|
|
 |
Fiche d'espèce de Copépode |
|
|
Calanoida ( Ordre ) |
|
|
|
Clausocalanoidea ( Superfamille ) |
|
|
|
Phaennidae ( Famille ) |
|
|
|
Xanthocalanus ( Genre ) |
|
|
| |
Xanthocalanus pinguis Farran, 1905 (F,M) | |
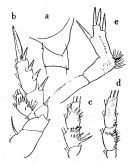
| | | | | | | Syn.: | Xanthocalanus profundus : Tanaka, 1960 a (p.89, figs.F, Rem.); | | | | Ref.: | | | Farran, 1905 (p.39, Descr.F, figs.F); 1908 b (p.48, fig.F, Rem.); Wolfenden, 1908 (p.35); With, 1915 (p.236, figs.F, juv.); Sars, 1925 (p.130, figs.F); Wilson, 1932 a (p.71, figs.F,M, Rem.); Rose, 1933 a (p.130, figs.F); Jespersen, 1934 (p.82); Sewell, 1948 (p.501); C.B. Wilson, 1950 (p.351, fig.F); Tanaka, 1960 a (p.87, figs.F, juv.M, p.90: Rem.); ? Grice & Hulsemann, 1968 (tab.2, p.332, figs.F); Bradford & al., 1983 (p.71); Tanaka & Omori, 1992 (p.269, Rem.); Chihara & Murano, 1997 (p.855, Pl.142: F,M); Vyshkvartzeva, 2002 (p.94, Rem.); Bradford-Grieve, 2004 b (p.630, tab.1); Vives & Shmeleva, 2007 (p.708, figs.F,M, Rem.) |  issued from : O. Tanaka in Publ. Sero Mar. Biol. Lab., 1960, VIII (1). [p.88, Fig.82]. Female (from Sagami and Suruga Bays, Japan): a, habitus (dorsal); b, forehead (lateral); c, last thoracic segment and genital segment (lateral, left side); d, rostrum; e, exopod and endopod of Mx1; f, Mx2; g, Mxp; h, P1; i, P2; j, endopod of P3; k, endopod of P4; l, P5. Nota: Head and 1st thoracic segment separate, 4th and 5th separate. Lateral distal corner of the last thoracic segment triangularly produced and terminates into downwardly pointing spine. Cephalothorax 4.07 mm; abdomen 1.34 mm. Abdominal segments and furca in the proportional lengths 42 : 23 : 13 : 11 : 11 = 100. Genital segment not swollen bow, ther is a tuft of short hairs near the genital opening (lateral view); dorsal surface haired near the proximal. The first 3 abdominal segments covered with small spines, the distal margins are fringed with fine teeth. Caudal rami little wider than long (8 : 7). Exopodite of A2 slightly longer than the endopodite. Md exopodite about as long as the endopodite; 2nd basal segment with 3 long inner marginal setae.Mx1 with elongate endopodite; outer lobe with 9 setae; endopodite with 9 setae. Mx2 with 7 bud-like, and 1 long worm-like sensory filaments on the endopodite; the curved spine of the 5th lobe very strong. P5 3-segmented. Terminal segment broad with 4 spines; posterior surface of the segment furnished with minute spines on the distal part; the inner margin bears several gorups of spinules. The 2nd segment rounded in shape, furnished with long acicular spines on the distal outer margin; the inner margin bears several rows of minute spinules. The 1st segment furnished with several rows of spinules on the inner margin. Immature Male: m, thoracic segments and urosome (lateral, left side); n, P5.
|
 issued from : O. Tanaka in Publ. Sero Mar. Biol. Lab., 1960, VIII (1). [p.90, Fig.83]. As Xanthocalanus profundus.
