|
|
 |
|
Calanoida ( Order ) |
|
|
|
Diaptomoidea ( Superfamily ) |
|
|
|
Pontellidae ( Family ) |
|
|
|
Pontella ( Genus ) |
|
|
| |
Pontella mediterranea (Claus, 1863) (F,M) | |
| | | | | | | Syn.: | Pontellina mediterranea Claus, 1863 (p.211, figs.M);
? Pontella mediterranea indica Wolfenden, 1905 (1906) (p.1021, Rem.F);
Pontellina mediterranea jaltensis Czerniavski,1868;
Pontella mediterranea jaltensis (Czerniavski, 1868);
no Pontella mediterranea gaboonensis : T. Scott, 1894 b (p.86) | | | | Ref.: | | | Giesbrecht, 1892 (p.461, 478, 774, figs.F,M); Thompson, 1888 d (p.143, figs.F,M); Giesbrecht & Schmeil, 1898 (p.143, Rem. F,M); Karavaev, 1894 (p.27, fig.M, Rem.); Pesta, 1920 (p.543); Sars, 1925 (p.353); Rose, 1929 (p.45), 1933 a (p.259, figs.F,M); Crisafi, 1960 e (p.293, figs.F,M, juv.); Porumb, 1970 (fiche CIESMM n°34); Razouls, 1972 (p.95, Annexe: p.92); Silas & Pillai, 1973 (1976) (p.776, 833: Rem); Sazhina, 1985 (p.74, figs.N); Santella & Ianora, 1990 (p.83, subitaneous and diapause eggs); Ianora & al., 1992 (p.401, fig.); Barthélémy & al., 1998 (p.721, genital area); Barthélémy, 1999 a (p.9, Fig.7, A); Lapernat & Razouls, 2002 (p.17, Pl. VI: Md); Avancini & al., 2006 (Pl. 73, figs.F,M, Rem.);Vives & Shmeleva, 2007 (p.514, figs.F,M, Rem.) | 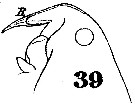 Issued from : W. Giesbrecht in Systematik und Faunistik der Pelagischen Copepoden des Golfes von Neapel und der angrenzenden Meeres-Abschnitte. – Fauna Flora Golf. Neapel, 1892. Atlas von 54 Tafeln. [Taf.40, Fig.39]. Female: forehead (lateral). R = rostrum.
|
 Issued from : W. Giesbrecht in Systematik und Faunistik der Pelagischen Copepoden des Golfes von Neapel und der angrenzenden Meeres-Abschnitte. – Fauna Flora Golf. Neapel, 1892. Atlas von 54 Tafeln. [Taf.24, Fig.48]. Frmale: 48, P5 (anterior view).
|
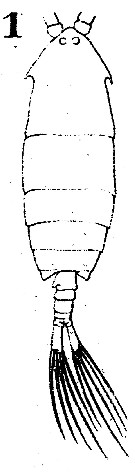 Issued from : W. Giesbrecht in Systematik und Faunistik der Pelagischen Copepoden des Golfes von Neapel und der angrenzenden Meeres-Abschnitte. – Fauna Flora Golf. Neapel, 1892. Atlas von 54 Tafeln. [Taf.40, Fig.1]. Male: habitus (dorsal).
|
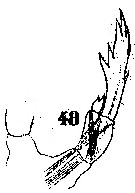
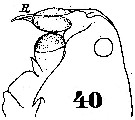 Issued from : W. Giesbrecht in Systematik und Faunistik der Pelagischen Copepoden des Golfes von Neapel und der angrenzenden Meeres-Abschnitte. – Fauna Flora Golf. Neapel, 1892. Atlas von 54 Tafeln. [Taf.40, Fig.40]. Male: forehead (lateral. R = rostrum.
