|
|
 |
Fiche d'espèce de Copépode |
|
|
Calanoida ( Ordre ) |
|
|
|
Diaptomoidea ( Superfamille ) |
|
|
|
Acartiidae ( Famille ) |
|
|
|
Acartia ( Genre ) |
|
|
|
Acanthacartia ( Sous-Genre ) |
|
|
| |
Acartia (Acanthacartia) bifilosa (Giesbrecht, 1881) (F,M) | |
| | | | | | | Syn.: | Dias bifilosus Giesbrecht,1881;
Acartia bifilosus : T. Scott, 1892 (p.244, fig.F);
no Acartia bifilosa: Shen & Bai, 1956 (p.224, figs.F,M); Chen & Zhang, 1965 (p.112, figs.F,M); Kim, 1985 (p.137, figs.); Yoo, 1991 (tab.1); Yoo & al., 1991 (p.257, fig.); Myung & al., 1994 (tab.1); Shim & Choi, 1996 (p., figs., tab.); Yoon & al., 1998 (p.923, figs. eggs, Nauplius, juv., F, M, Rem.) | | | | Ref.: | | | Giesbrecht, 1892 (p.507, 522, figs.F,M); Giesbrecht & Schmeil, 1898 (p.153); Steuer, 1923 (p.22, figs.F,M); Gurney, 1931 a (p.230, figs.F,M); Wilson, 1932 a (p.162, figs.F,M); Rose, 1933 a (p.275, figs.F,M); Redeke, 1934 (p.39, fig.F, Rem.); Jespersen, 1940 (p.70); Farran, 1948 a (n°12, p.3, figs.F); Brodsky, 1950 (1967) (p.425, figs.F,M); Crisafi & Crescenti, 1972 (1974) (p.231, figs.F,M, juv.); Kos, 1976 (Vol. II
, figs.F,M, Rem.); Brylinski, 1981 (p.257, figs.F, M); Schnack, 1982 (p.89, figs. Mx2, Md, Mxp); Brylinski, 1984 (p.961, figs.M: anomalies); Sazhina, 1985 (p.78, figs.N); Yoo & al., 1991 (p.257, fig.F); Behrends & al., 1997 (p.594, figs.F); Hirst & Castro-Longoria, 1998 (p.1119, figs.F,M, Rem.); Bradford-Grieve, 1999 (N° 181, p.5, figs.F,M); Barthélémy, 1999 (p.857, 864, figs.F); 1999 a (p.9, Fig.23, A, B); Bradford-Grieve & al., 1999 (p.885, 962, figs.F,M); Castro-Longoria & Williams, 1999 (p.215, figs.F,M); Soh & Suh, 2000 (p.322, 332, Rem.); G. Harding, 2004 (p.24, figs.F,M); Avancini & al., 2006 (p.113, Pl. 81, figs.F,M, Rem.); Vives & Shmeleva, 2007 (p.409, figs.F,M, Rem.); Laakmann & al., 2013 (p.862, figs.1, 2, 3, Table 1, 2, mol. Biol.) | 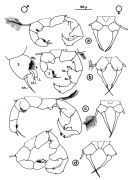 issued from : J.M. Brylinski in J. Plankton Res., 1981, 3 (2). [Fig.2, p.257]. Structure of P5 of the Acartia in the wet docks of the harbour of Dunkirk (Strait of Dover). Male and Female a: Acartia clausi; b: A. tonsa, c: A. discaudata, d: A. bifilosac.f.: curved finger, c.n.: curved needle, d.t.: distal tooth, l.: lamella, l.p.: lamellar process, p.t.: proximal tooth, s.: setae, sp.: spines, 3, segment 3 of left leg. Rem: P5 = fifth leg
|
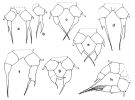 issued from : J.M. Brylinski in J. Plankton Res., 1984, 6 (6). [Fig.3,p.963]. female: various types of anomalies of P5 in the wet docks of the harbour of Dunkirk (Strait of Dover).
