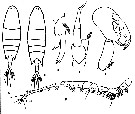|
|
 |
|
Calanoida ( Ordre ) |
|
|
|
Diaptomoidea ( Superfamille ) |
|
|
| |
| | | |
| Pontellidae Dana, 1853 ( Diaptomoidea ) | | Syn.: | Pontellinae Dana,1853 | | Ref.: | Claus, 1863 (p.93, 202); Giesbrecht, 1892 (p.30, 68); Giesbrecht & Schmeil, 1898 (p.131); Sars, 1902 (1903) (p.137); Esterly, 1905 (p.198); van Breemen, 1908 a (p.148); Gurney, 1931 a (p.64); Rose, 1933 a (p.256); Mori, 1937 (1964) (part., p.87, clé des G.); Brodsky, 1950 (1967) (p.81, 407); Gonzalez & Bowman, 1965 (p.253); Silas & Pillai, 1973 (1976) (p.772, 778, 779, Genera key); Andronov, 1974 a (p.1005); Björnberg & al., 1981 (p.657); Razouls, 1982 (p.549); Bowman & Abele, 1982 (p.9); Brodsky & al., 1983 (p.141, 145); Sazhina, 1985 (p.67, Nauplii); Mauchline, 1988 (p.715: cuticular pores); Zheng Zhong & al., 1984 (1989) (p.252, Genera key); Huys & Boxshall, 1991 (p.419); Razouls, 1993 (p.307); Madhupratap & al., 1996 (p.863, Table 5: %/copepods); Chihara & Murano, 1997 (p.865); Barthélémy, 1999 a (p.22); Bradford-Grieve & al., 1999 (p.885, 901, 904, 957, 958: Genera key); Bradford-Grieve, 1999 b (p.179, Def., Rem.); Ohtsuka & Huys, 2001 (p.461); Mulyadi, 2002 (p.22, Def.): Boxshall & Halsey, 2004 (p.12; 49; 162: Def.; p.164: Genera key); Vives & Shmeleva, 2007 (p.486, part., Key Genera key); Blanco-Bercial & al., 2011 (p.103, Table 1, Fig.2, 3, 4, Biol. mol, phylogeny); Laakmann & al., 2019 (p.330, fig. 2, 3, phylogenetic relationships)
Bradford-Grieve J.M., (2002 onwards). Key to calanoid copepod families. Version 1 : 2 oct 2002. http://www.crustacea.net/crustace/calanoida/index.htm  | | Rem.: | After Madhupratap & al. (1996), la famille des Pontellidae représente de 0,1 à 3,3 % des copepodes selon la saison dans la couche de mélange des eaux océaniques de la région ouest de l'Inde (Mer Arabe), en usant un filet type Multiple Plankton Closing Net à 200 µm de vide de maille (mesh aperture).