|
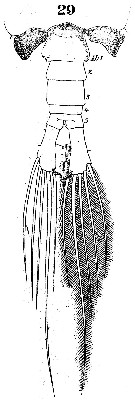 Issued from : W. Giesbrecht in Systematik und Faunistik der Pelagischen Copepoden des Golfes von Neapel und der angrenzenden Meeres-Abschnitte. – Fauna Flora Golf. Neapel, 1892. Atlas von 54 Tafeln. [Taf.40, Fig.29]. Male: 29, Th5 and urosome (dorsal).
|
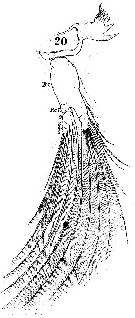 Issued from : W. Giesbrecht in Systematik und Faunistik der Pelagischen Copepoden des Golfes von Neapel und der angrenzenden Meeres-Abschnitte. – Fauna Flora Golf. Neapel, 1892. Atlas von 54 Tafeln. [Taf.24, Fig.20]. Male; 20, Md (posterior view).
|
 Issued from : W. Giesbrecht inMale: 16, Md (masticatory edge).
|
 Issued from : W. Giesbrecht in Systematik und Faunistik der Pelagischen Copepoden des Golfes von Neapel und der angrenzenden Meeres-Abschnitte. – Fauna Flora Golf. Neapel, 1892. Atlas von 54 Tafeln. [Taf.24, Fig.21]. Male: 21, P1 (posterior view).
|
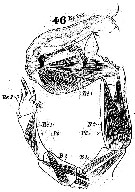 Issued from : W. Giesbrecht in Systematik und Faunistik der Pelagischen Copepoden des Golfes von Neapel und der angrenzenden Meeres-Abschnitte. – Fauna Flora Golf. Neapel, 1892. Atlas von 54 Tafeln. [Taf.24, Fig.46]. Male: 46, P5 (posterior view).
|
 Issued from : W. Giesbrecht in Systematik und Faunistik der Pelagischen Copepoden des Golfes von Neapel und der angrenzenden Meeres-Abschnitte. – Fauna Flora Golf. Neapel, 1892. Atlas von 54 Tafeln. [Taf.24, Fig.47]. Male: left P5 (posterior view).
|
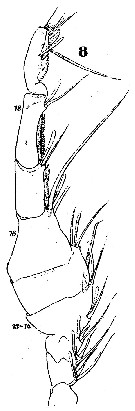 Issued from : W. Giesbrecht in Systematik und Faunistik der Pelagischen Copepoden des Golfes von Neapel und der angrenzenden Meeres-Abschnitte. – Fauna Flora Golf. Neapel, 1892. Atlas von 54 Tafeln. [Taf.24, Fig.8]. Male: 8, right A1
|
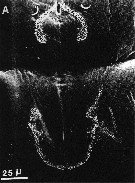 issued from : A. Ianora, A. Miralto & S. Vanucci in Mar Biol., 1992, 113. [p.403, Fig.2, A]. SEM micrographs. Female & Male: A, surface attachment structure (mass of fine setules arranged in two semicircles on a flattened area of the anterodorsal surface of the cephalosome). For the interpretation of this structure: see in Anomalocera patersoni.
|
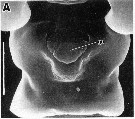 issued from : R.-M. Barthélémy in Thèse Doct. Univ. Provence (Aix-Marseille I), 1999. [Fig.7, A]. Female (off Banyuls, Gulf of Lion): external ventral view genital double-somite. Scale bar: 0.050 mm.
|
 issued from : P.E. Lapernat & C. Razouls in Vie Milieu, 2002, 52 (1). [p.28, Pl. VI, fig.9]. Masticatory edge of Md gnathobase female (from off Malta, Mediterranean Sea). Nota: Itoh's index: 564 (number of teeth : 7) .
|
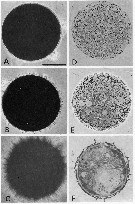 issued from : L. Santella & A. Ianora in Mar. Biol., 1990, 105. [p.84, Fig.1]. Pontella mediterranea. A: Subitaneous eggs with a smooth surface and B: those covered with short spines. C: Diapause eggs with thick spikes. D to F: Corresponding histological sections showing the presence of a thin outer coat enveloping smooth eggs (D) as compared to the multilayered structure in subitaneous eggs with short spines (E) or diapause eggs (F). Scale bar = 0.050 mm.