Rem: P5 = fifth leg
|
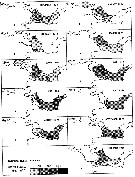
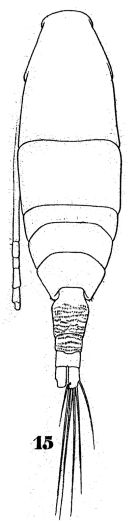 issued from : W. Giesbrecht in Fauna Flora Golf. Neapel, 1892, 19. [Taf.43, Fig.15]. Female: 15, habitus (dorsal).
|
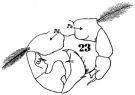 issued from : W. Giesbrecht in Fauna Flora Golf. Neapel, 1892, 19. [Taf.43, Fig.23]. Male: 23, P5.
|
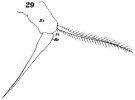 issued from : W. Giesbrecht in Fauna Flora Golf. Neapel, 1892, 19. [Taf.30, Fig.29]. Female: 29, P5.
|
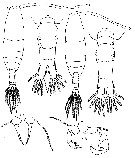 issued from : P. Crisafi & M. Crescenti in Boll. Pesca Piscic. Idrobiol., 1972 (1974), 27 (2). [p.247, Pl.VII]. Female (from Milazzo Harbour, Sicily): f, habitus (dorsal); f ad, posterior thoracic part and urosome (dorsal); , f P5, P5. Male: m, habitus (dorsal); m ad, posterior thoracic part and urosome (dorsal); m P5, P5.
|
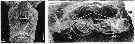 issued from : R.-M. Bathélémy in J. Mar. Biol. Ass. U.K., 1999, 79. [p.861, Fig.4, A-B]. Scanning electron micrograph. Female (from Elson Lagoon, Alaska): A, external ventral view of genital double-somite; B, internal genital area. Scale bars: 0.030 mm (A); 0.020 mm (B). Symbols: * = cuticular protuberance; arrowhead = lamellar flap; small arrow = genital slit; ap = apoderme; sd = seminal duct; sr = seminal repeptacle; ed = egg-laying duct.
|
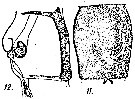 issued from : A. Steuer in Arb. zool. Inst. Innsbruck, 1923, 1 (5). [Taf. II, Figs.11, 12]. Female: 11, genital segment (ventral); 12, idem with spermatophore (lateral).
|
 issued from : M. Rose in Result. Camp. Scient. Prince Albert Ier, Monaco, 1929, 78. [Pl.III, Figs.8]. As Acartia bifilosa var. inermis. Female (from Loire Estuary and Gorringe Bank, off Gibraltar): Ab D, urosome with spermatophore (dorsal); Ab L, last thoracic segment and urosome (lateral); A1; P1 to P5. Male: D, habitus (dorsal); R, forehead (ventral); Ab L, urosome (lateral; with epibionts on the 4th segment); A1 (right).
|
 issued from : M. Rose in Result. Camp. Scient. Price Albert Ier, Monaco, 1929, 78. [Pl.IV, Figs.8]. Female: Md. Male: Ab D, urosome (dorsal; showing two aspects); A2; P1 to P5.
|
 issued from : J.M. Brylinski in J. Plankton Res., 1984, 6 (6). [Tableau.1, p.964]. Results of the countings of the normal and abnormal animals in samples analyzed to Acartia bifilosa in diferent regions.
|
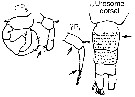 issued from : G. Harding in Key to the adullt pelagic calanoid copepods found over the continental shelf of the Canadian Atlantic coast. Bedford Inst. Oceanogr., Dartmouth, Nova Scotia, 2004. [p.24]. Female & Male.
|
 Issued from : H.Y. Soh & H.-L. Suh in J. Plankton Res., 2000, 22 (2). [p.332, Table I]. Distinctive characters of Acartia bifilosa. b: based on Giesbrecht (1992) and Brodsky (1950). Nota: Compare the distinctive characters with the closely related species A. omorii, A. hudsonica, A. hongi, A. omorii in the coastal waters of Korea.
|
 Issued from : M.G. Mazzocchi in Guida al Riconoscimento del plancton dei Mari Italiani, Vol. II, 2006. [p.89, Tav. 81]. After A. Comaschi. Female: a, habitus (dorsal); b, urosome (dorsal); c, same (lateral); d-e, left P5 (various aspects). B1 = basipod 1 = coxa; B2 = basipod 2 = basis; Re = exopod.