8 G.: Anomalocera, Calanopia, Epilabidocera, Ivellopsis, Labidocera, Pontella, Pontellina, Pontellopsis. |  Issued from : G.A. Boxshall & S.H. Halsey in An Introduction to Copepod Diversity. The Ray Society, 2004, No 166, Part. I. [p.162]. Armature formula of swimming legs P1 to P4. | | | | | (1) Anomalocera Templeton, 1837 | |
| | Syn.: | Irenaeus Goodsir, 1843; Claus, 1863 (p.204) | | Ref.: | Lubbock, 1853 b (p.165); Brady, 1878 (p.14); Giesbrecht, 1892 (p.72, 479); Giesbrecht & Schmeil, 1898 (p.145); Sars, 1902 (1903) (p.138); van Breemen, 1908 a (p.153); Wilson, 1932 a (p.142); Rose, 1933 a (p.256); Tanaka, 1964 c (p.266); Bradford, 1972 (p.30); Silas & Pillai, 1973 (1976) (p.772); Razouls, 1982 (p.582); Mauchline, 1988 (p.713); Huys & Boxshall, 1991 (p.51, 68); Razouls, 1993 (p.307); Mauchline, 1998 (p.95); Boxshall & Halsey, 2004 (p.164); Vives & Shmeleva, 2007 (p.487) | | Rem.: | Type : Anomalocera patersoni Templeton, 1837. Total: 3 spp. | | Remarques sur les dimensions et le sex-ratio: | | The mean female size is 3.655 mm (n = 6; SD = 0.9534), and the mean male size 3.475 mm (n = 6; SD = 0.7401). The size ratio (male: female) is 0.916 (n = 3; SD = 0.9539). The sex ratio (female: male) is 1. | 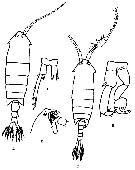 Issued from : F. Vives & Shmeleva inFauna Iberica, 2007, 29. [p.488, Fig. 264]. Anomalocera patersonii after Sars in Rose, 1933a. Female: A, habitus (dorsal view); B, P5. Male: C, habitus (dorsal view); D, forehead (lateral view); E, P5. | | | | | (2) Calanopia Dana, 1853 (part.) | |
| | Syn.: | Pontella (part.) : Dana,1846 | | Ref.: | Giesbrecht, 1892 (p.69, 441); Giesbrecht & Schmeil, 1898 (p.131); A. Scott, 1909 (p.175); Pesta, 1912 a (p.51, spp. key); Sewell, 1932 (p.340); Wilson, 1932 a (p.559); Mori, 1937 (1964) (p.88); Tanaka, 1964 c (p.250); Carvalho, 1952 a (p.149); Gonzalez & Bowman, 1965 (p.253); Bayly & Greenwood, 1966 (p.99, 104); Owre & Foyo, 1967 (p.96); Silas & Pillai, 1973 (1976) (Key of groups, p.773, 779 & suiv.); Razouls, 1982 (p.549); Zheng Zhong & al., 1984 (1989) (p.252, spp. Key); Mauchline, 1988 (p.713: cuticular pores); Ferrari, 1992 (p.392, tab.3); Razouls, 1993 (p.307); Mulyadi & Ueda, 1996 (p.914, spp. key); Chihara & Murano, 1997 (p.865); Mauchline, 1998 (p.95); Bradford-Grieve & al., 1999 (p.958, spp. Key); Bradford-Grieve, 1999 b (p.181, Def.); Ünal & Shmeleva, 2002 (p.8); Mulyadi, 2002 (p.23, 29, key p.31): Bradford-Grieve, 2004 (p.287); Boxshall & Halsey, 2004 (p.164); Vives & Shmeleva, 2007 (p.489, spp. Key); Al-Aidaroos & al., 2016 (p.17, Key to species: p.28-30); El-Sherbiny & Al-Aidaroos, 2017 (Rem., Table 2. on line) | | Rem.: | type: Pontella elliptica Dana,1849. Total: 17 spp. | | Remarques sur les dimensions et le sex-ratio: | | The mean female size is 1.768 mm (n = 32; SD = 0.4644), and the mean male size is 1.690 mm (n = 28; SD = 0.4352). The size ratio (Male: Female) is 0.92 (n = 15; SD = 0.647). The sex-ratio (Female: Male) is 1. | 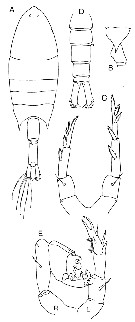 Issued from : J.M. Bradford-Grieve in NIWA Biodiv. Mem., 111, 1999. [p.185, Fig.134] from A. Scott (1909). Type species. Female: A, habitus (dorsal view); B, last thoracic segment and genital segment (left side); C, P5. Male: D, urosome (dorsal view); E, P5 (L = left leg; R = right leg). |
