & A. Ianora (Eds.), 1995. [p.40, Fig.3.3.4]. Male (SEM preparation): B, posterior margins of urosome (dorsal); C, asymmetrical caudal rami (dorsal). Bars: B 0.050 mm; C 0.100 mm.
|
 Issued from: M.G. Mazzocchi, G. Zagami, A. Ianora, L. Guglielmo & J. Hure in Atlas of Marine Zooplankton Straits of Magellan. Copepods. L. Guglielmo & A. Ianora (Eds.), 1995. [p.41, Fig.3.3.5]. Male (SEM preparation): A, protuberance on forehead ending with a short spine (dorsal view); B, P5; C and D, ear-like lobes on inner margins of basipod 2 of P5 (arrows in B). Bars: A 0.050 mm; B 0.100 mm; C, D 0.010 mm.
|
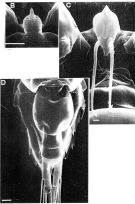 Issued from: M.G. Mazzocchi, G. Zagami, A. Ianora, L. Guglielmo & J. Hure in Atlas of Marine Zooplankton Straits of Magellan. Copepods. L. Guglielmo & A. Ianora (Eds.), 1995. [p.38, Fig.3.3.2]. Female (SEM preparation): B, forehead (dorsal) with characteristic protuberance ending with a sharp spine; C, rostrum with 2 filaments; D, urosome (dorsal). B 0.050 mm; C 0.005 mm; D 0.100 mm.
|
 Issued from : G.O. Sars in Résult. Camp. Scient. Prince Albert I, 69, pls.1-127 (1924). [Pl.LXII, figs.9-12]. Female: 9, habitus (dorsal); 10, forehead (lateral); 11, urosome (lateral left side). Male: 12, right P5.
|
 issued from : R.B.S. Sewell in The John Murray Expedition, 1933-34, Scientific Reports, VIII (1), 1947. [p.166, Fig.44, L]. Process on the posterior aspect of the 2nd basal segment of P1. Remarks: The shape of the hook-like or spine-like process shows some variation in different genera, but it is undoubtedly homologous throughout the whole series. The function of this organ is unknown.
|
 issued from : S. Ohtsuka, H.Y. Soh & S. Nishida in J. Crustacean Biol., 1997, 17 (4). [p.582, Fig.3, A, B]. Female (from S. Japan): A, right mandibular cutting edge; B, left cutting edge. v = ventral teeth; c = central teeth. Scale bars : 0.100 mm (A, B).
|
 issued from : S. Ohtsuka, H.Y. Soh & S. Nishida in J. Crustacean Biol., 1997, 17 (4). [p.583, Fig.4, F]. Female (S Japan): F, left side of labrum (posterior surface) with gland openings (small and large arrows). Scale bar: 0.010 mm.
|
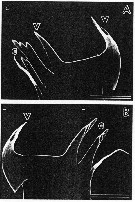
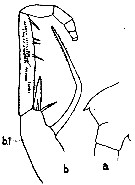 issued from : C.O. Esterly in Univ. Calif. Publs. Zool., 1905, 2 (4). [p.183, Fig.37]. Female (from San Diego Region): a, forehead (lateral, left side); b, Mxp (b.1 = 1st basal).
|
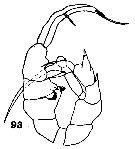 issued from : C.O. Esterly in Univ. Calif. Publs Zool., 1906, 3 (5). [Pl.14, Fig.93]. Male (from San Diego, California): 93, P5.
|
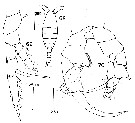 issued from : D.F.R. Arcos in Gayana, Zool., 1975, 32. [Lam.VIII, Figs.68-70]. Female (from Bahia de Concepcion, Chile): 69, P5. Male: 68, habitus (dorsal); 70, P5.
|
 issued from : T.E. Bowman in Smithson. Contr. Zool., 1971, 96. [p.47, Fig.43, d]. Female (from Florida): d, distal end of Mx2.
|
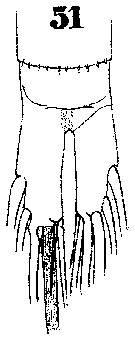 Issued from : W. Giesbrecht in Systematik und Faunistik der Pelagischen Copepoden des Golfes von Neapel und der angrenzenden Meeres-Abschnitte. – Fauna Flora Golf. Neapel, 1892. Atlas von 54 Tafeln. [Taf. 39, Fig. 51]. As Heterochäta spinifrons. Male: 51, anal segment and caudal rami.