| | | | | Ref. compl.: | | | T. Scott, 1902 (p.454); Sewell, 1948 (p.367, 419, 483, 487); Conover, 1959 (p.259, Table 1, 2, respiration); M.W. Johnson, 1961 (p.311, Table 2); H. Schulz, 1961 (p.57); Marshall & Orr, 1962 (tab.3); Cannicci, 1962 (p.349, Table3); ? Shih & al., 1971 (p.29, 200); Paulmier, 1971 (p.168); Martens, 1972 (p.15, fecal pellets); Arndt & Heidecke, 1973 (p.599, 603); Eriksson, 1973 a (p.95, fig.10, area abundance distibution); Castel & Lasserre, 1977 (p.129, fig.2, 3, 7); Ciszewski & Witek, 1977 (p.449, P/B quotient); Hernroth, 1978 (p.1, Rem.: p.5); Collins & Williams, 1981 (p.273, monthly distribution-salinity); Castel & Courties, 1982 (p.417, Table II, fig.4, spatial & monthly distribution); Tremblay & Anderson, 1984 (p.3); Chojnacki, 1983 a (p.435, length-weight relation); Chojnacki & Hussein, 1983 (p.53, Table 3, length-weight); d'Elbée, 1984 (p.24, Fig.3); Lam Hoi & al., 1985 (p.451, 460); Kuosa, 1989 (p.47, O2 vs. activity and survival); Jouffre & al., 1991 (p.489, lagoon); Viitasalo, 1992 (tab. 2); Castel, 1993 (p.145, long-term annual distribution); ? Hwang & Choi, 1993 (tab.3); Sellner & al., 1994 (p.249); Tanskanen, 1994 (p.397, carbon seasonal variability); Irigoien & Castel, 1995 (p.115, productivity); Irigoien & al., 1996 (p.163, gut clearance rate); Madhupratap & al., 1996 (p.77, Table 2: resting eggs); Marcus, 1996 (p.143); Meyer-Harms & von Bodungen, 1997 (p.181, feeding); Mauchline, 1998 (tab.18, 35, 40, 47, 61); Uriarte & al., 1998 (p.197, egg production, population development); Koski & Kuosa, 1999 (p.1779, egg production); Pinchuk & Paul, 2000 (p.4, table 1, % occurrence); Belmonte & Potenza, 2001 (p.173); Vieira & al., 2003 b (p.199); Lo & al., 2004 (p.89, tab.1); Katajisto, 2004 (p.751, dormancy and survival subitaneous eggs vs. anoxia & hypoxia); Hsiao & al., 2004 (p.325, tab.1); Wang & Zuo, 2004 (p.1, Table 2, dominance, origin); Lan & al., 2004 (p.332, tab.1, tab.2); Uriarte & Villate, 2005 (p.863, tab.I); David & al., 2005 (p.171); Uriarte & Villate, 2006 (p.565, resting eggs); Hansen F.C. & al., 2006 (p.39, production); Schulz J. & al., 2007 (p.47, vertical zonation analysis); Chojnacki & al., 2007 (p.42, Table 2); David & al., 2007 a (p.429, figs.2, 4, 5, Table 3, 4, 5, 6); Youn & Choi, 2007 (p.222: Table1, egg production); Holmborn & Gorokhova, 2008 (p.483); Lan Y.C. & al., 2008 (p.61, Table 1, % vs stations); Li J. & al., 2008 (p.95, effects of different diets); Holeton & al., 2009 (p.661, astaxanthin storage); Holmborn, 2009 (p.12); Telesh & al., 2009 (p.18: Table 2.1); Brylinski, 2009 (p.253: Tab.1, p.256: Rem.); Martynova & al., 2009 (p.133, C/N contents, length, starvation experiments); Sun & al., 2010 (p.1006, Table 2: Yellow Sea); Mazzocchi & Di Capua, 2010 (p.423); Dvoretsky & Dvoretsky, 2010 (p.991, Table 2); Hsiao S.H. & al., 2011 (p.475, Appendix I); Sun X.-H. & al., 2011 (p.741, figs. 5.3, 4, tab.I, II, production); Martynova & al., 2011 (p.1175, seasonal abundance); Dvoretsky & Dvoretsky, 2011 b (p.469, Table A, abundance, biomass); Vehmaa & al., 2011 (p.134, algae diets vs egg production); Sopanen & al., 2011 (p.1564, mortality vs algal toxicity); Postel, 2012 (p.327, Table 1, Fig.6); Schulz J. & al., 2012 (p.3, abundance vs. hydrography); Vehmaa & al., 2012 (p.1, Table 1, egg production, egg hatching vs pH); Huo & al., 2012 (p.1, Table 1: dominance); Li C. & al., 2013 (p.101, feeding); Ben Ltaief & al., 2017 (p.1, Table III, Summer relative abundance); Baumgartner & Tarrant, 2017 (p.387, resting eggs); Belmonte, 2018 (p.273, Table I: Italian zones)Richirt & al., 2019 (p.3, Table 1, fig.2, 3, 4, 5, abundance changes vs years 1998-2014, table 2: diversity index ) | | | | NZ: | 8 + 2 douteuses | | |