 Issued from : M. M. El-Sherbiny & A.M. Al-Aidaroos in Mar. Biodiv., 2017 [Table 2]. Summary list and characters of the species groups of the genus Calanopia. Nota: The genus Calanopia was subdivided into several groups by Bayly & Greenwood (1966), Silas & Pillai (1973) and Mulyadi & Ueda (1996) as shown in the table. However, these authors were unable to place C. media, C. sarsi, C. sewelli and C. tulina into one of the groups. | | | | | (3) Epilabidocera C.B. Wilson, 1932 | |
| | Syn.: | Paralabidocera : McMurrich,1916 (nom preoc.) | | Ref.: | C.B. Wilson, 1932 a (p.558); Davis, 1949 (p.63); Brodsky, 1950 (1967) (p.407, 413); Vervoort, 1951 (p.148, Rem.); Park, 1966 a (p.130, Rem.); Silas & Pillai, 1973 (1976) (p.772, 773); Razouls, 1982 (p.585); Gardner & Szabo, 1982 (p.409); Ferrari, 1992 (p.392, tab.3); Razouls, 1993 (p.307); Chihara & Murano, 1997 (p.871); Mauchline, 1998 (p.66: p.95: F); Bradford-Grieve, 1999 b (p.186, Def., Rem.); Boxshall & Halsey, 2004 (p.164) | | Rem.: | Type : Paralabidocera amphitrites McMurrich, 1916. Total: 1 or 2 spp. | | Remarques sur les dimensions et le sex-ratio: | | For only one or two species in the genus: the mean female size is 3.668 mm (n = 6; SD = 0,3814), and the mean male size is 2.914 mm (n = 7; SD = 0.4757). The size ratio (male: female) is 0.78 (n = 3; SD = 0.0372). The sex ratio is nearest of 1. | 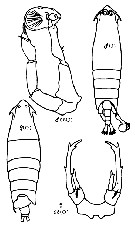 Issued from : K.A. Brodskii in fauna of USSR, Zool. Inst. Acad. Sci. USSR, 1950 (1967), 35. [p.413, Fig. 293]. Epilabidocera amphitrites (= Epilabidicera longipedata): Female and male. | | | | | (4) Ivellopsis Claus, 1893 | |
| | Ref.: | Giesbrecht & Schmeil,1898 (p.139); Wilson, 1932 a (p.558); Mori, 1937 (1964) (p.88); C.B. Wilson, 1950 (p.301, Rem.); Wickstead & Krishnaswamy, 1964 (p.27); Silas & Pillai, 1973 (1976) (p.772); Razouls, 1982 (p.583); 1993 (p.307); Mauchline, 1998 (p.66); Boxshall & Halsey, 2004 (p.164) | | Rem.: | Type: Pontella elephas Brady,1883. 2 spp. | | Remarques sur les dimensions et le sex-ratio: | | The mean female size is 3.127 mm (n = 4, SD = 0.2627), and the mean male size is 2.902 mm. (n = 4, SD = 0.3291). The size ratio (male: female) is 0.928. The sex ratio (male: female) is 1. |  Issued from : G.S. Brady in Rep. scient. Results Voy. Challenger, Zool., 1883, 8 (23). [Pl. XXXVIII, Figs.7-14). As Pontella elephas. Type species. Female: 8, A1; 12, P5; 14, urosome. Male: 7, habitus (dorsal view); 9, right A1; 10-11, teeth of denticulated plate on A1 (more hifgly magnified); 13, P5. | | | | | (5) Labidocera Lubbock, 1853 | |
