|
|
 |
Fiche d'espèce de Copépode |
|
|
Calanoida ( Ordre ) |
|
|
|
Eucalanoidea ( Superfamille ) |
|
|
|
Eucalanidae ( Famille ) |
|
|
|
Subeucalanus ( Genre ) |
|
|
| |
Subeucalanus monachus (Giesbrecht, 1888) (F,M) | |
| | | | | | | Syn.: | Eucalanus monachus Giesbrecht,1888; 1892 (p.132, 151, 772, figs.F,M); Giesbrecht & Schmeil, 1898 (p.21, Rem.); Wheeler, 1901 (p.167, figs.M); Thompson & Scott, 1903 (p.233, 242); Cleve, 1904 a (p.189); A. Scott, 1909 (p.20); Wolfenden, 1911 (p.204); Sewell, 1912 (p.353, 357); 1914 a (p.202); Pesta, 1920 (p.499); Sars, 1925 (p.22); Rose, 1925 (p.151); 1929 (p.15); Sewell, 1929 (p.51); Wilson, 1932 a (p.33,figs.F,M); Rose, 1933 a (p.69, figs.F,M); no Dakin & Colefax, 1940 (p.96, figs.); Wilson, 1942 a (p.184); Massuti Alzamora, 1942 (p.110); Lysholm & al., 1945 (p.9); Sewell, 1947 (p.46); C.B. Wilson, 1950 (p.209); Marques, 1951 a (p.21); 1953 (p.95); 1955 (p.17); Rose, 1956 (p.459); Ganapati & Shanthakumari, 1962 (p.7, 15); Fagetti, 1962 (p.10); Cervigon, 1962 (p.181, tables: abundance distribution); Vervoort, 1963 b (p.99-100: Rem.); Duran, 1963 (p.13); Kasturirangan, 1963 (p.18, 19, figs.F,M); Björnberg, 1963 (p.21, Rem.); Paiva, 1963 (p.20); Unterüberbacher, 1964 (p.16, Rem.); De Decker, 1964 (p.15, 22, 28); Ramirez, 1966 (p.8, figs.F, Rem.); Neto & Paiva, 1966 (p.19, Table III); Mazza, 1966 (p.69); 1967 (p.86, 331, fig.67, figs.F,M, juv., fig.67); Owre & Foyo, 1967 (p.37, figs.F,M); Vilela, 1968 (p.10, figs.F); Evans, 1968 (p.13, as monarchus); Vinogradov, 1968 (1970) (p.268, 269); Marques, 1968 a (p.396); Matthews, 1968 a (p.35, figs.F, Rem.); Park, 1970 (p.474); Corral Estrada, 1970 (p.76, figs.F, Rem.F,M); Timonin, 1971 (p.281, trophic group); Gamulin, 1971 (p.382, tab.3); Bainbridge, 1972 (p.61, Appendix Table I: vertical distribution vs day/night, Table II: %, Table IV: seasonal abundance); Apostolopoulou, 1972 (p.327, 334); Binet & al., 1972 (p.69); Kos, 1972 (Vol.I, figs.F,M, Rem.); Björnberg, 1973 (p.298, 386); Fleminger, 1973 (p.969, 978, 979, 982, 999, fig.F); Corral Estrada & Pereiro Muñoz, 1974 (tab.I); Vives & al., 1975 (p.35, tab.II, III, IV); Patel, 1975 (p.659); Marques, 1976 (p.987); Madhu Pratap & al., 1977 (p.138, Table 3: abundance vs. stations); Deevey & Brooks, 1977 (p.256, Table 2, Station "S"); Goswami & Goswami, 1979 (p.103, figs.); Stephen & Iyer, 1979 (p.228, tab.1, 3, 4, figs.3, 4); Binet, 1979 (p.400); Dessier, 1979 (p.54, 56, 201, 204); Vaissière & Séguin, 1980 (p.23, tab.2); Björnberg & al., 1981 (p.621, figs.F,M); Sreekumaran Nair & al., 1981 (p.493, fig.2cont.); Madhupratap & al., 1981 (p.262, Table 2: abundance vs. thermocline); Madhupratap & al., 1981 (p.266, fig.2l: abundance vs. geographic transect); Kovalev & Shmeleva, 1982 (p.82); Strickler, 1982 (Rem.: p.159, behavior); Marques, 1982 (p.752); Vives, 1982 (p.290); Scotto di Carlo & Ianora, 1983 (p.150); De Decker, 1984 (p.315); Cummings, 1984 (p.163, Table 2); Scotto di Carlo & al., 1984 (1042); Brenning, 1985 a (p.24, Table 2); Diouf & Diallo, 1987 (p.260); Lozano Soldevilla & al., 1988 (p.57); Wiebe & al., 1988 (tab.7); Pancucci-Papadopoulou & al., 1990 (p.199); Roe, 1984 (p.356, Rem.: ?); Scotto di Carlo & al., 1991 (p.270); Suarez & Gasca, 1991 (tab.2); Suarez, 1992 (App.1); Rosales & Sepulveda, 1992 (p.38); Seguin & al., 1993 (p.23); Webber & Roff, 1995 (tab.1); Weikert, 1995 (p.218, Rem.); Hajderi, 1995 (p.542); Siokou-Frangou, 1997 (tab.1); Hure & Krsinic, 1998 (p.20, 99); Gilabert & Moreno, 1998 (tab.1, 2); Mauchline, 1998 (tab.8); Hopcroft & al., 1998 (tab.2); Seridji & Hafferssas, 2000 (tab.1); Moraitou-Apostolopoulou & al., 2000 (tab.I); Weikert & al., 2001 (p.227, tab.4),, fig.6,8,9, Rem.); Beaugrand & al., 2002 (p.179, figs.5, 6); Vukanic, 2003 (139, tab.1); Koppelmann & al., 2004 (p.1, Rem.); Siokou-Frangou & al., 2005 (p.160); Isari & al., 2006 (p.241, tab.II); Koppelmann & Weikert, 2007 (p.266: tab.3); Morales-Ramirez & Suarez-Morales, 2008 (p.513, 519); Fernandes, 2008 (p.465, Tabl.2); Licandro & Icardi, 2009 (p.17, Table 4); Hafferssas & Seridji, 2010 (p.353, Table 3); Lidvanov & al., 2010 (p.356, Table 3); Medellin-Mora & Navas S., 2010 (p.265, Tab. 2); Fazeli & al., 2010 (p.153, Table 1, as monochus); Maiphae & Sa-ardrit, 2011 (p.641, Table 2); Glushko & Lidvanov, 2012 (p.138, Tableau 1); Zaafa & al., 2014 (p.67, Table I, occurrence); Record & al., 2018 (p.2238, Table 1: diapause);
Eucalanus vadicola F. Dahl, 1894 c (p.20, Rem.F,M);
no E. monachus : Dakin & Colefax, 1933 (p.204); 1940 (p.96, figs.F,M);
? Eucalanus monachus cop. : Isari & al., 2011 (p.51, Table 2, abundance vs distribution, in Thracian Sea); | | | | Ref.: | | | Bradford-Grieve, 1994 (p.88); Bradford-Grieve & al., 1999 (p.878, 912, figs.F,M); Goetze, 2003 (p.2322 & suiv.); Vives & Shmeleva, 2007 (p.877, figs.F,M, Rem.) | 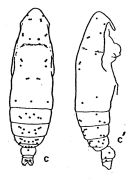 issued from : A. Fleminger in Fishery Bull. natn. Ocean. Atmos. Adm., 1973, 71 (4). [p.985, Fig.9]. As Eucalanus monachus. Female: c, habitus (dorsal), c', idem (lateral right side).