|
Carte de distribution de Acartia (Acanthacartia) bifilosa par zones géographiques
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |  Carte de 1996 Carte de 1996 | |
 issued from : P. Martens in M.S. Inst. Meeresk. Christian-Albrechts Univ., 1972. [p.19]. issued from : P. Martens in M.S. Inst. Meeresk. Christian-Albrechts Univ., 1972. [p.19].
Numbers of fecal pellets (n) by width classes (interval from 0.005 mm).
Nota: individuals in culture on Chaetoceros decipiens, C. socialis, Detonula cystifera, Skeletonema costatum and flagellates.
Mean size of fecal pellets: length = 134 ± 5 micrometers; width = 45 ± 16 micrometers. Volume male = 109335 µ3; female = 316679 µ3. |
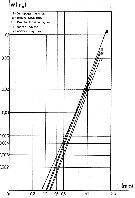 issued from : J. Chojnacki & M.M. Hussein in Zesz. nauk. Akad. Roln. Szczec., 1983, 103. [p.55, Fig.1]. issued from : J. Chojnacki & M.M. Hussein in Zesz. nauk. Akad. Roln. Szczec., 1983, 103. [p.55, Fig.1].
Total length - weight relationship in selected copepod species (copepodites I to V and adults) from the eastern sector of the Southern Baltic Sea.
Animals preserved in 4 % formalin and lengths in different copepodites and adults stages measured under stereomicroscope. Volume et weight calculated according to the simplified formula (Chojnacki & al., 1980). The results in fig. 1 present mean Lt (total length values for different developmental stades (nauplii not examined) by season and area. |
 issued from : J. Chojnacki & M.M. Hussein in Zesz. nauk. Akad. Roln. Szczec., 1983, 103. [p.54]. issued from : J. Chojnacki & M.M. Hussein in Zesz. nauk. Akad. Roln. Szczec., 1983, 103. [p.54].
Total length - weight relationship calculated according to the simplified formula proposed by J. Chojnacki, P. Ciszewski & Z. Witek, 1980). |
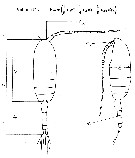 issued from : J. Chojnacki in Int. Revue ges. Hydrobiol., 1983, 68 (3). [p.436, Fig.1]. issued from : J. Chojnacki in Int. Revue ges. Hydrobiol., 1983, 68 (3). [p.436, Fig.1].
Length-weight relationship determined by geometrical method (Pattern from calanoid-form Pseudocalanus elongatus).
Lc = cephalothorax length; La = urosome length; Lan = antennula length; h : cephalothorax height; Ra = diameter of urosome cross-section; Ran = diameter of antennula cross-section.
A conversion factor of 1.025, reflecting the density (g per cm3) of the coastal Baltic water.
The correlation coefficient for the relationship studied was found to be about 0.96
|
 issued from : N.R. Collins & R. Williams in Mar. Biol., 1981, 64. [p.278, Fig.7]; issued from : N.R. Collins & R. Williams in Mar. Biol., 1981, 64. [p.278, Fig.7];
Acartia bifilosa var. inermis. Monthly distribution and abundance in Bristol Channel and Severn Estuary from November 1973 to February 1975, together with 33.5 p.1000 S isohaline. |
 Issued from : Jan Schulz & coll. in Progr. Oceanogr., 2012, 107; [p.8, Fig.4 [modified]); Issued from : Jan Schulz & coll. in Progr. Oceanogr., 2012, 107; [p.8, Fig.4 [modified]);
Seasonal patterns in the abundance of Acartia bifilosa in the Bornholm Basin (central Baltic Sea) between March 2002 and May 2003. The scaling is normalised to one and vertical lines indicate sampling dates.