| | Ref.: | Lubbock, 1853 (1854) (p.25) ; 1853 a (1854) (p.202); Giesbrecht, 1892 (p.70, 444); Giesbrecht & Schmeil, 1898 (p.132, spp. Key); Wheeler, 1901 (p.178); Sars, 1902 (1903) (p.141); Esterly, 1905 (p.199); van Breemen, 1908 a (p.149, key spp.); A. Scott, 1909 (p.164); Wilson, 1932 a (p.144, clé spp.); Sewell, 1932 (p.350); Rose, 1933 a (p.260, key spp.); Mori, 1937 (1964) (p.90, spp. Key); Dakin & Colefax, 1940 (p.101, spp. Key); Oliveira, 1946 (p.469); Brodsky, 1950 (1967) (p.408, spp. Key); Carvalho, 1952 a (p.148); Tanaka, 1964 c (p.252); Ramirez, 1966 (p.17); Fleminger & Tan, 1966 (p.291); Fleminger, 1967 (p.2, Rem.: polymorphism, species-groups); Björnberg, 1972 (p.59); Bradford, 1972 (p.11, 30); Fleminger, 1975 (p.392 & suiv., speciation); Silas & Pillai, 1973 (1976) (p.773, 793); Fleminger, 1979 (p.187, spp. Key); Björnberg & al., 1981 (p.659); Fleminger & al., 1982 (p.254, Rem.); Razouls, 1982 (p.551); Zheng Zhong & al., 1984 (1989) (p.253, spp. Key); Mauchline, 1988 (p.715); Ferrari, 1991 (p.115); Ferrari, 1992 (p.392, tab.3); Razouls, 1993 (p.307); Chihara & Murano, 1997 (p.866); Mauchline, 1998 (p.66, 93, 95; p.97: M); Bradford-Grieve & al., 1999 (p.958, 959: spp. Key); Bradford-Grieve, 1999 b (p.186, Def., Rem.); Mulyadi, 2002 (p.24, 46, keys F & M, p.47): Boxshall & Halsey, 2004 (p.164); Vives & Shmeleva, 2007 (p.495, spp. Key); Prusova & Al-Yamani, 2014 (p.1165, Key spp F & M in the ''darwinii'' species Group.); Hirabayashi & Ohtsuka, 2014 (p.21, Rem. p.29, Key to Indo-Wesr Pacific species groups in Labidocera detruncata species complex.; Mulyadi, 2014 (p.1629, Rem.: species-Groups); Abo-Taleb, 2019 (p.367, Key M, F from the Red Sea). | | Rem.: | Type: Labidocera darwinii. Total: 55 spp. + 4 indet. | | Remarques sur les dimensions et le sex-ratio: | | The mean female size is 2.506 mm (n = 56; SD = 0.4831 and the mean male size is 2.283 mm (n = 53; SD = 0.5182). The size ratio (Male: Female) is 0.91 (n = 52; SD = 0.0762). The sex ratio (Female: Male) is 1,04.
From the species showing sizes female and male we obtain the mean female size 2.532 mm (n = 46; SD = 0.4841) , and for male 2.254 mm (n = 46; SD = 0.5338). The size ratio (male: female) is 0.906 (n = 52; SD = 0.0762). The sex ratio (female: male) is probably 1 (56:53) | 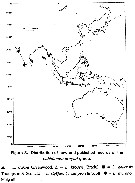 Issued from : Mulyadi in Treubia, 2002, 32 (2). [p.19, Fig.3]. Distribution of Labidocera kroyeri- Group. |
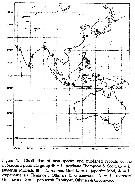 Issued from : Mulyadi in Treubia, 2002, 32 (2). [p.20, Fig.4]. Distribution of Labidocera pectinata- Group. |