Dorsal and lateral pattern of integumental organs (black point = sites occuring at 100% frequency, o = 80-99% frequency, x = 10-79% frequency, triangle are sites which are also visible in lateral view but which are assigned to dorsal sets);
|
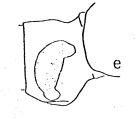 issued from : A. Fleminger in Fishery Bull. natn. Ocean. Atmos. Adm., 1973, 71 (4). [p.968, Fig.1, e (p.969)]. As Eucalanus monachus. Female: e, genital segment (lateral right side).
|
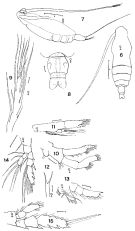 issued from : F.C. Ramirez in Bol. Inst. Biol. Mar., Mar del Plata, 1966, 11. [Lam.I, Figs.6-15]. As Eucalanus monachus. Female (off Mar del Plata): 6, habitus (dorsal); 7, idem (lateroventral); 8, urosome (dorsal); 9, distal segments of A1; 10, A2; 11, Md (mandibular palp); 12, rostrum (dorsal view); 13, P1; 14, P2; 15, P3. Nota: Urosome 3-segmented, genital segment as wide than long, anal segment and caudal rami fused.. Caudal rami slightly asymmetrical. A2 with proximal endopodal segment shorter than distal. 2nd basal segment of Md longer than exopod, and furnished on inner margin with 3 fine setae; endopodite 2-segmented, distal segment half of the length of 1st segment.
|
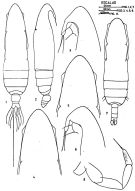 issued from : J. Corral Estrada in Tesis Doct., Univ. Madrid, A-129, Sec. Biologicas, 1970. [Lam.9]. As Eucalanus monachus. Female (from Canarias Is.): 1, habitus (dorsal); 2, idem (lateral right side); 3, forehead (lateral); 4, idem (dorsal, another specimen); 6, idem (lateral). Male: 7, habitus (dorsal); 8, P5.
|
 issued from : J. Corral Estrada in Tesis Doct., Univ. Madrid, A-129, Sec. Biologicas, 1970. [Lam.10]. As Eucalanus monachus. Female: 1, urosome (dorsal); 2, idem (ventral); 3, idem (lateral right side); 4, A2; 5, Md (mandibular palp); 6, Md (cutting edge); 7, Mx1.
|
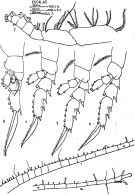 issued from : J. Corral Estrada in Tesis Doct., Univ. Madrid, A-129, Sec. Biologicas, 1970. [Lam.11]. As Eucalanus monachus. Female: 1-1a, A1; 2, Mxp; 3, P1; 4, P2; 5, P3; 6, P4. Nota: A1 23-segmented (segments 1+2, 24+25 fused), extending beyond caudal rami by 3 segments. Proportional lengths of segments: 80:32:21:34:32:32:58:36:40:38:48:46:52:58:50:55:50:48:42:42:38:34:44 = 1000
|
 issued from : J. Corral Estrada in Tesis Doct., Univ. Madrid, A-129, Sec. Biologicas, 1970. [Lam.12, figs.1-4]. As Eucalanus monachus. Female: 1, Mx2; 2, urosome (ventral, another specimen); 3, idem (dorsal); 4, idem (lateral left side). Nota: The urosomal segments ( furca included) in the proportional lengths 50:12:38 = 100.
|
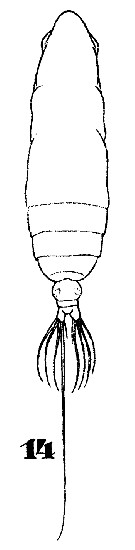 Issued from : W. Giesbrecht in Systematik und Faunistik der Pelagischen Copepoden des Golfes von Neapel und der angrenzenden Meeres-Abschnitte. – Fauna Flora Golf. Neapel, 1892, 19 , Atlas von 54 Tafeln. [Taf.35, Fig.14]. As Eucalanus monachus. Female: 14, habitus (dorsal).