|
 issued from : R.-M. Barthélémy in Thèse Doct. Univ. Provence (Aix-Marseille I), 1999. [Fig.7, A]. Female (off Banyuls, Gulf of Lion): external ventral view genital double-somite. Scale bar: 0.050 mm.
| | | | | Compl. Ref.: | | | Rose, 1925 (p.152); Massuti Alzamora, 1942 (p.97, Rem.); Demir, 1959 (p.176, Rem.); Giron-Reguer, 1963 (p.53); Mazza, 1964 (p.293, weight); Shmeleva, 1965 b (p.1350, lengths-volume -weight relation); Pavlova, 1966 (p.44); Chakroun, 1966 (p.67, Tableau); Mazza, 1966 (p.72); 1967 (p.329, 360, 377); Ehrhardt, 1967 (p.741, geographic distribution, Rem.); Evans, 1968 (p.14); Specchi, 1968 (p.491); Sazhina, 1968 (p.1554, resting eggs); Champalbert, 1969 a (p.598); Kovalev, 1969 a (p.174); 1970 a (p.87, Tableau 1, 2, comparison hyponeustonic & planctonic forms); Marcus, 1970 (p.10); Morris R.J., 1971 (p.275, lipids composition); Carli, 1971 (p.372, tab.1); Apostolopoulou, 1972 (p.328, 368, Rem.); Desgouille, 1973 (p.1, Rem.: p.141); Guglielmo, 1973 (p.399); Vives & al., 1975 (p.53, IV); Weikert, 1975 (p.137, chart); Champalbert & al., 1976 (1978) (p.263, geographic size comparison); 1978 (p.215, weight -CHN); Champalbert & Kerambrun, 1979 (p.357, weight-chimic composition v.s. conservation effect); Vaissière & Séguin, 1980 (p.23, tab.1); Grice & Marcus, 1981 (p.125, Dormant eggs, Rem.: p.134); Grice & Gibson, 1981 (1982) (p.49, eggs instantaneous and diapause); Vives, 1982 (p.295); Kovalev & Shmeleva, 1982 (p.85); Moraitou-Apostolopoulou, 1985 (p.303, occurrence/abundance in E Mediterranean Sea, Rem.: p.316); Regner, 1985 (p.11, Rem.: p.38); Jansa, 1985 (p.108, Tabl.I, II, III, IV); Comaschi Scaramuzza, 1987 (tab.1); Lozano Soldevilla & al., 1988 (p.60); Romano & al., 1996 (p.157, metabolism, diapause); Madhupratap & al., 1996 (p.77, Table 2: resting eggs); Marcus, 1996 (p.144); Hure & Krsinic, 1998 (p.103); Mauchline, 1998 (tab.40, 46); Lapernat, 1999 (p.26); Siokou-Frangou, 1999 (p.478); Seridji & Hafferssas, 2000 (tab.1); Plounevez & Champalbert, 2000 (p.175, Table III, IV, abundance vs fish); Lapernat & Razouls, 2001 (p.123, tab.1); Vukanic, 2003 (p.139, tab.1); Kovalev, 2003 (p.47); Zagorodnyaya & al., 2003 (p.52); Daly Yahia & al., 2004 (p.366, fig.4); Isari & al., 2006 (p.241, tab.II); Khelifi-Touhami & al., 2007 (p.327, Table 1); Hafferssas & Seridji, 2010 (p.353, Table 2); Mazzocchi & Di Capua, 2010 (p.427); Hafferssas & al., 2010 (p.1281, Table III, abundance vs spatial distribution); Gubanova & al., 2013 (in press, Rem.: p.7, Table 4); Lidvanov & al., 2013 (p.290, Table 2, % composition); Benedetti & al., 2016 (p.159, Table I, fig.1, functional characters); Belmonte, 2018 (p.273, Table I: Italian zones) | | | | NZ: | 2 + 1 doubtful | | |
|
Distribution map of Pontella mediterranea by geographical zones
|
| | | | | | | | |  issued from : A.A. Shmeleva in Bull. Inst. Oceanogr., Monaco, 1965, 65 (n°1351). [Table 6: 35 ]. Pontella mediterranea (from South Adriatic). issued from : A.A. Shmeleva in Bull. Inst. Oceanogr., Monaco, 1965, 65 (n°1351). [Table 6: 35 ]. Pontella mediterranea (from South Adriatic).