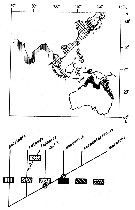 Issued from : A. Fleminger in UNESCO Techn. paers mar. Sci., 1986, 49. [p.92, Fig.7]. Present geographical distribution of the Labidocera pectinata species group., based on localities cited in Fleminger & al. (1982) and new unpublished data. Extent of shading offshore is merely for illustrative purposes and not intended to depict actual offshore distribution of individual species; in most cases offshore distribution is confined to waters inshore of the 100 m isobath. Cladogram in lower shows hypothetized phylogenetic relationships of species and shadings representing ranges of individual species. Circled nodes are hypothetized speciation events taht appear to have occurred in the vicinity of Wallacea Line. |
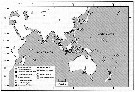 Issued from : T. Hirabayashi & S. Ohtsuka in ZooKeys, 2014, 447. [p.30, Fig. 8] Distribution of Labidocera detruncata species complex based on present occurrences.. |
 Issued from : T. Hirabayashi & S. Ohtsuka in ZooKeys, 2014, 447. [p.31]. Species groups in Labidocera detruncata species complex: Key to Indo-West Pacific. |
 Issued from : T. Hirabayashi & S. Ohtsuka in ZooKeys, 2014, 447. [p.32]. Species group in Labidocera madurae:: Key to Indo-West Pacific. |
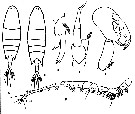 Issued from : F. Vives & Shmeleva in Fauna Iberica, 2007, 29. [p.505, Fig. 274]. Labidocera aestiva after Wheeler, 1901. Female: A, habitus (dorsal view); B, P5. Male: C, habitus (dorsal view); D, left P5; E, right P5; F, A1. | | | | | Machairopus Thompson, 1988 | |
| | Syn.: | non Machairopus Brady,1883 (p.104) | | Ref.: | I.C. Thompson, 1888 b (p.152); Giesbrecht, 1892 (p.531); Giesbrecht & Schmeil, 1898 (p.159) | | Rem.: | ? Pontellidae. Forme douteuse | | | | | Ref.: | Giesbrecht, 1892 (p.71, 461); Giesbrecht & Schmeil, 1898 (p.139, clé spp.); Wheeler, 1901 (p.179); van Breemen, 1908 a (p.152); A. Scott, 1909 (p.159); Sewell, 1932 (p.374); Wilson, 1932 a (p.149); Rose, 1933 a (p.257); Mori, 1937 (1964) (p.95); Tanaka, 1964 c (p.259); Ramirez, 1966 (p.16); Owre & Foyo, 1967 (p.96); Björnberg, 1972 (p.59); Silas & Pillai, 1973 (1976) (p.775, 779, 816); Björnberg & al., 1981 (p.659); Razouls, 1982 (p.565); Fleminger, 1986 (p.84, Rem.: p.90, fig.6: phtlogenetic relationships); Mauchline, 1988 (p.714); Ferrari, 1992 (p.392, tab.3); Razouls, 1993 (p.307); Chihara & Murano, 1997 (p.868); Mulyadi, 1997 (p.673, Rem.: groups); Mauchline, 1998 (p.66; p.95: F; p.97: M); Bradford-Grieve & al., 1999 (p.958, 959: spp. Key); Bradford-Grieve, 1999 b (p.198, Déf., Rem.); Mulyadi, 2000 (p.182, Keys F,M, p.190, 198, Rem.: 5 Groups + 1 unasigned); 2002 (p.26, 85, spp. Key in Indonesian waters: p.86); Boxshall & Halsey, 2004 (p.164); Vives & Shmeleva, 2007 (p.510, spp. Key); Jeong & al., 2008 b (p.99, key to species in Korean waters). | | Rem.: | Total: 47 spp. + 9 indet. | | Remarques sur les dimensions et le sex-ratio: | | The mean female size is 3.960 mm (n = 47; SD = 1.0931), and the mean male size is 3.444 mm (n = 44; SD = 0.9908). The size ratio (Male: Female) is 0.908 (n = 40; SD = 0.0709). The sex-ratio (F/M) is 1,03.