|
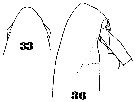 Issued from : W. Giesbrecht in Systematik und Faunistik der Pelagischen Copepoden des Golfes von Neapel und der angrenzenden Meeres-Abschnitte. – Fauna Flora Golf. Neapel, 1892, 19 , Atlas von 54 Tafeln. [Taf.35, Figs.33, 36]. As Eucalanus monachus. Female: 33, forehead (dorsal); 36, head (lateral).
|
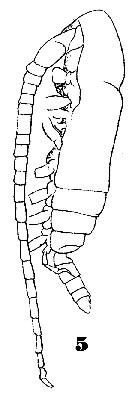 Issued from : W. Giesbrecht in Systematik und Faunistik der Pelagischen Copepoden des Golfes von Neapel und der angrenzenden Meeres-Abschnitte. – Fauna Flora Golf. Neapel, 1892, 19 , Atlas von 54 Tafeln. [Taf.35, Fig.5]. As Eucalanus monachus. Male: 5, habitus (lateral).
|
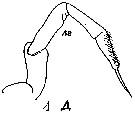 Issued from : M.C. Kos in Field guide for plankton. Zool Institute USSR Acad., Vol. I, 1972. After Giesbrecht, 1892. As Eucalanus monachus. Male: 1, left P5
| | | | | Ref. compl.: | | | Suarez-Morales & Gasca, 1998 a (p.109); Lapernat, 2000 (tabl.3, 4); CPR, 2004 (p.62, fig.187); Valdés & al., 2007 (p.103: tab.1); Khelifi-Touhami & al., 2007 (p.327, Table 1); Cabal & al., 2008 (289, Table 1); Schnack-Schiel & al., 2010 (p.2064, Table 2: E Atlantic subtropical/tropical); Goetze & Ohman, 2010 (p.2110, Table 1, biogeography); Mazzocchi & Di Capua, 2010 (p.425); Medellin-Mora & Navas S., 2010 (p.265, Tab. 2); Medellin-Mora & Navas S., 2010 (p.265, Tab. 2); Nowaczyk & al;, 2011 (p.2159, Table 2); Salah S. & al., 2012 (p.155, Tableau 1); Uysal & Shmeleva, 2012 (p.909, Table I); Belmonte & al., 2013 (p.222, Table 2, abundance vs stations); Jagadeesan & al., 2013 (p.27, Table 3, seasonal variation); Lidvanov & al., 2013 (p.290, Table 2, % composition); Siokou & al., 2013 (p.1313, fig. 7, 8, biomass, vertical distribution); Zakaria & al., 2016 (p.1, Table 1); Benedetti & al., 2016 (p.159, Table I, fig.1, functional characters); Marques-Rojas & Zoppi de Roa, 2017 (p.495, Table 1); El Arraj & al., 2017 (p.272, table 2, seasonal composition); Benedetti & al., 2018 (p.1, Fig.2: ecological functional group); Belmonte, 2018 (p.273, Table I: Italian zones); Chaouadi & Hafferssas, 2018 (p.913, Table II: occurrence). | | | | NZ: | 18 | | |
|
Carte de distribution de Subeucalanus monachus par zones géographiques
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | 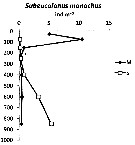 Issued from : I. Siokou, S. Zervoudaki & E. D. Christou in J. Plankton Res., 20013, 35 (6). [p.1319, Fig.5]. Issued from : I. Siokou, S. Zervoudaki & E. D. Christou in J. Plankton Res., 20013, 35 (6). [p.1319, Fig.5].
Vertical distribution of Subeucalanus monachus abundance (ind.m3 in the Aegean Sea. 1997.
M: March; S: September.
