|
|
 |
Fiche d'espèce de Copépode |
|
|
Calanoida ( Ordre ) |
|
|
|
Arietelloidea ( Superfamille ) |
|
|
|
Heterorhabdidae ( Famille ) |
|
|
|
Paraheterorhabdus ( Genre ) |
|
|
|
Antirhabdus ( Sous-Genre ) |
|
|
| |
Paraheterorhabdus (Antirhabdus) compactus (Sars, 1900) (F,M) | |
| | | | | | | Syn.: | Heterochaeta compacta Sars, 1900 (p.83, Descr.F, figs.F);
? Heterorhabdus brevicornis : Farran, 1926 (p.284, Rem.F);
Heterorhabdus compactus Sars, 1925 (p.226, figs.F,M); Farran, ? 1926 (p.284); 1929 (p.209, 267, Rem.); Rose, 1933 a (p.202, figs.F,M); Jespersen, 1934 (p.107); Lysholm & al., 1945 (p.35); Farran, 1948 e (n°16, p.3, figs.F,M); Brodsky, 1950 (1967) (p.348, figs.F,M); Grice, 1963 a (p.496); M.W. Johnson, 1963 (p.89, Table 1, 2); Tanaka, 1964 a (p.21, figs.F,M); Vidal, 1971 a (p.11, 22, 115, figs.F, M); Heptner, 1971 (p.154, figs.F,M); Harding, 1974 (p.141, tab.2, gut contents); Kos, 1976 (Vol. II, figs.F,M, Rem.); Deevey & Brooks, 1977 (p.256, tab.2, Station "S"); Björnberg & al., 1981 (p.650, figs.F,M); Roe, 1984 (p.358); Wiebe & al., 1988 (tab.7); Hattori, 1991 (tab.1, Appendix); Razouls, 1994 (p.161, figs.F,M); Shih & Young, 1995 (p.70); Nishida & Ohtsuka, 1996 (p.620); Kosobokova & al., 1998 (tab.2); Bradford-Grieve & al., 1999 (p.883, 944, figs.F,M); Kosobokova & Hirche, 2000 (p.2029, tab.2); Yamaguchi & al., 2002 (p.1007, tab.1); Auel & Hagen, 2002 (p.1013, tab.2); Hopcroft & al., 2005 (p.198, table 2); Vives & Shmeleva, 2007 (p.301, figs.F,M, Rem.); Khelifi-Touhami & al., 2007 (p.327, Table 1); Blachowiak-Samolyk & al., 2007 (p.2716, Table 2); Blachowiak-Samolyk & al., 2008 (p.2210, Table 3, biomass); Wishner & al., 2008 (p.163, Table 2, fig.8, oxycline); Gaard & al., 2008 (p.59, Table 1, N Mid-Atlantic Ridge); Galbraith, 2009 (pers. comm.); Homma & Yamaguchi, 2010 (p.965, Table 2)
Heterorhabdus (Paraheterorhabdus) compactus : Chihara & Murano, 1997 (p.819, Pl.122: F,M);
Ref. compl.: Damas & Koefoed, 1907 (p.400, tab.II); Hardy & Gunther, 1935 (1936) (p.181, Rem.); VWilson, 1942 a (p.190); Sewell, 1948 (p.349, 503, 512, 514, 567, 569); Fagetti, 1962 (p.30); De Decker & Mombeck, 1964 (p.12); Grice & Hulsemann, 1965 (p.224); Harding, 1966 (p.17, 66, 71); Grice & Hulsemann, 1967 (p.18); Dunbar & Harding, 1968 (p.319); Vinogradov, 1968 (1970) (p.201); Park, 1970 (p.477); Deevey, 1971 (p.224); Roe, 1972 (p.277, tabl.1, tabl.2); Björnberg, 1973 (p.345, 387); Vives & al., 1975 (p.50, tab.II, XII); Carter, 1977 (1978) (p.36); Vives, 1982 (p.293); Kosobokova, 1989 (p.26); Heinrich, 1990 (p.18); Mumm, 1993 (tab.1, fig.2); Richter, 1994 (tab.4.1a); Hanssen, 1997 (tab.3.1); Lapernat, 2000 (tabl.3, 4); Razouls & al., 2000 (p.343, Appendix); Kosobokova & Hirche, 2000 (p.2029, tab.2); Hop & al., 2006 (p.182, Table 4); Bucklin & al., 2010 (p.40, Table 1, Biol mol.); Homma & al., 2011 (p.29, Table 2, 3, abundance) | | | | Ref.: | | | Park, 2000 (p.85, figs.F,M, Rem.); Blanco-Bercial & al., 2011 (p.103, Table 1, Biol. mol, phylogeny) | 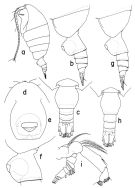 issued from : T. Park in Bull. Scripps Inst. Oceanogr. Univ. California, San Diego, 2000, 31. [p.208, Fig.56]. Female: a, habitus (left side); b, c, urosme of a small specimen ( Prosome length = 1,96), left, dorsal, respectively; d, forehead (dorsal); e, f, genital somite (ventral, left, respectively); g, h, urosome of a large specimen (PL = 2,32), left, dorsal, respectively; i, left A2 (posterior).