Sampling performed in stacked, 10m intervals from a few meters above the seafloor to the surface with a multinet (Hydro-bios, Kiel, 50 µm mesh size) on nine focus stations.
Compare with annual cycle in Acartia longiremis, Centropages hamatus, Temora longicornis, Oithona similis and other forms. |
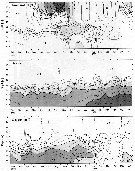 Issued from : Jan Schulz & coll. in Progr. Oceanogr., 2012, 107; [p.6, Fig.2]. Issued from : Jan Schulz & coll. in Progr. Oceanogr., 2012, 107; [p.6, Fig.2].
Vertical profiles of temperature, salinity and oxygen in the central Bornholm Basin (Baltic Sea) at position 55.3016° N, 15.7966° E. |
 Issued from : D.M. Martynova, M. Graeve & U.V. Bathmann in Polar Biol., 2009, 32. [p.136, Table 1. Issued from : D.M. Martynova, M. Graeve & U.V. Bathmann in Polar Biol., 2009, 32. [p.136, Table 1.
Biochemical parameters of Acartia bifilosa from the White Sea (66°20.2'N, 33°38.9'E). |
 Issued from : S. Sopanen, O. Setala, J. Piiparinen, K. Erler & A. Krem in J. Plankton Res., 2011, 33 (10). [p.1568, Figs. 2, 3]. Issued from : S. Sopanen, O. Setala, J. Piiparinen, K. Erler & A. Krem in J. Plankton Res., 2011, 33 (10). [p.1568, Figs. 2, 3].
Fig.2 (left side): Condition of the copepods A. bifilosa (shown as percentage of all copepods in each experiment)after 24h exposure to dinoflagellate Alexandrium ostenfeldii cell suspensions at different cell concentrations (50-1200 cells mL). The copepod condition is ranked based on observations on their behavorial and movement.
Fig.3 (right side): Condition of the copepods A. bifilosa exposed to A. ostenfeldii cell suspensions at different concentrations through time. The copepod condition is ranked based on observations on their behavior and movement. The condition ranks (0-3) used are 0 = dead, 1 and 2 = impaired, 3 = normal. Dotted line: animals incubated in sea water controls. Error bars represent standard deviation. |
 Issued from : A. Vehmaa, P. Larsson, C. Vidoudez, G. Pohmert, M. Reinikainen & J. Engström-Öst in J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol., 2011, 401. [p.136, Fig.1] Issued from : A. Vehmaa, P. Larsson, C. Vidoudez, G. Pohmert, M. Reinikainen & J. Engström-Öst in J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol., 2011, 401. [p.136, Fig.1]
The egg production of Acartia bifilosa on five different algae diets during four days.
FSW = filtered sea water (n = 18). Rho = Rhodomonas salina (n = 18). Ske = Skeletonema marinoi (n = 12). Scr = Scrippsiella hangoei (n = 11). 50/50 = 50% Ske + 50% Scr (n = 11).
The boxes show the range between the upper and lower quartiles; the bold horizontal bars indicate median; the whiskers show the smallest and largest values (1.5 times the interquartile range) and the values outside this range are presented as open dots. Data was pooled from two experiments.
Nota: Egg production was measured during two experiments (18-22 April and 2-6 June 2008) slightly after the spring phytoplankton bloom in the sea. Sampling took place in Storfjärden (SW coast of Finland).
The egg production is higher when feeding on the dinoflagellate S. hangoei, instead of a diet consisting of the diatom S. marinoi . In terms of cell stoichiometry, Scrippsiella was the best food source, whereas Skeletonema was the best diet for the copepods in terms of lipid concentrations. Skeletonemma contained the highest amounts and the most diverse set of fatty acids and sterols, but it maintened the lowest egg production.
The results show higher egg production on dinoflagellate than on diatom diets.