Female (from Sagami Bay, Japan; from the depth 1000 m): a, last thoracic segment and genital segment (lateral left side); b, P2; c, endopod of P3; d, endopod of P4; e, P5. Nota: General appearance as in the female of X. pinguis. Cephalothorax 3.53 mm; abdomen 1.06 mm.The abdominal segments and furca in the proportional lengths 38 : 23 : 17 : 11 : 11 = 100. A1 extends to the distal end of the 4th thoracic segment. A2 exopodite a little longer than the endopodite (8 : 7). Md, Mx1, Mx2 and Mxp as those of X. pinguis. The 2nd to 4th legs as those of X. pinguis, except slight differences in the number of the spines on the posterior surface of the endopodite P5. 3-segmented; the distal 2 segments fused. Terminal segment slender, with 4 spines; posterior surface of segment furnished with a longitudinal row of small spines. The 2nd segment furnished with hair-like spines on the outer distal margin; the posterior surface furnished with scattered denticles near the outer distal margin. The 1st segment finely denticulated on the inner margin. Remarks: The present specimen could possibly be an example of X. pinguis with a deformed P5 as had been pointed out by Farran. This is confirmed by Tanaka & Omori (1992,p.269) after re-examination of the female specimen.
|
 Issued from : G.O. Sars in Résult. Camp. Scient. Prince Albert I, 69, pls.1-127 (1924). [Pl.XXXV, figs.8-10]. Female: habitus (dorsal); 9, idem (lateral left side); 10, P5.
|
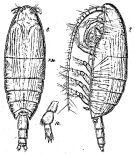
 issued from : G.P. Farran in Ann. Rep. Fish. Brch., Ireland, 1902-1903, II, App. 2, 1905. [Plate VIII, Figs.18-24]. Female (from W Ireland): 18-19, habitus (lateral and dorsal, respectively); 20, A1; 21, A2; 22, md (mandibular palp); 23, Mx1; 24, Mxp.
|
 issued from : G.P. Farran in Ann. Rep. Fish. Brch., Ireland, 1902-1903, II, App. 2, 1905. [Plate IX, Figs.1-6]. Female: 1, Mxp; 2-6, P1 to P5.
|
 issued from : G.D. Grice & K. Hulsemann in Pacif. Sci., 1968, 22 (3). [p.330, Figs.60-62]. Female (from SE Pacific): 60, endopod of Mx2; 61, P5; 62, P5. From different specimens. Nota: The terminal segment of P5 in the larger specimen (8.91 mm) is longer than the 2nd segment, and the terminal segment in the smaller specimen (8.00 mm) bears only 3 spines, contrary 4 spines in the larger specimen. A1 of both females consist of 24 free segments, with segments 8 and 9 fused, as reported by Tanaka (1960). The terminal part of Mx2 is provided with sensory appendages of various sizes.
|
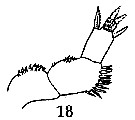 issued from : G.P. Farran in Fish. Ire. Sci. Invest., 1906, II [1908]. [Pl. IV, Fig.18]. Female (from 54°50'N, 10°30'W): 18, P5. Nota: The 1st segment of P5 has about 20 short stout spinules in 2 rows along the inner edge, the outer edge being smooth; the 2nd segment has about 6 inner-edge spinules similar to those on the 1st segment, the distal half of the outer edge bearing a cluster of lancet-shaped spinules; there are a pair of lateral and a pair of terminal spines on the 3rd segment, and the face of the segment bears a patch of slender spinules of two sizes near the tip.
|
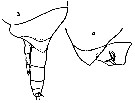 issued from : C. With in The Danish Ingolf-Expedition, Copepoda I, 1915, III, 4. [p.203, Text-fig. 77]. Female (from 61°05'N, 9°35'W) a, corner of the last thoracic segment and genital segment (lateral, left side). Nota: A1 extend to the end of the 4th thoracic segment. Copepodid V male: b, corner of last thoracic segmentwith P5 and urosome (lateral). Shape of the body differs from that of the adult by the comparatively better marked 5th thoracic segment, and by the urosome 4-segmented, comparative length and caudal rami: 5, 13, 9, 6, and 5. Right P5 with exopod 2-segmented; left P5 2-segmented, but less hirsute and with trace of segmentation in exopodal segment 2. Size: 4.43 mm; prosome 3.51 mm, urosome: 0.92 mm.
|
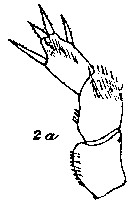 issued from : C. With in The Danish Ingolf-Expedition, Copepoda I, 1915, III, 4. [
Pl. VII, Fig.2, a]. Female: a, P5.