|
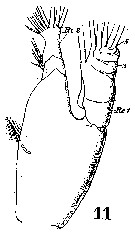 Issued from : W. Giesbrecht in Systematik und Faunistik der Pelagischen Copepoden des Golfes von Neapel und der angrenzenden Meeres-Abschnitte. - Fauna Flora Golf. Neapel, 1892. Atlas von 54 Tafeln. [Taf. 20 , Fig.11 ]. As Heterochäta spinifrons. Male: 11, Md (mandibular palp).
|
 Issued from : W. Giesbrecht in Systematik und Faunistik der Pelagischen Copepoden des Golfes von Neapel und der angrenzenden Meeres-Abschnitte. - Fauna Flora Golf. Neapel, 1892. Atlas von 54 Tafeln. [Taf. 20 , Fig.16]. As Heterochäta spinifrons. Male: 16, Mx2 (posterior view).
|
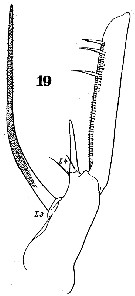 Issued from : W. Giesbrecht in Systematik und Faunistik der Pelagischen Copepoden des Golfes von Neapel und der angrenzenden Meeres-Abschnitte. - Fauna Flora Golf. Neapel, 1892. Atlas von 54 Tafeln. [Taf. 20 , Fig.19 ]. As Heterochäta spinifrons. Male: 19, basipod of Mxp (anterior view).
|
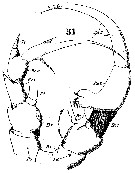 Issued from : W. Giesbrecht in Systematik und Faunistik der Pelagischen Copepoden des Golfes von Neapel und der angrenzenden Meeres-Abschnitte. - Fauna Flora Golf. Neapel, 1892. Atlas von 54 Tafeln. [Taf. 20 , Fig.31]. As Heterochäta spinifrons. Male: 31, P5 (anterior view). Ps = left P5; Pd = right P5; B1 = basipod 1 (= coxa); B2 = basipod 2 (= basis); Ri = endopod; Re = exopod.
|
 issued from : G.D. Grice in Fish. Bull. Fish and Wildl. Ser., 1962, 61. [p.221, Pl.24, Figs.10-11]. Female (from equatorial Pacific): 10, forehead (lateral); 11, Mx2. Nota: One of the distal 3 spines of Mx2 is small and slender.
|
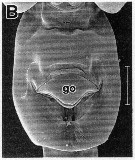 issued from : R.-M. Barthélémy in These Doct. Univ. Provence (Aix-Marseille I), 1999. [Fig.18, B]. Female (Gulf of Marseille: France): B, external ventral genital double-somite. go = genital operculum. Scale bar: 0.100 mm.
|
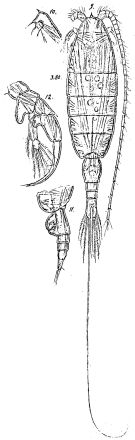
 Issued from : G.S. Brady in Rep. Scient. Results Voy. Challenger, Zool., 1883, 8 (23). [Pl. XIII]. As Heterochaeta spinifrons. Female: 1, habitus (dorsal); 2, A1; 4, A2; 5, Md; 6, Mx1; 7, Mx2; 8, Mxp; 9, exopod of P3; 11, P5; 12, urosome with spermatophore attached; 13, portion of spermarophore with spermatozoids (more highly magnified). Male: 3, left A1; 10, P5.
|
 Issued from : W. Giesbrecht in Systematik und Faunistik der Pelagischen Copepoden des Golfes von Neapel und der angrenzenden Meeres-Abschnitte. - Fauna Flora Golf. Neapel, 1892. Atlas von 54 Tafeln. [Taf. 20 , Fig.3 ]. As Heterochäta spinifrons. Male: 3, A1 (segments 1 to 16)
|
 Issued from : W. Giesbrecht in Systematik und Faunistik der Pelagischen Copepoden des Golfes von Neapel und der angrenzenden Meeres-Abschnitte. - Fauna Flora Golf. Neapel, 1892. Atlas von 54 Tafeln. [Taf. 20 , Fig.3 ]. As Heterochäta spinifrons. Male: 3, A1 (segments 15 to 25).