In the north Aegean Sea S. monachus (large copepod ) had an almost similar vertical pattern as Calanus helgolandicus, its maximum abundance was recorded in the 50-100 m layer (10.46 ind.m3 and 6% of copepods and decreased gradually down to 300 m (0.2 ind.m3) and10% of copepods. A slight increase was observed <500 m, but it relative abundance was important within the deep copepod community. The species was rarely found in the deep layers in the northern;
See for comparison :Calanus helgolandicus and hydrological parameters (temperature, salinity) profiles from the same authors. |
| | | | Loc: | | | South Africa (E & SW), Namibia, Angola, Baia Farta, Congo, off Ascension Is., G. of Guinea, off Lagos, Ivorian shelf, off Sierra Leone, off E St. Paul Is., Casamance, Dakar, Cape Verde Is. off Morocco-Mauritania, Cap Ghir, NW Cape Verde Is. , Canary Is., off Madeira, off W Cap Finisterre, Portugal, Azores, Brazil, Mouth of Tocantins, Barbados Is., Caribbean Colombia, Cariaco Basin, Bahia de Mochima (Venezuela), Caribbean Sea, Jamaica, E Costa Rica, G. of Mexico, Florida, Sargasso Sea, Station "S" (32°10'N, 64°30'W), off Woods Hole, off Newfoundland, Mauritania, Cap Ghir, Ibero-moroccan Bay, Gibraltar, Medit. (M'Diq, Alboran Sea, Habibas Is., Sidi Fredj coast, Algiers, El Kala shelf, Ligurian Sea, Tyrrhenian Sea, Taranto, Ionian Sea, Adriatic Sea, Aegean Sea, Thracian Sea, W Egyptian coast, Lebanon Basin, Marmara Sea), Red Sea, Gulf of Oman, G. of Aden, Arabian Sea, Kavaratti & Agatti Is. (only offside)Maldive Is., off Cochin, Sri Lanka, India (Saurashtra coast, Lawson's Bay, Gulf of Mannar, Palk Bay), G. of Bengal, S Burma, Andaman Sea, Philippines, Indonesia-Malaysia, Viet-Nam (Cauda Bay), China Seas, Japan, off Kuril Is., Bering Sea, Queen Charlotte Is., British Columbia, off Hawaii, Guaymas Basin, off Tuamotu Is., Central America, W Costa Rica, off Galapagos, off Peru, off Chile, off Valparaiso | | | | N: | 171 ? | | | | Lg.: | | | (45) F: 2,35-2; M: 2,25-2; (47) F: 2,35-2,13; M: 2,2; (73) F: 2,5-2,31; (75) F: 2,26-1,81; (180) F: 2,35; M: 2,35; (207) F: 2,84-2,73; (237) F: 2,05; M: 2,3; (334) F: 2,5; M: 2; (327) F: 2,68-2,14; (332) F: 2,74-2,13; M: 2,6-2,37; (333) F: 2,1-1,95; M: 1,86; (334) F: 2,5; M: 2 ; (432) F: 2,4-2,15; (449) F: 2,35-2,13; M: 2,2; {F: 1,81-2,84; M: 1,86-2,60} | | | | Rem.: | meso-bathypélagique.
Voir aussi les remarques en anglais | | | Dernière mise à jour : 25/10/2022 | |
|
|
 Toute utilisation de ce site pour une publication sera mentionnée avec la référence suivante : Toute utilisation de ce site pour une publication sera mentionnée avec la référence suivante :
Razouls C., Desreumaux N., Kouwenberg J. et de Bovée F., 2005-2026. - Biodiversité des Copépodes planctoniques marins (morphologie, répartition géographique et données biologiques). Sorbonne Université, CNRS. Disponible sur http://copepodes.obs-banyuls.fr [Accédé le 30 janvier 2026] © copyright 2005-2026 Sorbonne Université, CNRS
|
|
 |
 |