|
 issued from : C. With in The Danish Ingolf-Expedition, Copepoda I, 1915, III, 4. [Pl. VII, 2, b-c]. Female: b, labrum (oral view); c, lamina labialis and serrulata 6-dentata. Nota : The epistoma has in front a group of long slender bristles ; somewhat in front of the transverse row of bristles along the posterior margin a regular transverse series of fairly long setae, and just in front of this a group of irregularly placed bristles ; laterally 2 or 3 groups of short hairs. On the oral surface of the labrum (fig.2b), in front and laterally, 2 oblique almost parallel wide rows of bristles ; in the middle, on each side, 4 more or less fused wide areas of numerous short hairs or granules. The chitinous framework is on each side in front of the 3rd median circular spot produced into a beak-like structure ; somewhat behind, a transverse chitinous bar was found in the middle ; behind the 4th median circular spot a number of short granules. In front of the indistinct mamina labialis a large group of short hairs, consisting of an inner an douter part, the hairs decrease in size outwards ; between the ‘serrula 6-dentata’ a group of granules, and behind, outer and inner groups of of longer and shorter hairs (Pl. VII, fig.2c). Along the labial lobes inwards, marginal rows of long slender setae are found anteriorly and short spines posteriorly ; behind the lobes in the middle, areas of minute granules, and the lobes possess laterally groups of irregularly placed fairly long and slender bristles, limited inwards by an oblique row of somewhat shorter hairs.
|
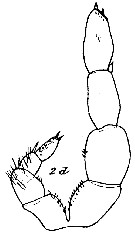 issued from : C. With in The Danish Ingolf-Expedition, Copepoda I, 1915, III, 4. [Pl. VII, Fig.2, d]. Copepodid V male: d, P5 (posterior view).
|
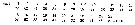 issued from : O. Tanaka in Publ. Sero Mar. Biol. Lab., 1960, VIII (1). [p. 87]. Female (from Sagami Bay, Japan): Proportions of segments of A1. Nota: A1 24-segmented, extends to the distal end of the 4th thoracic segment.
| | | | | Ref. compl.: | | | Pearson, 1906 (p.20); Holmes, 2001 (p.57); Bradford-Grieve, 2004 (p.285) | | | | NZ: | 9 | | |
|
Carte de distribution de Xanthocalanus pinguis par zones géographiques
|
| | |  Carte de 1996 Carte de 1996 | |
| | | | Loc: | | | off W Canary Is., Azores, off Woods Hole, Davis Strait, SW Iceland, W Ireland, Japan (Izu region), Marshall Is., G. of California (Guaymas Basin), off SW Galapagos, off Juan Fernandez Is. | | | | N: | 15 | | | | Lg.: | | | (1) F: 7,3; (4) F: 5,41; 4,59; (7) F: 5,19; (24) F: 5,1; (32) F: 4,5; (45) F: 5,25-4,5; M: 5; (58) F: 4,5; [? (100) F: 8,91; 8]; (866) M: 4,5-5; (867) F: 4,8, 5,06; {F: 4,50-8,91; M: 4,50-5,00} | | | | Rem.: | bathypélagique. Hyperbenthique.
Cette espèce a été récoltée à l'origine par plus de 5.500 m de profondeur. Les longueurs des femelles données par Sars (1925) (1) et Grice & Hulsemann (1968) (100) sont exceptionnellement élevées, respectivement 7,30 mm, et 8 - 8,91 mm, mais loin de correspondre aux longueurs chez Bathycalanus sverdrupi (Megacalanidae) qui est le plus grand des calanoïdes connus (17-18 mm).
Voir aussi les remarques en anglais | | | Dernière mise à jour : 09/05/2016 | |
|
|
 Toute utilisation de ce site pour une publication sera mentionnée avec la référence suivante : Toute utilisation de ce site pour une publication sera mentionnée avec la référence suivante :
Razouls C., Desreumaux N., Kouwenberg J. et de Bovée F., 2005-2026. - Biodiversité des Copépodes planctoniques marins (morphologie, répartition géographique et données biologiques). Sorbonne Université, CNRS. Disponible sur http://copepodes.obs-banyuls.fr [Accédé le 10 février 2026] © copyright 2005-2026 Sorbonne Université, CNRS
|
|
 |
 |