|
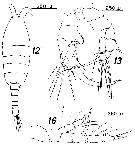 Issued from : D.F.R. Arcos in Bol. Soc. De Concepcion, 47. [p.222, Figs.12, 13, 16]. Female (from 47°59'-48°43'S, 74°04'-74°59'W): 16, P5. Male: 12, habitus (dorsal); 13, P5
|
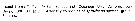 Heterorhabdus spinifrons Heterorhabdus spinifrons female: 1 - See key to species groups of Heterorhabdus: ''spinifrons'' Group (p.90, 91). 2 - Forehead with a spiniform process. 3 - Anterior wall of genital proninence without lobes (Fig.59-g, i). 4 - Dorsally, genital somite relatively short, with smoothly bulging lateral margins. Mx1 with 1 seta on basis and 3 sete on endopod (Fig.60-f). 5- Laterally, genital prominence reaching posterior end of somite, without posterior lobes (Fig.59-b).
|
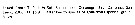 Heterorhabdus spinifrons Heterorhabdus spinifrons male: 1 - See key to species groups of Heterorhabdus: ''spinifrons'' Group (p.90, 91). 2 - Forehead with a spiniform process. 3 - In right P5, basal inner lobe relatively long and somewhat fingerlike, medial projection of 2nd exopodal segment (Fig.61-g) with small terminal spiniform process and relatively well developed distal lobe. 4 - Basal inner lobe of right P5 (Fig.61-e) almost as long as segment, pointing distomediad. Endopod of Mx1 with 3 seta. 5 - 2nd exopodal segment of left P5 (Fig.61-i) with outer spine longer than conical process as measured along medial margin. Terminal spine of 3rd exopodal segment of right P5 about 1/6 length of segment (Fig.61-e).
|
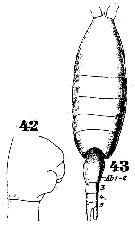 Issued from : W. Giesbrecht in Systematik und Faunistik der Pelagischen Copepoden des Golfes von Neapel und der angrenzenden Meeres-Abschnitte. – Fauna Flora Golf. Neapel, 1892. Atlas von 54 Tafeln. [Taf.39, Figs.42, 43]. As Heterochäta spinifrons. Female: 42, abdominal segments 1 and 2 (lateral); 43, habitus (dorsal).
| | | | | Ref. compl.: | | | Cleve, 1904 a (p.191); Pearson, 1906 (p.27); Wilson, 1942 a (p.190); Massuti Alzamora, 1942 (p.95, Rem.); Lysholm & al., 1945 (p.35); Sewell, 1948 (p.349, 503, 509, 516, 519, 521, 530, 534, 539, 547, 558, 567); C.B. Wilson, 1950 (p.240); King & Hida, 1955 (p.11); Fagetti, 1962 (p.30); Ganapati & Shanthakumari, 1962 (p.8, 15); V.N. Greze, 1963 a (tabl.2); Grice, 1963 a (p.496); Ahlstrom & Thrailkill, 1963 (p.57, Table 5, abundance); Björnberg, 1963 (p.53, Rem.); Unterüberbacher, 1964 (p.29); De Decker & Mombeck, 1964 (p.12); Grice & Hulsemann, 1965 (p.224); Pavlova, 1966 (p.44); Mazza, 1966 (p.71); 1967 (p.367); Fleminger, 1967 a (tabl.1); Grice & Hulsemann, 1967 (p.18); De Decker, 1968 (p.45); Morris, 1970 (p.2301); Park, 1970 (p.477); Timonin, 1971 (p.281, trophic group); Deevey, 1971 (p.224); Roe, 1972 (p.277, tabl.1, tabl.2); Bainbridge, 1972 (p.61, Appendix Table III: occurrence); Apostolopoulou, 1972 (p.328, 362); Björnberg, 1973 (p.345, 387); Guglielmo, 1973 (p.399); de Bovée, 1974 (p.109, 124); Vives & al., 1975 (p.49, tab.II, III); Deevey & Brooks, 1977 (p.256, tab.2, Station "S"); Carter, 1977 (1978) (p.36); Dessier, 1979 (p.206); Vaissière Séguin, 1980 (p.23, tab.1); Pipe & Coombs, 1980 (p.223, vertical occurrence); Vives, 1982 (p.293); Kovalev & Shmeleva, 1982 (p.84); Dessier, 1983 (p.89, Tableau 1, Rem., %); Guangshan & Honglin, 1984 (p.118, tab.); Tremblay & Anderson, 1984 (p.5: Rem.); De Decker, 1984 (p.317); Cummings, 1984 (p.163, Table 2); Scotto di Carlo & al., 1984 (1043); Regner, 1985 (p.11, Rem.: p.36); Brenning, 1985 a (p.28, Table 2); Madhupratap & Haridas, 1986 (p.105, tab.1); Lozano Soldevilla & al., 1988 (p.59); Heinrich, 1990 (p.18); Pancucci-Papadopoulou & al., 1990 (p.199); Madhupratap & Haridas, 1990 (p.305, fig.3: vertical distribution night/day; fig.7: cluster); Suarez & al., 1990 (tab.2); Suarez & Gasca, 1991 (tab.2); Suarez, 1992 (App.1); Hattori, 1991 (tab.1, Appendix); Scotto di Carlo & al., 1991 (p.270); Kouwenberg, 1994 (tab.1); Shih & Young, 1995 (p.70); Errhif & al., 1997 (p.422); Hure & Krsinic, 1998 (p.66, 102); Suarez-Morales & Gasca, 1998 a (p.110); Lapernat, 1999 (p.20, 55); 2000 (tab.3); Razouls & al., 2000 (p.343, Appendix); Lopez-Salgado & al., 2000 (tab.1); d'Elbée, 2001(tabl. 1); Lapernat & Razouls, 2001 (p.123, tab.1); Holmes, 2001 (p.16); Vukanic, 2003 (139, tab.1); Hsiao & al., 2004 (p.326, tab.1); Lo & al., 2004 (p.89, tab.1); Dias & Araujo, 2006 (p.51, Rem., chart); Dur & al., 2007 (p.197, Table IV); Neumann-Leitao & al., 2008 (p.799: Tab.II, fig.6); Fernandes, 2008 (p.465, Tabl.2); Lan Y.C. & al., 2008 (p.61, Table 1, % vs stations); Galbraith, 2009 (pers. comm.); Licandro & Icardi, 2009 (p.17, Table 4); Williamson & McGowan, 2010 (p.273, Table 3, Pacific central gyres: N and S); Schnack-Schiel & al., 2010 (p.2064, Table 2: E Atlantic subtropical/tropical); Hidalgo & al., 2010 (p.2089, Table 2); Mazzocchi & Di Capua, 2010 (p.425); Medellin-Mora & Navas S., 2010 (p.265, Tab. 2); Hsiao S.H. & al., 2011 (p.475, Appendix I); Pillai H.U.K. & al., 2011 (p.239, Table 3, vertical distribution); Hidalgo & al., 2012 (p.134, Table 2) ; in CalCOFI regional list (MDO, Nov. 2013; M. Ohman, comm. pers.); Lidvanov & al., 2013 (p.290, Table 2, % composition); Bonecker & a., 2014 (p.445, Table II: frequency, horizontal & vertical distributions); Dias & al., 2015 (p.483, Table 2, abundance, biomass, production); Benedetti & al., 2016 (p.159, Table I, fig.1, functional characters); El Arraj & al., 2017 (p.272, table 2); Benedetti & al., 2018 (p.1, Fig.2: ecological functional group); Belmonte, 2018 (p.273, Table I: Italian zones); Dias & al., 2018 (p.1, Table 5: % vs. season); | | | | NZ: | 22 | | |
|
Carte de distribution de Heterorhabdus spinifrons par zones géographiques
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |  issued from : C. de O. Dias & A.V. Araujo in Atlas Zoopl. reg. central da Zona Econ. exclus. brasileira, S.L. Costa Bonecker (Edit), 2006, Série Livros 21. [p.51]. issued from : C. de O. Dias & A.V. Araujo in Atlas Zoopl. reg. central da Zona Econ. exclus. brasileira, S.L. Costa Bonecker (Edit), 2006, Série Livros 21. [p.51].
Chart of occurrence in Brazilian waters (sampling between 22°-23° S)
Nota: sampling only 2 specimens. |
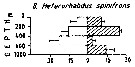 Issued from : M. Madhupratap & P. Haridas in J. Plankton Res., 12 (2). [p.310, Fig.3]. Issued from : M. Madhupratap & P. Haridas in J. Plankton Res., 12 (2). [p.310, Fig.3].
Vertical distribution of calanoid copepod (mean +1 SE), abundance No/100 m3. 8- Heterorhabdus spinifrons.
Night: shaded, day: unshaded.