The sex ratio is probably 1 (48:44 = 1.09) |  Issued from : Mulyadi inTreubia, 2002, 32 (2). [p.21, Fig.5]. Distribution of Pontella alata- Group. |
 Issued from : A. Feleminger in UNESCO Techn. papers mar. Sci., 1986, 49. [p.91]. Cladograms showing hypothethized phylogenetic relationships in pontellid copepod species groups indigenous to the Indo-Australian region. Circled nodes represent hypothetized speciation events that appear on the basis of present distributions to have occurred in the vicinity of Wallacea. Cladistic analyses based on sexually modified morphology. Species indicated by number are undescribed. Nota: Pontellid copepods are abundant and species rich in the Indo-Australian region. 69 species in the three principal genera, Labidocera, Pontella, Pontellopsis, 48 being endemic in the region. Most are or appear to be stenothermal, and all live in the upper few meters of the mixed layer. Up to now, the author has examined the systematics and distribution of five species groups of these pontellids ( Pontella, Labidocera). With few exceptions, these species are short ranging and inhabit coastal or neritic waters. The aurthor has assumed from their morphologic and geographic relationships that allopatric speciation is the principal, and likely the sole, process of cladogenesis in this family. Hypothetized phylogenetic relationships for each group based on sexually modified apomorphies are shown in figure 6. Every group has at least one apparent speciation event associated with Wallacea. About 30 % of cladogenesis in the groups appears to indicate a past Wallacean barrier. |
 Issued from : F. Vives & Shmeleva inFauna Iberica, 2007, 29. [p.512, Fig. 279]. Pontella atlantica after Giesbrecht, 1893. Female: A, habitus (dorsal view); B, urosome (dorsal view); C, P5. Male: D, habitus (dorsal view); E P5 (L = left leg; R = right leg). | | | | | (7) Pontellina Dana, 1853 | |
| | Syn.: | Calanops Claus, 1863 (p.211) | | Ref.: | Giesbrecht, 1892 (p.73, 497); Giesbrecht & Schmeil, 1898 (p.149); A. Scott, 1909 (p.174); Sewell, 1932 (p.390); Wilson, 1932 a (p.155); Rose, 1933 a (p.265); Mori, 1937 (1964) (p.99); Oliveira, 1946 (p.472); Tanaka, 1964 c (p.270); Silas & Pillai, 1973 (1976) (p.772, 778); Fleminger & Hulsemann, 1974 (p.63, 70, Déf., Rev.); Hulsemann & Fleminger, 1975 (p.174); Björnberg & al., 1981 (p.659); Razouls, 1982 (p.583); Van der Spoel & Heyman, 1983 (p.147, 162); Zheng Zhong & al., 1984 (1989) (p.256); Mauchline, 1988 (p.715: pores cuticulaires); Hulsemann & Fleminger, 1990 (p.99); Ferrari, 1992 (p.392, tab.3); Razouls, 1993 (p.308); Chihara & Murano, 1997 (p.873); Mauchline, 1998 (p.97: F, M); Bradford-Grieve & al., 1999 (p.958, 960: clé spp.); Bradford-Grieve, 1999 b (p.203, figs.F,M, Rem.); Mulyadi, 2002 (p.155, Def.): Boxshall & Halsey, 2004 (p.164); Vives & Shmeleva, 2007 (p.515) | | Rem.: | Type: Pontella plumata Dana,1849. Total: 5 spp. (dont 1 douteuse). | | Remarques sur les dimensions et le sex-ratio: | | La moyenne des longueurs des femelles est de 1,616 mm (n= 4; S= 0,109; Cv= 0,067) et de 1,488 mm pour les mâles (n= 4; S= 0,068; Cv= 0,046). Le rapport des longueurs (M/F) est de 0,923 (n= 4; S= 0,057; Cv= 0,062). |  Issued from : J.M. Bradford-Grieve inNIWA Biodiversity Memoir, 111, 1999 [p.206, Fig.153]. Pontellina plumata. Female (from Bradford, 1999) : A, habitus (dorsal view); B, P5. Male (from Fleminger & Hulsemann, 1974): C, habitus (dorsal view); D, same (lateral, right side); E, P5 (L = left leg; R = right leg); F, P5 chela (lateral view). | | | | | (8) Pontellopsis Brady, 1883 | |