Dimensions, volume and Weight wet. Means for 50-60 specimens. Volume and weight calculated by geometrical method. Assumed that the specific gravity of the Copepod body is equal to 1, then the volume will correspond to the weight. |
 Issued from : R. J. Morris in Comp. Biochem. Physiol., 1971, 40B. [p.277, Table 1]. Issued from : R. J. Morris in Comp. Biochem. Physiol., 1971, 40B. [p.277, Table 1].
Total lipid and saponification for Pontella mediterranea from the Mediterranea Sea. |
| | | | Loc: | | | Morocco-Mauritania, off E Canary Is., Ibero-moroccan Bay, Medit. (Alboran Sea, Algiers, Gulf of Annaba, Banyuls, G. of Lions, Marseille, Toulon Harbour, Villefranche-s-Mer, Ligurian Sea, Genova, Tyrrhenian Sea, Gulf of Napoli, Milazzo, Messina, Malta, Tripoli, Adriatic Sea, Venice, Ionian Sea, Aegean Sea, Dardanelles, Marmara Sea, Black Sea (rare), Lebanon Basin), ? Laccadive-Maldive Islands (in Wolfenden, 1905 (1906) (p.1021) | | | | N: | 69 | | | | Lg.: | | | (46) F: 3-2,9; M: 2,85-2,7; (340) M: 2,4; (449) F: 3-2,9; M: 2,85-2,7; (478) F: 3,265-2,796; M: 2,612-2,556; (789) [Gulf of Marseille] F: 2,81-2,77; M: 2,54-2,50; [Black Sea: Bosphore] F: 2,785-2,755; M: 2,50-2,46; {F: 2,755-3,265; M: 2,400-2,850} | | | | Rem.: | epipelagic; 2000 m (off Malta).
Silas and Pillai (1973, p.833) remark: Two varieties have been described the first, var. jaltensisindica. Wolfenden's bief description of var. indica is based on a single female 3.1 mm long which is said to differ from the typical female as described by Giesbrecht (1892, Pl.24, fig.48) in the size of the external spines of the exopod of P5, as well as the size and structure of the endopodites. There is no subsequent record of this variety from the Indian Ocean. Sewell (1948, p.432) remarked that the record of occurrence of Anomalocera patersoni, Pontella mediterranea and Parapontella brevicornis from the Maldive and the Laccadive by Wolfenden (1906) could be explained by accidental mixing of collections from this region and the Atlantic Ocean.
Demir (1959) found large numbers of the species on the northeast coast of the Aegean Sea during spring and early summer and concludes that the species hyponeustonic is transported from the Aegean to the Black Sea
After Romano & al. (1996) from copepods collected in the Bay of Naples and maintened at 20°C show a diapause. | | | Last update : 07/06/2020 | |
|
|
 Any use of this site for a publication will be mentioned with the following reference : Any use of this site for a publication will be mentioned with the following reference :
Razouls C., Desreumaux N., Kouwenberg J. and de Bovée F., 2005-2026. - Biodiversity of Marine Planktonic Copepods (morphology, geographical distribution and biological data). Sorbonne University, CNRS. Available at http://copepodes.obs-banyuls.fr/en [Accessed February 28, 2026] © copyright 2005-2026 Sorbonne University, CNRS
|
|
 |
 |