Samples collected from 6 stations located off Cochin (India), SE Arabian Sea, November 1983, with a Multiple Closing Plankton Net (mesh aperture 300 µm), in vertical hauls at 4 depth intervalls (0-200, 200-400, 400-600, 600-1000 m). |
| | | | Loc: | | | Antarct. (Indian), sub-Antarct. (Indian, SE Pacif.), South Africa (E & W), Namibia, off E Tristan da Cunha, off Trinidade Is., off S St. Helena Is., Brazil, Congo, G. of Guinea, off Lagos, Cape Verde Is., off NW Cape Verde Is., off Mauritania, Morocco-Mauritania, Canary Islands, off Madeira, off Portugal, off Rio de Janeiro, Campos Basin, off Amazon, Venezuela, Caribbean Sea, Caribbean Colombia, Caribbean, G. of Mexico, Cuba, Florida, Sargasso Sea, off Bermuda (Station "S"), G. of Maine, Woods Hole, S Iceland, Wyville Thomson Ridge, off SW Ireland, Azores, Bay of Biscay, off Cabo Finisterre, Ibero-moroccan Bay, Medit. (Alboran Sea, Castellon, Banyuls, G. of Lion, Ligurian Sea, Tyrrhenian Sea, Milazzo, Messina, off Malta, Adriatic Sea, Ionian Sea, Aegean Sea, Lebanon Basin), G. of Aden, Arabian Sea, Laccadive Is., off Minicoy Is., Natal, Indian, India (Lawson's Bay), Bay of Bengal, Andaman Sea (Batten Island), S Indian (subtropical convergence), Indonesia-Malaysia, Philippines, China Seas (East China Sea, South China Sea), Taiwan (SW, E, N: Mienhua Canyon), Japan (Izu), off S Japan, off Sanriku, Nansei Is., Bering Sea, Station "P", off British Columbia, Pacif. (W equatorial), Australia (Great Barrier), N Tasman Sea, New Zealand, off S Tasmania, Pacif. (central sutropical N), off S Hawaii, off California, San Diego, W Baja California, Pacif. (equatorial), Pacific (central gyres: N and S), NE Easter Is., SE Galapagos, off Peru, Pacif. (SE tropical), Chile (N-S, off Santiago), Straits of Magellan (Pacific and Central area) | | | | N: | 148 | | | | Lg.: | | | (1) F: 3,3; (11) F: 3,433; (16) F: 3,4-2,8; M: 3,05-2,85; (17) F: 3; (22) F: 3,5-3; M: 3,4-2,95; (24) F: 4; (34) F: 2,14; M: 3,14; (35) F: 3,6; (36) F: 3,82-3,49; M: 3,59-3,43; (38) F: 3,12-2,96; M: 3,4-2,7; (45) F: 3,5-3; M: 3,3-2,95; (46) F: 3,15-3; (73) M: 3,04-2,77; (101) F: 3,57-2,1; M: 3,2-2,41; (121) F: 3,48; M: 3,19-2,95; (142) F: 3,4; (199) F: 3,5-2,74; M: 2,96-2,2; (205) M: 3,4-3,2; (207) F: 3,4-2,92; M: 3,2-2,76; (237) F: 2,5; M: 2,01; (260) F: 3,4-2,92; M: 3,16-2,88; (340) F: 3; (432) F: 3,8-3,3; (449) F: 3,4-3; M: 3,4-2,95; (808) F: 3,46-3,07; (824) F: 4-3,04; M: 3,84-3; (909) F: 3,4-3,9; M: 2,6-3,5; {F: 2,10-4,0; M: 2,01-3,84} | | | | Rem.: | "Spinifrons" Group.
épi à bathypélagique.
Sampling depth (Antarct., sub-Antarct.) : 0-600 m.
Des confusions sont possibles par les anciens auteurs entre cette espèce et les nouvelles espèces décrites par Park (2000) en Indo-Pacifique.
Voir aussi les remarques en anglais | | | Dernière mise à jour : 24/10/2022 | |
|
|
 Toute utilisation de ce site pour une publication sera mentionnée avec la référence suivante : Toute utilisation de ce site pour une publication sera mentionnée avec la référence suivante :
Razouls C., Desreumaux N., Kouwenberg J. et de Bovée F., 2005-2026. - Biodiversité des Copépodes planctoniques marins (morphologie, répartition géographique et données biologiques). Sorbonne Université, CNRS. Disponible sur http://copepodes.obs-banyuls.fr [Accédé le 11 février 2026] © copyright 2005-2026 Sorbonne Université, CNRS
|
|
 |
 |