| | Syn.: | Monops Lubbock, 1853 b (p.122); Giesbrecht, 1892 (p.72, 486); Wheeler, 1901 (p.182); Crisafi, 1960 e (p.280); Razouls, 1972 (Annexe: p.95, Rem.);
Pontella (part.) Dana, 1846;
Pontellina (part.) Dana,1852;
Pseudomonops Claus, 1892;
Pontellopsis (part.) Brady, 1883 (p.85) | | Ref.: | Giesbrecht & Schmeil, 1898 (p.145, spp. Key); Esterly, 1906 a (p.75); A. Scott, 1909 (p.170); Sewell, 1932 (p.384); Wilson, 1932 a (p.157); Rose, 1933 a (p.263); Mori, 1937 (1964) (p.97); Tanaka, 1964 c (p.266); Owre & Foyo, 1967 (p.98); Björnberg, 1972 (p.59); Pillai, P, 1975 (p.239); Silas & Pillai, 1973 (1976) (p.777, 779, 835); Björnberg & al.,1981 (p.660); Razouls, 1982 (p.576); Zheng Zhong & al., 1984 (1989) (p.256, spp. Key); Mauchline, 1988 (p.715); Razouls, 1993 (p.308); Chihara & Murano, 1997 (p.871); Mauchline, 1998 (p.97: F, M); Bradford-Grieve & al., 1999 (p.958, 960: spp. Key); Bradford-Grieve, 1999 b (p.205, Rem.); Mulyadi, 2002 (p.28, 122, F & M Keys in Indonesian waters: p.123): Boxshall & Halsey, 2004 (p.164); Vives & Shmeleva, 2007 (p.517, spp. Key); Suarez-Morales & Kozak, 2012 (p.14, fig.6, spp. key from Eastern Pacific) | | Rem.: | Crisafi (1960) fait l'historique du genre ainsi que de ses divers synonymes. L'auteur conclut que la loi d'antériorité est en faveur du genre Monops Lubbock,1853. Les caractères qui définissent le genre Monops semblent suffisants pour que celui-ci soit maintenu, ainsi l'opinion émise par Crisafi parait tout à fait justifiée. Giesbrecht (1892) met en synonymie Monops grandis et Pontella regalis mais conserve le nom de genre établi par Lubbock. Cependant en 1898, Giesbrecht et Schmeil se réfèrent au genre Pontellopsis créé par Brady (1883) reconnaissant une certaine importance générique à la présence ou non de crochets à la tête alors que Lubbock n'en fait pas mention. On note que le genre Labidocera comprend des espèces avec ou sans crochets latéraux ce qui infirment la prééminence de ce critère. Le nombre et la disposition des lentilles oculaires semblent bien primordiaux pour établir les coupures génériques donnant ainsi raison à Lubbock. Cependant, en raison de l'habitude acquise et du fait qu'il n'y a pas d'inconvénient à conserver le nom de genre de Brady, il parait préférable de laisser à l'auteur d'une future révision de la famille des Pontellidae le soin de décider des dénominations les plus correctes.
Total: 25 spp. + 2 indet. (plusieurs espèces douteuses) | | Remarques sur les dimensions et le sex-ratio: | | The mean female size is 2.573 mm (n = 46; SD = 0.8902), and the mean male size is 2.128 mm (n = 37; SD = 0.6506). The size ratio (Male: Female) is 0.852 (n = 19; SD = 0.6506). The sex ratio (female: male) is 1.35 |  Issued from : F. Vives & Shmeleva in Fauna Iberica, 2007, 29. [p.520, Fig. 284]. Pontellopsis villosa after Gisebrecht, 1893. Female: A, habitus (dorsal view); B-C, P5. Male: D, habitus (dorsal view); E, forehead (lateral view); F, left P5; G, right P5; H, right A1. | | | | | | | | | | | | |
|
|
 Toute utilisation de ce site pour une publication sera mentionnée avec la référence suivante : Toute utilisation de ce site pour une publication sera mentionnée avec la référence suivante :
Razouls C., Desreumaux N., Kouwenberg J. et de Bovée F., 2005-2026. - Biodiversité des Copépodes planctoniques marins (morphologie, répartition géographique et données biologiques). Sorbonne Université, CNRS. Disponible sur http://copepodes.obs-banyuls.fr [Accédé le 15 janvier 2026] © copyright 2005-2026 Sorbonne Université, CNRS
|
|
 |
 |