|
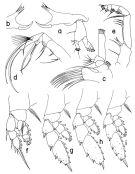 issued from : T. Park in Bull. Scripps Inst. Oceanogr. Univ. California, San Diego, 2000, 31. [p.209, Fig.57]. Female: a, left Md (posterior); b, masticatory edge of right Md (posterior); c, left Mx1 (posterior); d, left Mx2 (posterior); e, right Mxp (anterior); f, P1; g, P2; h, P3; i, P4. P1-4 = swimming legs 1-4 (anterior).
|
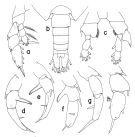 issued from : T. Park Bull. Scripps Inst. Oceanogr. Univ. California, San Diego, 2000, 31. [p.210, Fig.58].
Female: a, P5 (anterior).
Male: b, urosome (dorsal); c, P5 (with exopods omitted), anterior; d, e, f, exopod of right P5 (anterior, posterior, tilted clockwise, respectively); g, h, exopod of left P5 (anterior, tilted counterclockwise, respectively).)
|
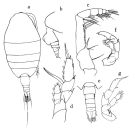 issued from : O. Tanaka in Publs Seto Mar. Biol. Lab., 1964, XII (1). [p.22, Fig.184]. As Heterorhabdus compactus. Female: a, habitus (dorsal); b, last thoracic segment and urosome (lateral left side); c, Mxp; d, P5. Nota: The urosome segments and furca are in the proportional lengths as 47:9:9:13:22 = 100. A1 extends to themiddle of the last thoracic segment. Male: e, urosome (dorsal); f, right P5; g, left P5. Nota: The lateral margin of the 2nd urosomal segment is furnished with two groups of short hairs on the right side.
|
 Issued from : G.O. Sars in Résult. Camp. Scient. Prince Albert I, 69, pls.1-127 (1924). [Pl.LXII, figs.1-8]. As Heterorhabdus compactus. Female: 1, habitus (dorsal); 2, idem (lateral left side); 3, right Md (biting edge); 4, left Md (biting edge); 5, P5; 6, anal segment and caudal rami. Male: left A1; 8, P5.
|
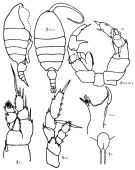 Issued from : K.A. Brodskii in Calanoida of the Far Eastern Seas and Polar Basin of the USSR. Opred. Fauna SSSR, 1950, 35 (Israel Program for Scientific Translations, Jerusalem, 1967) [p.348, Fig.244]. As Heterorhabdus compactus. Female (from central Arctic): habitus (dorsal and lateral right side); R, rostrum; MLe, Md (biting edge, left side view); S1, P1; S5, P5. Male (from NW pacif.): S5, P5 (Le = left leg).