Acartia bifilosa is a selective species, able to switch betsween filtration and ambush-feeding (see Tiselius & Jonsson, 1990). |
| | | | Loc: | | | Arct. (S Beaufort Sea, Barents Sea), N Atlant., off Woods Hole, Bay of Fundy, Greenland, Iceland, Shetland Is., Firth of Forth, North Sea, Norway, Bristol Channel, Southampton, E English Channel, Pas de Calais, Dunkirk Harbour, Zuiderzee, Elbe (estuaire), Bay of Kiel, Gulf of Mecklenburger, Pomeranian Bight, Baltic Sea, Bornholm Basin, G. of Finland, Storfjärden, Öregrund Archipelago, Bay of Biscay, Belon estuary, Urdaibai estuary, St.-Jean-de-Luz, Arcachon Bay, Gironde Estuary, Portugal (Mondego Bay), Gibraltar, Medit. (Strait of Messina, W Sardinia, Thau lagoon, ), Black Sea, ? Viet-Nam (Cauda Bay), China Seas (Bohai Sea, Yellow Sea, East China Sea, South China Sea, Jiaozhou Bay, Taiwan (E, N, NW), S Korea, N Japan, Okhotsk Sea, ? Alaska. | | | | N: | 83 (Arct.: 7; Atlant. N.: 22; English Channel: 6; North Sea: 3; Baltic: 24; Medit.: 10, Black Sea: 1; ? Pacif.: 6 | | | | Lg.: | | | (22) F: 1,1; M: 1,1-1; (45) F: 1,25-1; M: 1,25-1; (164) F: 1,1-1,02; (167) F: 0,9-0,77; M: 0,86-0,77; (168) F: 1,241-1,146; M: 1,146-1,071; (284) F: 0,924-0,672; M: 0,854-0,672; (1123) F: 1,119-0,786; M: 1,165-0,667; {F: 0,672-1,25; M: 0,667-1,25} | | | | Rem.: | littoral, ± saumâtre (cf. Sewell, 1948, p.324, 367).
Des confusions ont été possibles avec A. hongi décrite en 2000 dans le Pacifique nord (mers de Chine, Corée et Japon).
La présence de A. bifilosa est à confirmer dans le Pacifique, notamment dans les mers de Chine (cf. in Shih Young, 1995 p.66) bien qu'elle soit signalée par Wang & al. (2002, p.348) dans la Mer Bo Hai, et en Alaska.
La P5 femelle peut présenter des anomalies (cf. Behrends & al., 1997).
Cette espèce pourrait avoir été introduite en Méditerranée et en Mer Noire par des navires, ou correspondre à une forme relicte glaciaire.
Acartia bifilosa inermis Rose,1929 (F,M)
Ref.: Rose,1929 (p.48, figs.F,M); 1933 a (p.275, figs.F,M); Trinast,1976 (p.57); Hirst & Castro-Longoria, 1998 (p.1119, figs.F,M, Rem.); Bradford-Grieve, 1999 (N°181, p.5, figs.F,M); Vives & Shmeleva, 2007 (p.409, figs.F,M, Rem.)
Ref. compl.: Williams & Collins, 1985 (p.27); Vieira & al., 2003 b (p.199)
Loc.: Portugal (Mondego Estuary), France : Estuaire de la Loire (St-Nazaire), Gibraltar W, chenal de Bristol, estuaire de la Forth, Severn
Lg.: (325) F: 1,1; M: 1,1.
W. Zhang confirme la présence de cette espèce dans les mers de Chine (comm. pers., 2006)
Voir aussi les remarques en anglais | | | Dernière mise à jour : 17/09/2020 | |
|
|
 Toute utilisation de ce site pour une publication sera mentionnée avec la référence suivante : Toute utilisation de ce site pour une publication sera mentionnée avec la référence suivante :
Razouls C., Desreumaux N., Kouwenberg J. et de Bovée F., 2005-2026. - Biodiversité des Copépodes planctoniques marins (morphologie, répartition géographique et données biologiques). Sorbonne Université, CNRS. Disponible sur http://copepodes.obs-banyuls.fr [Accédé le 05 février 2026] © copyright 2005-2026 Sorbonne Université, CNRS
|
|
 |
 |