|
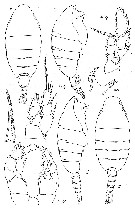 issued from : M.V. Heptner in Trudy. Inst. Okeanol., 1971, 92. [p.155, Fig.38]. As Heterorhabdus compactus. Female & Male (from Kuril-kamchatka Trench).
|
 Issued from : C. Razouls in Ann. Inst. océanogr., Paris, 1994, 70 (1). [p.161]. As Heterorhavdus compactus. Caractéristiques morphologiques de Paraheterorhabdus compactus femelle et mâle adultes. Terminologie et abbréviations: voir à Calanus propinquus.
| | | | | Ref. compl.: | | | Park & Ferrari, 2009 (p.143, Table 5, Appendix 1, biogeography); Dvoretsky & Dvoretsky, 2010 (p.991, Table 2); Kosobokova & Hopcroft, 2010 (p.96, Table 1, fig.7); Kosobokova & al., 2011 (p.29, Table 2, figs.4, 8, Rem.: Arctic Basins); Smoot & Hopcroft, 2016 (p.1, fig.7, vertical distribution) | | | | NZ: | 17 | | |
|
Carte de distribution de Paraheterorhabdus (Antirhabdus) compactus par zones géographiques
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Loc: | | | Antarct. (SW Atlant., SW Pacif.), South Georgia, sub-Antarct. (SW Atlant.), South Africa (E), S Atlant., off NW Cape Verde Is., Morocco-Mauritania, Canary Is., off Madeira off Portugal, Ibero-moroccan Bay, off W Cabo Finisterre, Azores, SW Atlant., Brazil, Caribbean Sea, G. of Mexico, Sargasso Sea, off Bermuda: Station ‘’ S’’ (32°10’N, 64°30’W), off E Cape Cod, S Davis Strait, Fram Strait, Spitsbergen, Greenland Sea, S Iceland, Arct. (Barents Sea, Laptev Sea, Nansen Basin, Amundsen Basin, Makarov Basin,, Fletcher's Ice Is., Canadian abyssal plain, Lomonosov Ridge, Chukchi Sea, Canada Basin), ? Bay of Biscay, W Gibraltar, W Medit. (Gulf of Annaba), Natal, Madagascar (Nosy Bé), Arabian Sea, S Indian, Indonesia-Malaysia, China Seas (South China Sea), Japan, Nansei Is., Kuril Is., Bering Sea (Aleutian Basin), S Aleutian Is., Station Knot, off British Columbia, off N California, Guaymas Basin, Pacif. (SE tropical), off SE Easter Is., N Chile | | | | N: | 64 | | | | Lg.: | | | (1) F: 2,3; (22) F: 3,4-3; M: 3,4-2,9; (23) F: 3,5-2,9; M: 3,6-2,95; (35) F: 3,2; M: 2,88; (121) M: 2,59; (134) F: 3,35; (199) F: 2,58-2,28; M: 2,13-1,98; (377) F: 3,29; M: 2,98; (808) F: 2,9-2,36; (824) F: 3,32-2,24; M: 3,2-2,08; (1232) F: 2,9-3,5; M: 2,9-3,6; {F: 2,24-3,50; M: 1,98-3,60} | | | | Rem.: | Abyssale & bathypélagique.
Sampling depth (Antarct., sub-Antarct.) : 250-1000 m.
(méso-bathypélagique in Roe, 1972; 1984).
Pour Park (2000, p.88), cette espèce pourrait constituer des variétés ou sous-espèces.
Voir aussi les remarques en anglais | | | Dernière mise à jour : 07/12/2020 | |
|
|
 Toute utilisation de ce site pour une publication sera mentionnée avec la référence suivante : Toute utilisation de ce site pour une publication sera mentionnée avec la référence suivante :
Razouls C., Desreumaux N., Kouwenberg J. et de Bovée F., 2005-2026. - Biodiversité des Copépodes planctoniques marins (morphologie, répartition géographique et données biologiques). Sorbonne Université, CNRS. Disponible sur http://copepodes.obs-banyuls.fr [Accédé le 14 mars 2026] © copyright 2005-2026 Sorbonne Université, CNRS
|
|
 |
 |